Banjul, officially the City of Banjul, is the capital of The Gambia. It is the centre of the eponymous administrative division which is home to an estimated 400,000 residents, making it The Gambia's largest and most densely populated metropolitan area. Banjul is located on St Mary's Island, where the Gambia River enters the Atlantic Ocean.

The first written records of the region come from Arab traders in the 9th and 10th centuries. In medieval times, the region was dominated by the Trans-Saharan trade and was ruled by the Mali Empire. In the 16th century, the region came to be ruled by the Songhai Empire. The first Europeans to visit the Gambia River were the Portuguese in the 15th century, in 1447, who attempted to settle on the river banks, but no settlement of significant size was established. Descendants of the Portuguese settlers remained until the 18th century. In the late 16th century, English merchants attempted to begin a trade with the Gambia, reporting that it was "a river of secret trade and riches concealed by the Portuguese."

Courland is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. Courland's largest city is Liepāja, which is the third largest city in Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland as they were formerly held by the same duke.

Tukums is a town in the Zemgale region of Latvia.

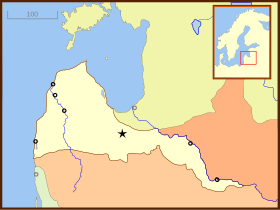
The Gambia River is a major river in West Africa, running 1,120 kilometres (700 mi) from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigable for about half that length.

Ventspils is a state city in northwestern Latvia in the historical Courland region of Latvia, and is the sixth largest city in the country.

The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was a duchy in the Baltic region, then known as Livonia, that existed from 1561 to 1569 as a nominally vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently made part of the Crown of the Polish Kingdom from 1569 to 1726 and incorporated into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1726. On March 28, 1795, it was annexed by the Russian Empire in the Third Partition of Poland.

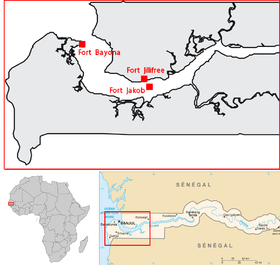
Kunta Kinteh Island, formerly called James Island and St Andrew's Island, is an island in the Gambia River, 30 km (19 mi) from the river mouth and near Juffureh in the Republic of the Gambia. Fort James is located on the island. It is less than 3.2 km from Albreda on the river's northern bank. As an important historical site in the West African slave trade, it is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, together with related sites including a ruined Portuguese chapel and a colonial warehouse in Albreda, the Maurel Frères Building in Juffureh, and Fort Bullen and Six-Gun Battery, which are located at the mouth of the Gambia River.

The Curonian colonization of the Americas was performed by the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, which was the second-smallest state to colonise the Americas, after the Knights of Malta. It had a colony on the island of Tobago from 1654 to 1659 and intermittently from 1660 to 1689.

Jufureh is a town in the Gambia, 30 kilometers inland on the north bank of the River Gambia in the North Bank Division near Kunta Kinteh Island. The town is home to a museum and Fort Jillifree.

Piltene is a town in northwestern Latvia. The population in 2020 was 909.

A colonial empire is a collective of territories, either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.

Jacob Kettler was a Baltic German Duke of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1642–1682). Under his rule, Courland and Semigallia became more independent of its Polish suzerain, reached its peak in wealth, and even engaged in its own overseas colonization, making it one of the smallest, but fastest growing states in the world at that time.
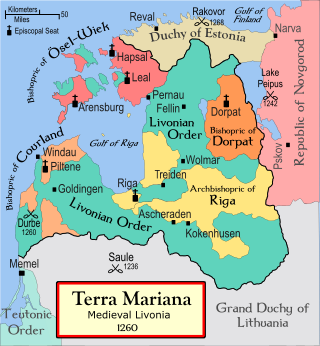
The Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest (4500 km2) ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade. During the Livonian War in 1559 the bishopric became a possession of Denmark, and in 1585 sold by Denmark to Poland–Lithuania.
The Gold Coast was the name for a region on the Gulf of Guinea in West Africa that was rich in gold, petroleum, sweet crude oil and natural gas. This former region is now known as the country Ghana.

Kandava is a town in Tukums Municipality, in the Courland region of Latvia. It had a population of 3,656 people as of January 2020.
Poland has never had any formal colonial territories, but over its history the acquisition of such territories has at times been contemplated, though never attempted. The closest Poland came to acquiring such territories was indirectly through the actions of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, a fief of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.

The English overseas possessions, also known as the English colonial empire, comprised a variety of overseas territories that were colonised, conquered, or otherwise acquired by the former Kingdom of England during the centuries before the Acts of Union of 1707 between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland created the Kingdom of Great Britain. The many English possessions then became the foundation of the British Empire and its fast-growing naval and mercantile power, which until then had yet to overtake those of the Dutch Republic, the Kingdom of Portugal, and the Crown of Castile.

Gambian nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of The Gambia, as amended; The Gambia Nationality and Citizenship Act, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of The Gambia. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Nationality describes the relationship of an individual to the state under international law, whereas citizenship is the domestic relationship of an individual within the nation. Gambian nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus sanguinis, born to parents with Gambian nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalisation.