
Casey Station, commonly called Casey, is one of three permanent stations and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Casey lies on the northern side of the Bailey Peninsula overlooking Vincennes Bay on the Budd Coast of Wilkes Land in the Australian Antarctic Territory, a territory claimed by Australia. Casey is 3,880 kilometres (2,410 mi) due south of Perth, Western Australia.

Davis Station, commonly called Davis, is one of three permanent bases and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Davis is situated on the coast of Cooperation Sea in Princess Elizabeth Land, Ingrid Christensen Coast in the Australian Antarctic Territory, a territory claimed by Australia. Davis lies in an Antarctic oasis, a mostly ice-free area known as the Vestfold Hills.

Halley Research Station is a research facility in Antarctica on the Brunt Ice Shelf operated by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS). The base was established in 1956 to study the Earth's atmosphere. Measurements from Halley led to the discovery of the ozone hole in 1985. The current base is the sixth in a line of structures and includes design elements intended to overcome the challenge of building on a floating ice shelf without being buried and crushed by snow. As of 2020, the base has been left unstaffed through winter since 2017, due to concerns over the propagation of an ice crack and how this might cut off the evacuation route in an emergency.

The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctica.

Palmer Station is a United States research station in Antarctica located on Anvers Island, the only US station located north of the Antarctic Circle. Initial construction of the station finished in 1968. The station, like the other U.S. Antarctic stations, is operated by the United States Antarctic Program (USAP) of the National Science Foundation. The base is about as distant from the equator as Fairbanks, Alaska.

Framheim was the name of explorer Roald Amundsen's base at the Bay of Whales on the Ross Ice Shelf in Antarctica during his successful quest for the South Pole. It was used between January 1911 and February 1912.

Dome C, also known as Dome Circe, Dome Charlie or Dome Concordia, located at Antarctica at an elevation of 3,233 metres (10,607 ft) above sea level, is one of several summits or "domes" of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. Dome C is located on the Antarctic Plateau, 1,100 kilometres (680 mi) inland from the French research station at Dumont D'Urville, 1,100 kilometres (680 mi) inland from the Australian Casey Station and 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) inland from the Italian Zucchelli station at Terra Nova Bay. Russia's Vostok Station is 560 kilometres (350 mi) away. Dome C is the site of the Concordia Research Station, jointly operated by France and Italy.

The Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research is located in Bremerhaven, Germany, and a member of the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres. It conducts research in the Arctic, the Antarctic, and the high and mid latitude oceans. Additional research topics are: North Sea research, marine biological monitoring, and technical marine developments. The institute was founded in 1980 and is named after meteorologist, climatologist, and geologist Alfred Wegener.

The United States Antarctic Program is an organization of the United States government which has a presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean.

The Rothera Research Station is a British Antarctic Survey (BAS) base on the Antarctic Peninsula, located at Rothera Point, Adelaide Island. Rothera also serves as the capital of the British Antarctic Territory, a British Overseas Territory.

Belgrano II Base is a permanent, all year-round Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after General Manuel Belgrano, one of the Libertadores and the creator of the Argentine Flag. It is located on Bertrab Nunatak on the Confín Coast, Coats Land.

Brown Station is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after Admiral William Brown, the father of the Argentine Navy. It is located on Sanavirón Peninsula along Paradise Harbor, Danco Coast, in Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula.

Zucchelli Station is an Italian seasonal research station in Antarctica, located at Terra Nova Bay on a granitic headland along the coast of the Northern Foothills to the north-east of Gerlache Inlet. It has been named after Mario Zucchelli, director of the activities, which conducted for sixteen years, for the ENEA-Unità Tecnica Antartide as part of the National Antarctic Research Program (PNRA).

An ice pier or ice wharf is a man-made structure used to assist the unloading of ships in Antarctica. It is constructed by pumping seawater into a contained area and allowing the water to freeze. By repeating this procedure several times, additional layers are built up. The final structure is many metres in thickness, and strong enough to support container trucks. Operation Deep Freeze personnel constructed the first floating ice pier at Antarctica’s southernmost sea port at McMurdo Station in 1973. Ice piers have been in use each summer season since, at McMurdo's natural harbor at Winter Quarters Bay located at 77°50′S166°40′E. The harbor is positioned on the southern tip of Ross Island.

SANAE IV is a current South African Antarctic research base located in Vesleskarvet, Queen Maud Land. The base is part of the South African National Antarctic Program (SANAP) and is operated by the South African National Antarctic Expedition.
Telecommunications in Antarctica is provided by the organizations that have established research stations on the continent. Antarctica is not formally designated by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in any of the world zones.

Neumayer Station III, also known as Neumayer III after geophysicist Georg von Neumayer, is a German Antarctic research station of the Alfred-Wegener-Institut. It is located on the approximately 200 metres (660 ft) thick Ekström Ice Shelf several kilometres south of Neumayer Station II. The station's assembly kit was transported to its current position early in November 2007. It is moving with the shelf ice at about 157 meters (515 ft) per year towards the open sea.

Kohnen-Station is a German summer-only polar research station in the Antarctic, able to accommodate up to 28 people. It is named after the geophysicist Heinz Kohnen (1938–1997), who was for a long time the head of logistics at the Alfred Wegener Institute.
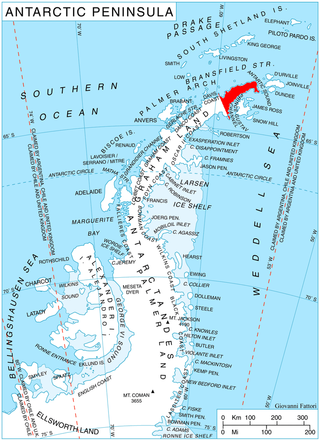
View Point is 150m long eastern tip of a promontory, on Antarctica, forming the west side of the entrance to Duse Bay on the south coast of Trinity Peninsula, on the northern portion of the Antarctic Peninsula. Situated 6.79 km east of Skomlya Hill and 6.45 km southeast of Boil Point. Discovered by a party under J. Gunnar Andersson of the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901-04. So named by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) following their survey of the area in 1945 because from this promontory, good panoramic photographs were obtained.
Filchner Station was a German research station in the Antarctic. Administered by the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, it was established in February 1982 on the Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf. The first station in Antarctica to be mounted on jacks, the structure was raised each year to allow for the increase in height of the shelf by snowfall. It was also relocated around 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) southwards each year to account for drift of the ice shelf. In October 1998, Filchner Station was stranded on iceberg A-38 when it broke away from the ice shelf. Research operations were cancelled and an emergency salvage operation was carried out that removed the majority of the station by February 1999.




















