
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve and if necessary equipped with extraction devices such as pumpjacks. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in difficult-to-access locations, e.g., offshore. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs and technology during the 20th century.

A submersible pump (or electric submersible pump is a device which has a hermetically sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body. The whole assembly is submerged in the fluid to be pumped. The main advantage of this type of pump is that it prevents pump cavitation, a problem associated with a high elevation difference between the pump and the fluid surface. Submersible pumps push fluid to the surface, rather than jet pumps, which create a vacuum and rely upon atmospheric pressure. Submersibles use pressurized fluid from the surface to drive a hydraulic motor downhole, rather than an electric motor, and are used in heavy oil applications with heated water as the motive fluid.

In the oil and gas industry, the term wireline usually refers to the use of multi-conductor, single conductor or slickline cable, or "wireline", as a conveyance for the acquisition of subsurface petrophysical and geophysical data and the delivery of well construction services such as pipe recovery, perforating, plug setting and well cleaning and fishing. The subsurface geophysical and petrophysical information results in the description and analysis of subsurface geology, reservoir properties and production characteristics.
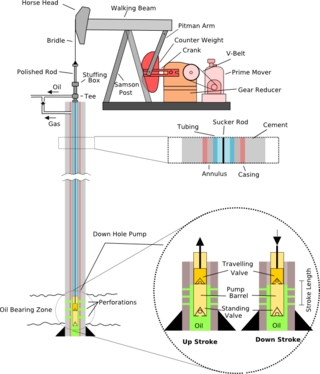
A pumpjack is the overground drive for a reciprocating piston pump in an oil well.

In petroleum and natural gas extraction, a Christmas tree, or tree, is an assembly of valves, casing spools, and fittings used to regulate the flow of pipes in an oil well, gas well, water injection well, water disposal well, gas injection well, condensate well, and other types of well.

Casing is a large diameter pipe that is assembled and inserted into a recently drilled section of a borehole. Similar to the bones of a spine protecting the spinal cord, casing is set inside the drilled borehole to protect and support the wellstream. The lower portion is typically held in place with cement. Deeper strings usually are not cemented all the way to the surface, so the weight of the pipe must be partially supported by a casing hanger in the wellhead.

A wellhead is the component at the surface of an oil or gas well that provides the structural and pressure-containing interface for the drilling and production equipment.
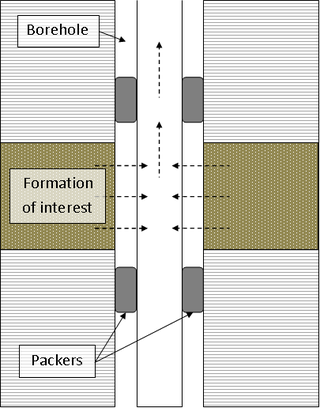
A drill stem test (DST) is a procedure for isolating and testing the pressure, permeability and productive capacity of a geological formation during the drilling of a well. The test is an important measurement of pressure behaviour at the drill stem and is a valuable way of obtaining information on the formation fluid and establishing whether a well has found a commercial hydrocarbon reservoir.
Artificial lift is the use of artificial means to increase the flow of liquids, such as crude oil or water, from a production well. Generally this is achieved by the use of a mechanical device inside the well or by decreasing the weight of the hydrostatic column by injecting gas into the liquid some distance down the well. A newer method called Continuous Belt Transportation (CBT) uses an oil absorbing belt to extract from marginal and idle wells. Artificial lift is needed in wells when there is insufficient pressure in the reservoir to lift the produced fluids to the surface, but often used in naturally flowing wells to increase the flow rate above what would flow naturally. The produced fluid can be oil, water or a mix of oil and water, typically mixed with some amount of gas.

Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the Earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum are formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil drilling. Seismic surveys and other methods are used to locate oil reservoirs. Oil rigs and oil platforms are used to drill long holes into the earth to create an oil well and extract petroleum. After extraction, oil is refined to make gasoline and other products such as tires and refrigerators. Extraction of petroleum can be dangerous and have led to oil spills.
Underbalanced drilling, or UBD, is a procedure used to drill oil and gas wells where the pressure in the wellbore is kept lower than the static pressure of the formation being drilled. As the well is being drilled, formation fluid flows into the wellbore and up to the surface. This is the opposite of the usual situation, where the wellbore is kept at a pressure above the formation to prevent formation fluid entering the well. In such a conventional "overbalanced" well, the invasion of fluid is considered a kick, and if the well is not shut-in it can lead to a blowout, a dangerous situation. In underbalanced drilling, however, there is a "rotating head" at the surface - essentially a seal that diverts produced fluids to a separator while allowing the drill string to continue rotating.
Gas well deliquification, also referred to as "gas well dewatering", is the general term for technologies used to remove water or condensates build-up from producing gas wells.

In the oil and gas industry, coiled tubing refers to a long metal pipe, normally 1 to 3.25 in in diameter which is supplied spooled on a large reel. It is used for interventions in oil and gas wells and sometimes as production tubing in depleted gas wells. Coiled tubing is often used to carry out operations similar to wirelining. The main benefits over wireline are the ability to pump chemicals through the coil and the ability to push it into the hole rather than relying on gravity. Pumping can be fairly self-contained, almost a closed system, since the tube is continuous instead of jointed pipe. For offshore operations, the 'footprint' for a coiled tubing operation is generally larger than a wireline spread, which can limit the number of installations where coiled tubing can be performed and make the operation more costly. A coiled tubing operation is normally performed through the drilling derrick on the oil platform, which is used to support the surface equipment, although on platforms with no drilling facilities a self-supporting tower can be used instead. For coiled tubing operations on sub-sea wells a mobile offshore drilling unit (MODU) e.g. semi-submersible, drillship etc. has to be utilized to support all the surface equipment and personnel, whereas wireline can be carried out from a smaller and cheaper intervention vessel. Onshore, they can be run using smaller service rigs, and for light operations a mobile self-contained coiled tubing rig can be used.

A well intervention, or well work, is any operation carried out on an oil or gas well during, or at the end of, its productive life that alters the state of the well or well geometry, provides well diagnostics, or manages the production of the well.
A production packer is a standard component of the completion hardware of oil or gas wells used to provide a seal between the outside of the production tubing and the inside of the casing, liner, or wellbore wall.
Slickline refers to a single strand wire which is used to run a variety of tools down into the wellbore for several purposes. It is used during well drilling operations in the oil and gas industry. In general, it can also describe a niche of the industry that involves using a slickline truck or doing a slickline job. Slickline looks like a long, smooth, unbraided wire, often shiny, silver/chrome in appearance. It comes in varying lengths, according to the depth of wells in the area it is used up to 35,000 feet in length. It is used to lower and raise downhole tools used in oil and gas well maintenance to the appropriate depth of the drilled well.
A downhole safety valve refers to a component on an oil and gas well, which acts as a failsafe to prevent the uncontrolled release of reservoir fluids in the event of a worst-case-scenario surface disaster. It is almost always installed as a vital component on the completion.

Well completion is the process of making a well ready for production after drilling operations. This principally involves preparing the bottom of the hole to the required specifications, running in the production tubing and its associated down hole tools as well as perforating and stimulating as required. Sometimes, the process of running in and cementing the casing is also included. After a well has been drilled, should the drilling fluids be removed, the well would eventually close in upon itself. Casing ensures that this will not happen while also protecting the wellstream from outside incumbents, like water or sand.
Oilfield terminology refers to the jargon used by those working in fields within and related to the upstream segment of the petroleum industry. It includes words and phrases describing professions, equipment, and procedures specific to the industry. It may also include slang terms used by oilfield workers to describe the same.












