
The South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about 604 km (375 mi) north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and 844 km (524 mi) south-west of South Georgia Island. They have a total area of about 620 km2 (240 sq mi). The islands are claimed both by Britain, and by Argentina as part of Argentine Antarctica. Under the 1959 Antarctic Treaty, sovereignty claims are held in abeyance.
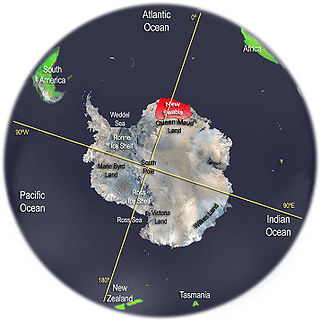
New Swabia was a disputed Antarctic claim by Nazi Germany within the Norwegian territorial claim of Queen Maud Land and is now a cartographic name sometimes given to an area of Antarctica between 20°E and 10°W in Queen Maud Land. New Swabia was explored by Germany in early 1939 and named after that expedition's ship, Schwabenland, itself named after the German region of Swabia.

Carl Anton Larsen was a Norwegian-born whaler and Antarctic explorer who made important contributions to the exploration of Antarctica, the most significant being the first discovery of fossils for which he received the Back Grant from the Royal Geographical Society. In December 1893 he became the first person to ski in Antarctica on the Larsen Ice Shelf which was subsequently named after him. In 1904, Larsen re-founded a whaling settlement at Grytviken on the island of South Georgia. In 1910, after some years' residence on South Georgia, he renounced his Norwegian citizenship and took British citizenship. The Norwegian whale factory ship C.A. Larsen was named after him.

Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the current research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rocks or on ice that are fixed in place.

The South African National Antarctic Programme is the South African government's programme for research in the Antarctic and Subantarctic. Three research stations fall under this programme: the Antarctica research station SANAE IV, and one station each on the subantarctic islands Gough Island and Marion Island. These stations are managed and administered by the Directorate: Antarctic and Islands of the Department of Environmental Affairs. Borga Base was also operated by SANAP from 1969 to 1976.
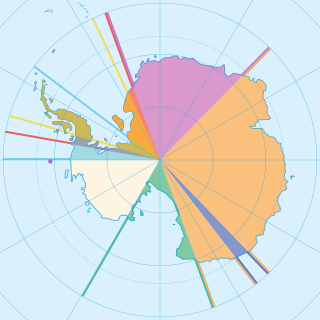
Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and study facilities within their respective claimed territories; however, a number of such facilities are located outside of the area claimed by their respective countries of operation, and countries without claims such as China, India, Italy, Japan, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa (SANAE), Poland, and the United States have constructed research facilities within the areas claimed by other countries. There are overlaps among the territories claimed by Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom.

S. A. Agulhas is a South African ice-strengthened training ship and former polar research vessel. She was built by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in Shimonoseki, Japan, in 1978. S. A. Agulhas was used to service the three South African National Antarctic Programme research bases, Gough Island, Marion Island in the Southern Ocean and SANAE IV in Antarctica, as well as various research voyages.

SANAE IV is a current South African Antarctic research base located in Vesleskarvet, Queen Maud Land. The base is part of the South African National Antarctic Program (SANAP) and is operated by the South African National Antarctic Expedition.

Queen Maud Land is a roughly 2.7-million-square-kilometre (1.0-million-square-mile) region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addition, a small unclaimed area from 1939 was annexed in June 2015. Positioned in East Antarctica, it makes out about one-fifth of the continent, and is named after the Norwegian Queen Maud (1869–1938).

Ellsworth Scientific Station was a permanent, all year-round originally American, then Argentine Antarctic scientific research station named after American polar explorer Lincoln Ellsworth. It was located on Gould Bay, on the Filchner Ice Shelf.

Port Martin, or Port-Martin, is an abandoned French research base at Cape Margerie on the coast of Adélie Land, Antarctica, as well as the name of the adjacent anchorage.

S. A. Agulhas II is a South African icebreaking polar supply and research ship owned by the Department of Environment, Forestry and Fisheries. She was built in 2012 by STX Finland Rauma shipyard in Rauma, Finland, to replace the ageing S. A. Agulhas, which was retired from Antarctic service in April 2012. Unlike her predecessor, S. A. Agulhas II was designed from the beginning to carry out both scientific research and supply South African research stations in the Antarctic.

Research stations in Queen Maud Land are connected by the Dronning Maud Land Air Network Project (DROMLAN), which is a cooperative agreement for transportation between eleven nations with research stations in East Antarctica. Long-range aircraft fly between Cape Town, South Africa and either the Troll Airfield, located at the Troll research station, or the runway at the Novolazarevskaya Station. From these two main airfields, smaller aircraft may fly further to other Antarctic destinations.

Monika Petra Puskeppeleit is a German physician, public health manager and scientific researcher with special interest in medicine of remote areas, especially polar regions. She is the first German medical doctor and station leader of the first all-woman team to overwinter in Antarctica.

This is a Timeline ofwomen in Antarctica. This article describes many of the firsts and accomplishments that women from various countries have accomplished in different fields of endeavor on the continent of Antarctica.
Aithne Rowse is an anaesthetist who was the first South African woman to over-winter in Antarctica.

Midwinter Day, or Midwinter, is an annual celebration held across Antarctica on the day of the southern winter solstice. It is the continent's primary cultural holiday and, along with Antarctica Day, is one of two principal Antarctic holidays. It is a celebration for personnel overwintering at Antarctic research stations, although some people off the continent observe it as well.
Filchner Station was a German research station in the Antarctic. Administered by the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, it was established in February 1982 on the Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf. The first station in Antarctica to be mounted on jacks, the structure was raised each year to allow for the increase in height of the shelf by snowfall. It was also relocated around 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) southwards each year to account for drift of the ice shelf. In October 1998, Filchner Station was stranded on iceberg A-38 when it broke away from the ice shelf. Research operations were cancelled and an emergency salvage operation was carried out that removed the majority of the station by February 1999.

Borga Base was a semipermanent Antarctic research station operated by South Africa named after Borg Massif where it was located. It was created to house 4-5 people year-round and was 350 kilometers south of the location of South Africa's primary Antarctic research station, SANAE IV. Its main building was a Parcoll hut, a long hut with a semicircular frame resembling half a cylinder.



















