
Tianshui is a prefecture-level city in Gansu province, China, and is the province's second-largest city. Located in the southeast of the province, the city strides along the upper reaches of the Wei River and at the boundary of the Loess Plateau and the Qinling Mountains. As of the 2020 census, its population was 2,984,659 inhabitants, of which 1,212,791 lived in the built-up area made of the 2 urban districts of Qinzhou and Maiji. The city and its surroundings have played an important role in the early history of China, as still visible in the form of historic sites such as the Maijishan Grottoes.

Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture in southern Gansu Province, China, bordering Linxia to the north, Dingxi to the northeast, Longnan to the east and Aba to the south. It includes Xiahe and the Labrang Monastery, Luqu, Maqu and other mostly Tibetan towns and villages. Gannan has an area of 40,898 km2 (15,791 sq mi) and its capital is Hezuo city (Zoi). In the first year of the proclamation of Gannan Autonomous District, the district-seat was at the Labrang Town of Sangqu.

Pingliang is a prefecture-level city in eastern Gansu province, China, bordering Shaanxi province to the south and east and the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region to the north. The city was established in 376 AD. It has a residential population of 2,125,300 in 2019. The urban population is almost 900,000.

Bairi Tibetan Autonomous County, also known as Tianzhu from its Chinese name, is in the prefecture-level city of Wuwei in the central part of Gansu province, China, bordering Qinghai province to the south and west. It has an area of 7,147 km2 (2,759 sq mi) and approximately 230,000 inhabitants (2003). Its administrative seat is Rabgyai Town (Huazangsi).

Baiyin is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Gansu province, People's Republic of China. Established in the 1950s as a base for mining non-ferrous metals, its mines are becoming exhausted in recent decades, requiring the city to reinvent its economy. Located around 60 km (37 mi) from Gansu's capital Lanzhou, it is part of the Lanzhou-Baiyin Economic Belt.

Dingxi, also known as Longyou is a prefecture-level city in the southeast of Gansu province, People's Republic of China. As of the 2020 census, its population was 2,524,097 inhabitants, of which 422,383 lived in the built-up area made of Anding urban district.

Wuwei is a prefecture-level city in northwest central Gansu province. In the north it borders Inner Mongolia, in the southwest, Qinghai. Its central location between three western capitals, Lanzhou, Xining, and Yinchuan makes it an important business and transportation hub for the area. Because of its position along the Hexi Corridor, historically the only route from central China to western China and the rest of Central Asia, many major railroads and national highways pass through Wuwei.

Lintao County simplified Chinese: 临洮县; traditional Chinese: 臨洮縣; pinyin: Líntáo Xiàn) is administratively under the control of Dingxi, Gansu province, China. In ancient times, Lintao was centered on present day Min County.

Min County or Minxian is administratively under the control of the prefecture-level city of Dingxi, in the south of Gansu province, China. In ancient times, it was known as Lintao County due to its location along the Tao River. It was founded as Minzhou (岷州) in 544, named after the Min Mountains in the south of the county. The county received its present name in 1913. In 1985 it became subordinate to Dingxi. Min county is well known by Angelica sinensis which is a Chinese traditional medicine.

Jingtai County is a county in the middle of Gansu Province, bordering Inner Mongolia to the north. It is under the administration of Baiyin City and located at its northwest end. Covering an area of 5,483 square kilometres (2,117 sq mi), it governs 8 towns and 3 townships, which then in turn govern 15 residential communities and 135 administrative villages. Its postal code is 730400, and its population as of the 2010 Chinese Census was 225,755 people, which the county government reports has grown to about 238,900 as of 2019.

Jingyuan County is a county in the east of Gansu Province. It is under the administration of Baiyin City, and consists of two separate tracts of territory to the north and south of Pingchuan District. The northern tract borders Ningxia to the north. The southern area consists of an irrigated area around the Yellow River and the northern area is semi-arid highlands.

Gulang County is a county in central Gansu province, China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the northeast. It is under the administration of Wuwei City. Its postal code is 733100, and its population in 2006 was 393,200 people. Located in the east of the Hexi Corridor and to the south of the Tengger Desert, it borders Jingtai County to the east, Tianzhu County to the south, Liangzhou District to the northwest, and Inner Mongolia's Alxa Left Banner to the northeast.
The Shiyang River (石羊河), previously called the Gu River (谷水), flows through the eastern Hexi Corridor in the China.
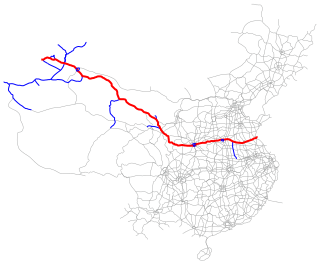
The Lianyungang–Khorgas Expressway, designated as G30 and commonly referred to as the Lianhuo Expressway, is 4,243-kilometre-long expressway (2,636 mi) in China that connects the cities of Lianyungang, in the province of Jiangsu, and Khorgas, in the autonomous region of Xinjiang, on the border with Kazakhstan. At Khorgas, there is a border crossing into Kazakhstan. The expressway is the longest contiguous expressway in China with a single numeric designation, stretching across the country from the Yellow Sea on the east coast to the Kazakhstan border in the west. It passes through the provinces of Jiangsu, Anhui, Henan, Shaanxi, Gansu, and Xinjiang.
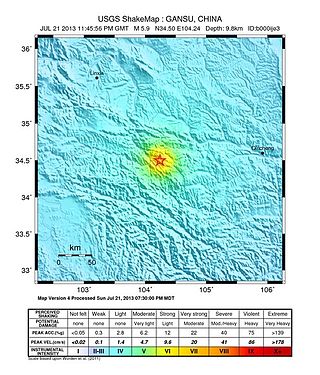
On 22 July 2013, a series of earthquakes occurred in Dingxi, Gansu. The first quake struck at 07:45 China Standard Time with an epicenter located at the border of Min County and Zhang County. The magnitude of the initial earthquake was placed at 6.6 by the China Earthquake Data Center with a focal depth of 20.0 kilometres (12 mi). It was measured at 5.9 by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and Mw 6.0 by the European Alert System. Another strong quake occurred about one hour later, measuring 5.6 magnitude by the USGS. As of 18:00 CST, 22 July 2013, 422 aftershocks had been recorded. The earthquakes were also felt in the nearby cities of Tianshui and Lanzhou in Gansu, as well as Xi'an, Baoji, and Xianyang in neighbouring Shaanxi.

Taoyang is a town and the county seat of Lintao County, Dingxi, Gansu, China. It is located centrally in Lintao at a junction of major roads.

Balipu is a town of Lintao County, Dingxi, Gansu, China. Its name is based on the location being eight li from the county seat of Lintao, Taoyang.
Zhang Lingping is a former Chinese politician who his entire career in northwest China's Gansu province. He was investigated by China's top anti-graft agency in August 2020. Previously he served as party secretary of both cities of Jinchang and Dingxi. He was a delegate to the 12th National People's Congress.
Huajialing Town is a township-level administrative unit under the jurisdiction of Tongwei County, Dingxi City, Gansu Province, People's Republic of China. It is located roughly equidistant from the seats of Tongwei, Huining and Anding.

China National Highway 666, also known as the Jingtai-Lanzhou Highway, is a national highway in China, which connects Jingtai County and Lanzhou in Gansu. The highway is 141 km (88 mi) long.

















