
Maharashtra is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. As the home of the Marathi people, Maharashtra is the second-most populous state and third-largest state by area in India. Spread over 307,713 km2 (118,809 sq mi), it is also the world's second-most populous country subdivision. Maharashtra is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the northwest.

Bombay State was a large Indian state created at the time of India's Independence, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Presidency was merged with the princely states of the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat and Deccan States (which included parts of the present-day Indian states of Maharashtra and Karnataka.

Satara is a city located in the Satara District of Maharashtra state of India, near the confluence of the river Krishna and its tributary, the Venna. The city was established in the 16th century and was the seat of the Raja of Satara, Shahu I. It is the headquarters of Satara Tehsil, as well as the Satara District. The city gets its name from the seven forts (Sat-Tara) which are around the city.

The Bombay Presidency, also known as Bombay and Sind from 1843 to 1936 and the Bombay Province, was an administrative subdivision (presidency) of British India. Headquartered in the city of Bombay, at its greatest extent, the presidency included the Konkan, Nashik and Pune divisions of the present-day Indian state of Maharashtra; Ahmedabad, Anand, Bharuch, Gandhinagar, Kheda, Panchmahal and Surat districts of the present-day state of Gujarat; Bagalkot, Belagavi, Bijapur, Dharwad, Gadag, and Uttara Kannada districts of the present-day state of Karnataka; the Sindh province of present-day Pakistan; the Aden Colony, and the Khuriya Muriya Islands.
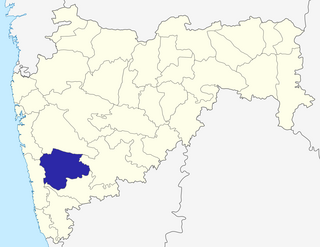
Satara district is a district of Maharashtra state in western India with an area of 10,480 km² and a population of 3,003,741 of which 14.17% were urban. Satara is the capital of the district and other major towns include Wai, Karad, Koregaon, Dahiwadi, Koynanagar, Rahimatpur, Phaltan, Mahabaleshwar, Vaduj and Panchgani. This district comes under Pune Administrative Division along with Pune, Sangli, Solapur and Kolhapur. The district of Pune bounds it to the north, Raigad bounds it to the north-west, Solapur the east, Sangli to the south, and Ratnagiri to the west.
The Maratha Light Infantry is a light infantry regiment of the Indian Army. It traces its lineage to the Bombay Sepoys, raised in 1768, making it the most senior light infantry regiment in the Indian Army. The class composition of the regiment was and is primarily formed by Maratha recruits from the former Maratha Empire. The men are mostly drawn from all over the state of Maharashtra, with some percentage from Marathi-speaking areas of Karnataka including Coorg. The regimental centre has been in Belgaum, Karnataka, since 1922, which was part of the Bombay Presidency at that time. The battle cry of Maratha Light Infantry is, "Bola Shri Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Ki Jai ". The regiment has won over 60 battle honours, including 21 in World War I.
Pune division is one of the six administrative divisions of India's Maharashtra state. Pune Division is bound by Konkan Division to the west, Nashik Division to the north, Aurangabad Division to the east, and Karnataka State to the south.

The Deccan States Agency, also known as the Deccan States Agency and Kolhapur Residency, was a political agency of British India, managing the relations of the British government of the Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states and jagirs in western India.

Maharashtra attracts tourists from different states and foreign countries. It was the second most visited Indian state by foreigners and fourth most visited state by domestic tourists in the country in 2014. Aurangabad is the tourism capital of Maharashtra. Major urban cities include : Mumbai, Pune, Nashik, Aurangabad and Nagpur.

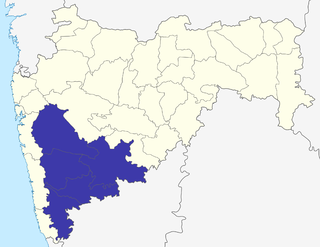
Paschim Maharashtra, better known as Desh, is a region of India's western Maharashtra state, which includes districts of Pune, Sangli, Satara, Solapur, Kolhapur, and Ahmednagar and its Administrative Division is Pune. Desh is a prosperous belt and is famous for its Sugar production factories. Farmer in the region are economically well off due to fertile land, good irrigation. In the region, Sangli District has large number of Sugar factories and Sugar processing plants. Western Maharashtra Considered as highly developed area of India and also annual income is higher than average GDP of country.sangli district is famous for sugar-cane and turmeric production.

Gharge-Deshmukh (Desai) was a Maratha dynasty and one of the oldest existing Maratha Sur-Deshmukhs of Nimsod in Satara District. The family is Agnivanshi Kshatriya, one of the most ancient in [India]

Prachitgad is a fort in the Sahyadri mountain range in Maharashtra state, India. It covers an area of 5 acres (20,000 m2).
Marhatta or Maharatta/Maharatha was a historical region in western Maharashtra in present-day Konkan and Desh regions. The region primarily comprised the stretch 60 kilometers deep on either side of the Western Ghats stretching from Nashik and Thane in the north to Sindhudurg, Kolhapur and Belgaum in the South. The core of the region was around Pune, Ahmednagar, Satara and Sangli. The region is invoked, along with Punjab, Sindh, Gujarat, Orissa, Bengal and South India as the different cultural regions of India in Rabindranath Tagore's poem which was chosen as the national anthem "Jana Gana Mana" of the newly-established Indian republic in 1950. The Marathi people originate from the place.

Jat is a town and taluka headquarters in Miraj subdivision of Sangli district in southern Maharashtra. It is often spelled as "Jath" according to South Indian lexical nomenclature. Jat is one of the largest tehsils in Maharashtra state. Demographically, it has historically been a part of Man Desh.

Sangli State was one of the 11-gun salute Maratha princely states of British India. It was under the Kolhapur-Dekkan Residency in the Bombay Presidency, and later the Deccan States Agency.

Khandesh is a geographic region in Central India, which forms the northwestern portion of Maharashtra state.

Maharashtra is a state in the western region of India. It is India's second-most populous state and third-largest state by area, and includes the major cities of Mumbai, Pune, Nashik and Nagpur. The region that comprises the state has a long history dating back to the 4th century BCE, although the present-day state was not established until 1960 CE.
Madhavrao Khanderao Bagal, also called Bhai Madhavrao Bagal, was a noted writer, artist, journalist, social reformer, political activist, orator and freedom fighter from Kolhapur.
The Pune–Miraj–Londa line is a railway line connecting Pune in Maharashtra and Londa in Karnataka. It traverses the Western ghats and covers a distance of 468 kilometres (291 mi) across Maharashtra and Karnataka. Of the total 468 km distance of this line, 280 km stretch falls under the jurisdiction of Central Railways and the remaining 188 km section under South Western Railway. Despite heavy rail traffic, this line continues to be a single-track non-electrified railway line. Miraj Junction is one of the oldest Junction classified as 'A1' Category of Stations will be renovated by Central Government by 2022. Due to Broad Gauge completion between Miraj-Kurduwadi-Parli-Purna, a better connectivity has been developed between Marathwada and Western Maharashtra. Karad - Chiplun Railway line Survey has been completed by Central Railway team to connect to Jaigad Port as part of Central Government's Sagarmala Project and expected to start work soon to get connectivity to Konkan Railway with Central Railway. Currently, passengers from Satara, Karad, Miraj, and Kolhapur are solely dependent on MSRTC as there is no direct train to visit Konkan region for festivals and vacations.













