An energy crisis or energy shortage is any significant bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy. In literature, it often refers to one of the energy sources used at a certain time and place, in particular, those that supply national electricity grids or those used as fuel in industrial development. Population growth has led to a surge in the global demand for energy in recent years. In the 2000s, this new demand – together with Middle East tension, the falling value of the US dollar, dwindling oil reserves, concerns over peak oil, and oil price speculation – triggered the 2000s energy crisis, which saw the price of oil reach an all-time high of $147.30 per barrel ($926/m3) in 2008.
Primary energy (PE) is the energy found in nature that has not been subjected to any human engineered conversion process. It encompasses energy contained in raw fuels and other forms of energy, including waste, received as input to a system. Primary energy can be non-renewable or renewable.

Energy policies are the government's strategies and decisions regarding the production, distribution, and consumption of energy within a specific jurisdiction. Energy is essential for the functioning of modern economies because they require energy for many sectors, such as industry, transport, agriculture, housing. The main components of energy policy include legislation, international treaties, energy subsidies and other public policy techniques.

Japan is a major consumer of energy, ranking fifth in the world by primary energy use. Fossil fuels accounted for 88% of Japan's primary energy in 2019. Japan imports most of its energy due to scarce domestic resources. As of 2022, the country imports 97% of its oil and is the larger liquefied natural gas (LNG) importer globally.

The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy industry is a crucial part of the infrastructure and maintenance of society in almost all countries.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation, regulation, court decisions, public participation, and other techniques.

Energy in the United Kingdom came mostly from fossil fuels in 2021. Total energy consumption in the United Kingdom was 142.0 million tonnes of oil equivalent in 2019. In 2014, the UK had an energy consumption per capita of 2.78 tonnes of oil equivalent compared to a world average of 1.92 tonnes of oil equivalent. Demand for electricity in 2023 was 29.6 GW on average, supplied through 235 TWh of UK-based generation and 24 TWh of energy imports.
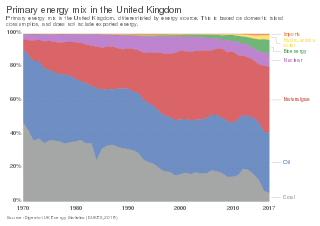
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.
The energy policy of India is to increase the locally produced energy in India and reduce energy poverty, with more focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear, solar and wind energy. Net energy import dependency was 40.9% in 2021-22. The primary energy consumption in India grew by 13.3% in FY2022-23 and is the third biggest with 6% global share after China and USA. The total primary energy consumption from coal, crude oil, natural gas, nuclear energy, hydroelectricity and renewable power is 809.2 Mtoe in the calendar year 2018. In 2018, India's net imports are nearly 205.3 million tons of crude oil and its products, 26.3 Mtoe of LNG and 141.7 Mtoe coal totaling to 373.3 Mtoe of primary energy which is equal to 46.13% of total primary energy consumption. India is largely dependent on fossil fuel imports to meet its energy demands – by 2030, India's dependence on energy imports is expected to exceed 53% of the country's total energy consumption.

The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal. Federal policies for energy in Australia continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production. Australia is the 10th most coal-dependent country in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage and the coal industry produces over 30% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. In 2018 Australia was the 8th highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the world.

Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to cheaper energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerabilities. International energy relations have contributed to the globalization of the world leading to energy security and energy vulnerability at the same time.

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. In 2019, nearly 75% of new installed electricity generation capacity used renewable energy and the International Energy Agency (IEA) has predicted that by 2025, renewable capacity will meet 35% of global power generation.

Fossil fuel phase-out is the gradual reduction of the use and production of fossil fuels to zero, to reduce deaths and illness from air pollution, limit climate change, and strengthen energy independence. It is part of the ongoing renewable energy transition, but is being hindered by fossil fuel subsidies.

China is the world's leader in electricity production from renewable energy sources, with over triple the generation of the second-ranking country, the United States. China's renewable energy sector is growing faster than its fossil fuels and nuclear power capacity, and is expected to contribute 43% of global renewable capacity growth. China's total renewable energy capacity exceeded 1,000 GW in 2021, accounting for 43.5 per cent of the country's total power generation capacity, 10.2 percentage points higher than in 2015. The country aims to have 80 per cent of its total energy mix come from non-fossil fuel sources by 2060, and achieve a combined 1,200 GW of solar and wind capacity by 2030. In 2023, it was reported that China was on track to reach 1,371 gigawatts of wind and solar by 2025, five years ahead of target due to new renewables installations breaking records. In 2024, it was reported that China would reach its target by the end of July 2024, six years ahead of target.
The environmental benefits of renewable energy technologies are widely recognised, but the contribution that they can make to energy security is less well known. Renewable technologies can enhance energy security in electricity generation, heat supply, and transportation. Since renewable energy is more evenly distributed than fossil fuels at the global level, the use of renewable energy technologies can also lead to decentralized and self-sufficient energy systems and reduce energy dependencies among countries.
Energy subsidies are measures that keep prices for customers below market levels, or for suppliers above market levels, or reduce costs for customers and suppliers. Energy subsidies may be direct cash transfers to suppliers, customers, or related bodies, as well as indirect support mechanisms, such as tax exemptions and rebates, price controls, trade restrictions, and limits on market access.

Energy laws govern the use and taxation of energy, both renewable and non-renewable. These laws are the primary authorities related to energy. In contrast, energy policy refers to the policy and politics of energy.
Energy security of the People's Republic of China concerns the need for the People's Republic of China to guarantee itself and its industries long- term access to sufficient energy and raw materials. China has been endeavoring to sign international agreements and secure such supplies; its energy security involves the internal and foreign energy policy of China. Currently, China's energy portfolio consists mainly of domestic coal, oil and gas from domestic and foreign sources, and small quantities of uranium. China has also created a strategic petroleum reserve, to secure emergency supplies of oil for temporary price and supply disruptions. Chinese policy focuses on diversification to reduce oil imports, which used to rely almost exclusively on producers in the Middle East.

Russia supplies a significant volume of fossil fuels to other European countries. In 2021, it was the largest exporter of oil and natural gas to the European Union, (90%) and 40% of gas consumed in the EU came from Russia.

An energy transition is a major structural change to energy supply and consumption in an energy system. Currently, a transition to sustainable energy is underway to limit climate change. Most of the sustainable energy is renewable energy. Therefore, another term for energy transition is renewable energy transition. The current transition aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from energy quickly and sustainably, mostly by phasing-down fossil fuels and changing as many processes as possible to operate on low carbon electricity. A previous energy transition perhaps took place during the Industrial Revolution from 1760 onwards, from wood and other biomass to coal, followed by oil and later natural gas.