Related Research Articles

Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). One prominent example is carbon emission trading for CO2 and other greenhouse gases which is a tool for climate change mitigation. Other schemes include sulfur dioxide and other pollutants.

A carbon tax is a tax levied on the carbon emissions from producing goods and services. Carbon taxes are intended to make visible the hidden social costs of carbon emissions. They are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by essentially increasing the price of fossil fuels. This both decreases demand for goods and services that produce high emissions and incentivizes making them less carbon-intensive. When a fossil fuel such as coal, petroleum, or natural gas is burned, most or all of its carbon is converted to CO2. Greenhouse gas emissions cause climate change. This negative externality can be reduced by taxing carbon content at any point in the product cycle.
An environmental tax, ecotax, or green tax is a tax levied on activities which are considered to be harmful to the environment and is intended to promote environmentally friendly activities via economic incentives. One notable example is a carbon tax. Such a policy can complement or avert the need for regulatory approaches. Often, an ecotax policy proposal may attempt to maintain overall tax revenue by proportionately reducing other taxes ; such proposals are known as a green tax shift towards ecological taxation. Ecotaxes address the failure of free markets to consider environmental impacts.

The Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) is a ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for environmental protection, food production and standards, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in the entire United Kingdom. Concordats set out agreed frameworks for co operation, between it and the Scottish Government, Welsh Government and Northern Ireland Executive, which have devolved responsibilities for these matters in their respective nations.
The United Kingdom's Climate Change Programme was launched in November 2000 by the British government in response to its commitment agreed at the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED). The 2000 programme was updated in March 2006 following a review launched in September 2004.

The Climate Change Levy (CCL) is a tax on energy delivered to non-domestic users in the United Kingdom.
Various energy conservation measures are taken in the United Kingdom.
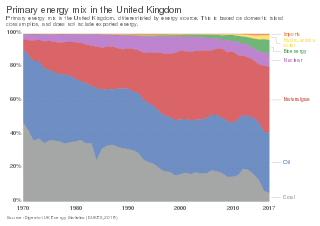
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.
The Fossil Fuel Levy (FFL) is a levy paid by suppliers of electricity from non-renewable energy sources in the United Kingdom. The costs are shared by the suppliers and consumers, as a proportion of the cost is passed on to consumers in the cost of the electricity supplied. The Fossil Fuel Levy was imposed to fund the Non-Fossil Fuel Obligation.
The Code for Sustainable Homes was an environmental assessment method for rating and certifying the performance of new homes in United Kingdom. First introduced in 2006, it is a national standard for use in the design and construction of new homes with a view to encouraging continuous improvement in sustainable home building. In 2015 the Government in England withdrew it, consolidating some standards into Building Regulations.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.
The CRC Energy Efficiency Scheme was a mandatory carbon emissions reduction scheme in the United Kingdom which applied to large energy-intensive organisations in the public and private sectors. It was estimated that the scheme would reduce carbon emissions by 1.2 million tonnes of carbon per year by 2020. In an effort to avoid dangerous climate change, the British Government first committed to cutting UK carbon emissions by 60% by 2050, and in October 2008 increased this commitment to 80%. The scheme has also been credited with driving up demand for energy-efficient goods and services.

The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme was a cap-and-trade emissions trading scheme for anthropogenic greenhouse gases proposed by the Rudd government, as part of its climate change policy, which had been due to commence in Australia in 2010. It marked a major change in the energy policy of Australia. The policy began to be formulated in April 2007, when the federal Labor Party was in Opposition and the six Labor-controlled states commissioned an independent review on energy policy, the Garnaut Climate Change Review, which published a number of reports. After Labor won the 2007 federal election and formed government, it published a Green Paper on climate change for discussion and comment. The Federal Treasury then modelled some of the financial and economic impacts of the proposed CPRS scheme.

Carbon emission trading (also called carbon market, emission trading scheme (ETS) or cap and trade) is a type of emissions trading scheme designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). A form of carbon pricing, its purpose is to limit climate change by creating a market with limited allowances for emissions. Carbon emissions trading is a common method that countries use to attempt to meet their pledges under the Paris Agreement, with schemes operational in China, the European Union, and other countries.

The oil and gas industry plays a central role in the economy of the United Kingdom. Oil and gas account for more than three-quarters of the UK's total primary energy needs. Oil provides 97 per cent of the fuel for transport, and gas is a key fuel for heating and electricity generation. Transport, heating and electricity each account for about one-third of the UK's primary energy needs. Oil and gas are also major feedstocks for the petrochemicals industries producing pharmaceuticals, plastics, cosmetics and domestic appliances.

The economics of climate change mitigation is a contentious part of climate change mitigation – action aimed to limit the dangerous socio-economic and environmental consequences of climate change.
The reduction of carbon emissions, along with other greenhouse gases (GHGs), has become a vitally important task of international, national and local actors. If we understand governance as the creation of “conditions for ordered rule and collective action” then, given the fact that the reduction of carbon emissions will require concerted collective action, it follows that the governance of carbon will be of paramount concern. We have seen numerous international conferences over the past 20 years tasked with finding a way of facilitating this, and while international agreements have been infamously difficult to reach, action at the national level has been much more effective. In the UK, the Climate Change Act 2008 committed the government to meeting significant carbon reduction targets. In England, these carbon emissions are governed using numerous different instruments, which involve a variety of actors. While it has been argued by authors like Rhodes that there has been a “hollowing out” of the nation state, and that governments have lost their capabilities to govern to a variety of non-state actors and the European Union, the case of carbon governance in England actually runs counter to this. The government body responsible for the task, the Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC), is the “main external dynamic” behind governing actions in this area, and “rather than hollowing out central co-ordination”. The department may rely on other bodies to deliver its desired outcomes, but it is still ultimately responsible for the imposition of the rules and regulations that “steer (carbon) governmental action at the national level”. It is therefore evident that carbon governance in England is hierarchical in nature, in that “legislative decisions and executive decisions” are the main dynamic behind carbon governance action. This does not deny the existence of a network of bodies around DECC who are part of the process, but they are supplementary actors who are steered by central decisions. This article focuses on carbon governance in England as the other countries of the UK all have devolved assemblies who are responsible for the governance of carbon emissions in their respective countries.

Fracking in the United Kingdom started in the late 1970s with fracturing of the conventional oil and gas fields near the North Sea. It was used in about 200 British onshore oil and gas wells from the early 1980s. The technique attracted attention after licences use were awarded for onshore shale gas exploration in 2008. The topic received considerable public debate on environmental grounds, with a 2019 high court ruling ultimately banning the process. The two remaining high-volume fracturing wells were supposed to be plugged and decommissioned in 2022.
A carbon pricing scheme in Australia was introduced by the Gillard Labor minority government in 2011 as the Clean Energy Act 2011 which came into effect on 1 July 2012. Emissions from companies subject to the scheme dropped 7% upon its introduction. As a result of being in place for such a short time, and because the then Opposition leader Tony Abbott indicated he intended to repeal "the carbon tax", regulated organizations responded rather weakly, with very few investments in emissions reductions being made. The scheme was repealed on 17 July 2014, backdated to 1 July 2014. In its place the Abbott government set up the Emission Reduction Fund in December 2014. Emissions thereafter resumed their growth evident before the tax.

Green economy policies in Canada are policies that contribute to transitioning the Canadian economy to a more environmentally sustainable one. The green economy can be defined as an economy, "that results in improved human well-being and social equity, while significantly reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities." Aspects of a green economy would include stable growth in income and employment that is driven by private and public investment into policies and actions that reduce carbon emissions, pollution and prevent the loss of biodiversity.
References
- ↑ Consultation outcome - Simplifying the Climate Change Agreements Scheme
- ↑ Department of Energy and Climate Change CCA-B02 Climate Change Agreements Energy Intensive eligibility criteria - guidance for sector associations and participants