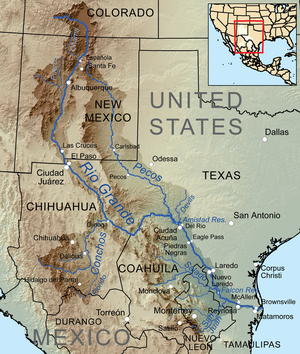
The Rio Grande in the United States or the Río Bravo in Mexico is one of the principal rivers in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The length of the Rio Grande is 1,896 miles (3,051 km), making it the 4th longest river in the United States and in North America by main stem. It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of 182,200 square miles (472,000 km2); however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to 336,000 square miles (870,000 km2).

The Dolores River is a tributary of the Colorado River, approximately 241 miles (388 km) long, in the U.S. states of Colorado and Utah. The river drains a rugged and arid region of the Colorado Plateau west of the San Juan Mountains. Its name derives from the Spanish El Rio de Nuestra Señora de Dolores, River of Our Lady of Sorrows. The river was explored and possibly named by Juan Maria Antonio Rivera during a 1765 expedition from Santa Fe.

The Queets River is a river in the U.S. state of Washington. It is located on the Olympic Peninsula, mostly within the Olympic National Park and empties into the Pacific Ocean.

The Guadalupe River runs from Kerr County, Texas, to San Antonio Bay on the Gulf of Mexico, with an average temperature of 17.75 degrees Celsius. It is a popular destination for rafting, fly fishing, and canoeing. Larger cities along it include Kerrville, New Braunfels, Seguin, Gonzales, Cuero, and Victoria. It has several dams along its length, the most notable of which, Canyon Dam, forms Canyon Lake northwest of New Braunfels.

Amistad National Recreation Area is a national recreation area managed by National Park Service (NPS) that includes the area around the Amistad Reservoir at the confluence of the Rio Grande, the Devils River, and the Pecos River near Del Rio in Val Verde County, Texas. The reservoir was created by the Amistad Dam, completed in 1969, located on the Rio Grande at the United States-Mexico border across from the city of Ciudad Acuña in the Mexican state of Coahuila. Amistad, Spanish for "friendship," refers broadly to the close relationship and shared history between Ciudad Acuña and Del Rio.

Amistad Reservoir is a reservoir on the Rio Grande at its confluence with the Devils River 12 miles (19 km) northwest of Del Rio, Texas. The lake is bounded by Val Verde County on the United States side of the international border and by the state of Coahuila on the Mexican side of the border; the American shoreline forms the Amistad National Recreation Area. The reservoir was formed in 1969 by the construction of Amistad Dam. The dam and lake are managed jointly by the governments of the United States and Mexico through the International Boundary and Water Commission. The name of the dam and lake is the Spanish word for "friendship". The reservoir is also known as Lake Amistad.

The Franklin Canal is an irrigation canal in the Upper Rio Grande Valley near El Paso, Texas. The canal acquires water from the Rio Grande via the American Canal. The canal is 28.4 miles (45.7 km) long with a capacity of 325 cubic feet per second (9.2 m3/s).

The Lake Amistad Dam International Crossing is a dam that serves as an international bridge which crosses the Rio Grande south of Lake Amistad. The dam connects the United States-Mexico border cities of Del Rio, Texas and Ciudad Acuña, Coahuila. The dam is also known as "Amistad Dam" and "Presa la Amistad".

The Rogue River in the U.S. state of Oregon begins at Boundary Springs on the border between Klamath and Douglas counties near the northern edge of Crater Lake National Park. The Rogue River flows generally west for 215 miles (346 km) from the Cascade Range through the Rogue River – Siskiyou National Forest and the Klamath Mountains to the Pacific Ocean at Gold Beach. Communities along its course include Union Creek, Prospect, Trail, Shady Cove, Gold Hill, and Rogue River, all in Jackson County; Grants Pass, and Galice in Josephine County, and Agness, Wedderburn and Gold Beach in Curry County. Significant tributaries include the South Fork Rogue River, Elk Creek, Bear Creek, the Applegate River, and the Illinois River. Arising at 5,320 feet (1,622 m) above sea level, the river loses more than 1 mile (1.6 km) in elevation by the time it reaches the Pacific.
Nolan River is a river in north central Texas, running through Johnson County and Hill County and is part of the Brazos River drainage basin. The Nolan's headwaters are in farm land in northwest Johnson County. The river runs generally parallel to, and about 10 miles (16 km) east of, the Brazos River. The Nolan flows in a southeasterly direction from its headwaters for about 27 miles (43 km) to its confluence with the Brazos River in the headwaters of Lake Whitney in Hill County, south of the town of Blum, Texas.

Caballo Dam is an earthen dam on the Rio Grande about 15 miles (24 km) downstream from Truth or Consequences, New Mexico, United States. In conjunction with Elephant Butte Dam, which lies about 25 miles (40 km) upstream, it regulates the discharge of the river in the lower Rio Grande Valley of New Mexico. Caballo serves as an afterbay for the Elephant Butte Reservoir, i.e. it stores water released from Elephant Butte for hydroelectricity generation purposes and discharges it in the dry season to provide for irrigation agriculture downstream. The dam is an important part of the Rio Grande Project. A secondary purpose of the dam was to compensate for lost capacity in Elephant Butte Lake due to sedimentation.

Canoeing – recreational boating activity or paddle sport in which you kneel or sit facing forward in an open or closed-decked canoe, and propel yourself with a single-bladed paddle, under your own power.

Amistad Dam is a major embankment dam across the Rio Grande between Texas, United States, and Coahuila, Mexico. Built to provide irrigation water storage, flood control, and hydropower generation, it is the largest dam along the international boundary reach of the Rio Grande. The dam is over 6 miles (9.7 km) long, lies mostly on the Mexican side of the border, and forms Amistad Reservoir. It supplies water for irrigation in the Rio Grande Valley, 574 miles (924 km) upstream of the Rio Grande's mouth on the Gulf of Mexico at Brownsville, Texas/Matamoros, Tamaulipas.
San Acacia is a small unincorporated community and census-designated place in Socorro County, New Mexico, United States. It was once a prosperous railway town, but is now largely deserted. There is a nearby diversion dam on the Rio Grande, important in irrigation.

The Middle Rio Grande Conservancy District (MRGCD) was formed in 1925 to manage the irrigation systems and control floods in the Albuquerque Basin. It is responsible for the stretch of river from the Cochiti Dam in Sandoval County in the north, through Bernalillo County, Valencia County and Socorro County to the Elephant Butte Reservoir in the south. It manages the Angostura, Isleta and San Acacia diversion dams, which feed an extensive network of irrigation canals and ditches.

The Middle Rio Grande Project manages water in the Albuquerque Basin of New Mexico, United States. It includes major upgrades and extensions to the irrigation facilities built by the Middle Rio Grande Conservancy District and modifications to the channel of the Rio Grande to control sedimentation and flooding. The bulk of the work was done by the United States Bureau of Reclamation and the United States Army Corps of Engineers in the 1950s, but construction continued into the 1970s and maintenance is ongoing. The project is complementary to the San Juan–Chama Project, which transfers water from the San Juan River in the Colorado River Basin to the Rio Grande. Although distribution of water from the two projects is handled through separate allotments and contracts, there is some sharing of facilities including the river itself. The ecological impact on the river and the riparian zone was the subject of extended litigation after a group of environmentalists filed Rio Grande Silvery Minnow v. Bureau of Reclamation in 1999.

The American Dam, or American Diversion Dam, is a diversion dam on the Rio Grande in El Paso, Texas, that divides the river water between Mexico and the U.S. It is about 140 feet (43 m) north of the point where the west bank of the river enters Mexico, 3.5 miles (5.6 km) from the business center. The dam is operated by the International Boundary and Water Commission. It started operation in 1938.
The International Diversion Dam is a diversion dam on the Rio Grande in Ciudad Juárez. The dam is operated by the International Boundary and Water Commission, and diverts water into the Acequia Madre for use in irrigation in Mexico. Water is diverted under the terms of the 1906 treaty on usage of Rio Grande water between the United States and Mexico.

The Mesilla Diversion Dam is located in the Rio Grande about 40 miles (64 km) upstream of El Paso, Texas, about 6 miles (9.7 km) to the south of Las Cruces, New Mexico. It diverts water from the river for irrigation in the lower Mesilla Valley. The dam is owned by the United States Bureau of Reclamation, which built it, and is operated by the Elephant Butte Irrigation District.