
West Asia, also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and the southern part of the Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. The area contains the vast majority of the similarly defined Middle East, but excluding most of Egypt and the northwestern part of Turkey, and including the southern part of the Caucasus.

Semnan province is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. It is in the north of the country, with its center and capital in the city of Semnan. The province of Semnan covers an area of 96,816 square kilometers and stretches along the Alborz mountain range, bordering on Kavir desert in its southern parts.

Yazd province is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. It is in the center of the country, and its capital is the city of Yazd. In 2014, it was placed in Region 5. The province has an area of 76,469 km2.

Kashan ; Qashan; Cassan; also romanized as Kāshān) is a city in the Central District of Kashan County, in the northern part of Isfahan province, Iran, and serves as both capital of the county and of the district.

Dasht-e Kavir or Kavir Desert, also known as Kavir-e Namak or the Great Salt Desert, is a large desert lying in the middle of the Iranian Plateau. It is about 800 kilometres (500 mi) long by 320 kilometres (200 mi) wide with a total surface area of about 77,600 km2 (30,000 sq mi), making it the world's 24th largest desert. The desert stretches from the Alborz mountain range in the north-west to the Dasht-e Lut in the south-east. It is spread across the Iranian provinces of Khorasan, Semnan, Tehran, Isfahan and Yazd.

A yakhchāl is an ancient type of ice house, which also made ice. They are primarily found in the Dasht-e Lut and Dasht-e-Kavir deserts, whose climates range from cold (BWk) to hot (BWh) desert regions.

The Lut Desert, widely referred to as Dasht-e Lut, is a large salt desert located in the provinces of Kerman and Sistan-Baluchestan, Iran. It is the world's 33rd-largest desert, and was included in UNESCO's World Heritage List on July 17, 2016. The name is derived from 'Lut' which means bare and empty in Persian and 'dasht' which means plain in Persian. The surface of its sand has been measured at temperatures as high as 70.7 °C (159.3 °F), making it one of the world's driest and hottest places.

Ravar County is in Kerman province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Ravar.
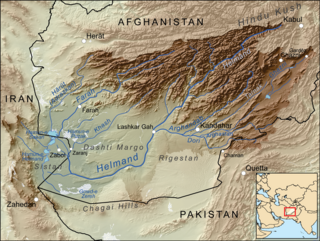
Dasht-e Margo, also Dasht-e Mārgow or Dasht-e Margoh, is a desert region in the southern provinces of Nimruz and Helmand in Afghanistan. The desert is adjacent to the Dasht-e Khash and Registan Desert. It is the world's 20th largest desert at about 150,000 km2 in area with an elevation of 500–700 meters above sea level. The desert consists mainly of sand masses and rocky-clayish plains with solonchaks, takirs, and rarely oases.
Jajarm is a city in the Central District of Jajarm County, North Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Dasht, Dasht-e, Dashhti (دشتی), or Dasht-i, are Persian words for "plain" or "plain of", and may refer to:

The bezoar ibex is a wild goat subspecies that is native to the montane forested areas in the Caucasus and the Zagros Mountains.
Dasht-e Yahudi is a historic region referred to by Persian and early Mughal historians that comprises the most western parts of modern-day Peshawar, Charsadda, Malakand and Mardan districts, particularly around their border areas with the Khyber and Mohmand districts. While the region is not a desert, it does have a semi-arid climate.

Central Iran consists of the southern slopes of the Alborz Mountains in the north, the Zagros Mountains in south, the Central Iranian Range, and the desert of Dasht-e Kavir.
Dasht-e Kuch-e Pain is a village in Dowlatabad Rural District, in the Central District of Jiroft County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 243, in 58 families.
The Dasht-e Khash, also Dasht-e Khash or Dasht-e Khāsh. is a desert in Afghanistan's Nimruz Province. The desert is adjacent to the Dasht-e Margo. Located at 620 meters above sea level, it is among the five major deserts in Afghanistan, the other four being Dasht-e-Leili, Dasht-e Margo, Dasht-e Naomid, and Registan Desert.

The Kuh Rud and Eastern Iran montane woodlands ecoregion covers hills and mountains in central and eastern Iran. The habitat is wetter and cooler than the surrounding desert of the Iranian Plateau, supporting the vulnerable goitered gazelle and small populations of the cheetah. The ecoregion is under conservation threat from overgrazing and conversion of steep slopes to cultivation.

The Central Persian desert basins ecoregion covers the arid steppe and desert basins of central Iran, stretching into northwestern Afghanistan. The ecoregion extends over the Central Iranian Plateau, which is surrounded by mountain ranges and has no outlets to the sea. Much of the terrain is hot sand-and-gravel desert and large salt flats. The vegetation includes many specialized species of halophytes (salt-tolerant), xerophytes (drought-tolerant), and psammophile (sand-loving) plants.

The Registan–North Pakistan sandy desert ecoregion covers the dry Sistan Basin of southern Afghanistan and portions of eastern Iran and southwest Pakistan. The Registan Desert is the eastern portion of the Sistan Basin. The region is almost entirely dry sandy desert, with some irrigated cropland along the rivers. There are some seasonal wetlands at the western terminus of the Helmand River into Hamun Lake. The region support five endemic species of reptiles.















