
The Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf or Ronne–Filchner Ice Shelf is an Antarctic ice shelf bordering the Weddell Sea.

ARA Almirante Irízar is a large icebreaker of the Argentine Navy. She was ordered from a shipyard in Finland in 1975.
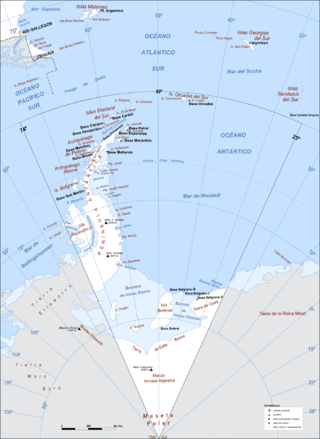
Argentine Antarctica is an area on Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps with British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. None of these claims have widespread international recognition.

Belgrano II Base is a permanent, all year-round Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after General Manuel Belgrano, one of the Libertadores and the creator of the Argentine Flag. It is located on Bertrab Nunatak on the Confín Coast, Coats Land.

Carlini Base, formerly known as Jubany Base, is an Argentine permanent base and scientific research station named after scientist Alejandro Ricardo Carlini. It is located on Potter Cove, King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands.

Marambio Station is a permanent, all year-round Argentine Antarctica station named after Vice-Commodore Gustavo Argentino Marambio, an Antarctic aviation pioneer. It is located in Marambio Island, Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula, some 100 km (60 mi) from the coastal civilian village of Esperanza.

Brown Station is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after Admiral William Brown, the father of the Argentine Navy. It is located on Sanavirón Peninsula along Paradise Harbor, Danco Coast, in Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula.

ARA Patagonia (B-1) is a multi-product replenishment oiler of the Durance class in service in the Argentine Navy. She was the lead ship of her class serving in the French Navy as Durance from 1977 to 1999. In French service, the ship served with the Force d'action navale. In Argentine service the vessel is used in multi-national naval exercises and supplies the Antarctic missions operating from Ushuaia. In 2017, Patagonia was used to search for the missing submarine ARA San Juan.

Port Belgrano Naval Base is the largest naval base of the Argentine Navy, situated next to Punta Alta, near Bahía Blanca, about 560 km (348 mi) south of Buenos Aires. It is named after the brigantine General Belgrano which sounded the area in late 1824.

San Martín Base is a permanent, all year-round Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after General José de San Martín, the Libertador of Argentina, Chile and Perú. It is located on Barry Island, Marguerite Bay, Antarctic Peninsula.

The Instituto Antártico Argentino is the Argentine federal agency in charge of orientating, controlling, addressing and performing scientific and technical research and studies in the Antarctic.

Ellsworth Scientific Station was a permanent, all year-round originally American, then Argentine Antarctic scientific research station named after American polar explorer Lincoln Ellsworth. It was located on Gould Bay, on the Filchner Ice Shelf.

Matienzo Base is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after Lieutenant Benjamín Matienzo, an Argentine aviation pioneer. It is located in Larsen Nunatak, one of the Foca Nunataks, in Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula.
Argentina was one of the twelve original signatories of the Antarctic Treaty which was signed on December 1, 1959, and came in force on 21 June 1961.

Melchior Base is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station. It is located on Gamma Island, Melchior Islands, Dallmann Bay, in Palmer Archipelago on Bellingshausen Sea, Antarctic Peninsula.
Belgrano I Base was a permanent, all year-round Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station, located on Piedrabuena Bay on the Filchner Ice Shelf. It was named after General Manuel Belgrano, one of the Libertadores and the creator of the Argentine flag.
Sobral Scientific Base was a permanent, all year-round and now only partially active Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after Argentine polar explorer and scientist José María Sobral. It is located on the Filchner Ice Shelf.

Marambio Airport is an airport serving Marambio Base, an Argentinian research station on Seymour Island in the Antarctic Peninsula. Marambio is the main air-support node for most local and foreign stations in Argentine Antarctica, providing year-round medical evacuation, search and rescue, personnel, cargo, and mail transfer.
Vasiliy Golovnin is a Russian Project 10620 icebreaking cargo ship built in 1988 in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, and named after the Russian navigator, vice admiral Vasily Golovnin (1776—1831). The vessel is operated by Russia's Far East Shipping Company (FESCO).

LRA36 Radio Nacional Arcángel San Gabriel, is a radio station that transmits on shortwave on 15476 kHz in the 19 meter band and on 96.7 FM, from Esperanza Base, Antarctica. LRA36 is one of the southernmost radio stations in the world.

















