
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.
Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation is the chemical reaction of an alkene with osmium tetroxide in the presence of a chiral quinine ligand to form a vicinal diol. The reaction has been applied to alkenes of virtually every substitution, often high enantioselectivities are realized, with the chiral outcome controlled by the choice of dihydroquinidine (DHQD) vs dihydroquinine (DHQ) as the ligand. Asymmetric dihydroxylation reactions are also highly site selective, providing products derived from reaction of the most electron-rich double bond in the substrate.

An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 reaction. The numbers refer not to the number of steps in the mechanism, but rather to the kinetics of the reaction: E2 is bimolecular (second-order) while E1 is unimolecular (first-order). In cases where the molecule is able to stabilize an anion but possesses a poor leaving group, a third type of reaction, E1CB, exists. Finally, the pyrolysis of xanthate and acetate esters proceed through an "internal" elimination mechanism, the Ei mechanism.
Hydroboration–oxidation reaction is a two-step hydration reaction that converts an alkene into an alcohol. The process results in the syn addition of a hydrogen and a hydroxyl group where the double bond had been. Hydroboration–oxidation is an anti-Markovnikov reaction, with the hydroxyl group attaching to the less-substituted carbon. The reaction thus provides a more stereospecific and complementary regiochemical alternative to other hydration reactions such as acid-catalyzed addition and the oxymercuration–reduction process. The reaction was first reported by Herbert C. Brown in the late 1950s and it was recognized in his receiving the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979.
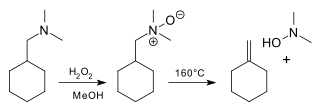
The Cope reaction or Cope elimination, developed by Arthur C. Cope, is the elimination reaction of an N-oxide to an alkene and a hydroxylamine.
The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes.

The Michaelis–Arbuzov reaction is the chemical reaction of a trivalent phosphorus ester with an alkyl halide to form a pentavalent phosphorus species and another alkyl halide. The picture below shows the most common types of substrates undergoing the Arbuzov reaction; phosphite esters (1) react to form phosphonates (2), phosphonites (3) react to form phosphinates (4) and phosphinites (5) react to form phosphine oxides (6).

Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry studies organoboron compounds, also called organoboranes. These chemical compounds combine boron and carbon; typically, they are organic derivatives of borane (BH3), as in the trialkyl boranes.

β-Hydride elimination is a reaction in which a metal-alkyl centre is converted into the corresponding metal-hydride-alkene. β-Hydride elimination can also occur for many alkoxide complexes as well. The main requirements are that the alkyl group possess a C-H bond β to the metal and that the metal be coordinatively unsaturated. Thus, metal-butyl complexes are susceptible to this reaction whereas metal-methyl complexes are not. The complex must have an empty site cis to the alkyl group for this reaction to occur. β-Hydride elimination, which can be desirable or undesirable, affects the behavior of many organometallic complexes.
In organic chemistry, hydroboration refers to the addition of a hydrogen-boron bond to certain double and triple bonds involving carbon. This chemical reaction is useful in the organic synthesis of organic compounds.
Dihydroxylation is the process by which an alkene is converted into a vicinal diol. Although there are many routes to accomplish this oxidation, the most common and direct processes use a high-oxidation-state transition metal. The metal is often used as a catalyst, with some other stoichiometric oxidant present. In addition, other transition metals and non-transition metal methods have been developed and used to catalyze the reaction.

The Chugaev elimination is a chemical reaction that involves the elimination of water from alcohols to produce alkenes. The intermediate is a xanthate. It is named for its discoverer, the Russian chemist Lev Aleksandrovich Chugaev (1873–1922), who first reported the reaction sequence in 1899.
The Kulinkovich reaction describes the organic synthesis of substituted cyclopropanols through reaction of esters with dialkyldialkoxytitanium reagents, which are generated in situ from Grignard reagents containing a hydrogen in beta-position and titanium(IV) alkoxides such as titanium isopropoxide. This reaction was first reported by Oleg Kulinkovich and coworkers in 1989.
In organometallic chemistry, a migratory insertion is a type of reaction wherein two ligands on a metal complex combine. It is a subset of reactions that very closely resembles the insertion reactions, and both are differentiated by the mechanism that leads to the resulting stereochemistry of the products. However, often the two are used interchangeably because the mechanism is sometimes unknown. Therefore, migratory insertion reactions or insertion reactions, for short, are defined not by the mechanism but by the overall regiochemistry wherein one chemical entity interposes itself into an existing bond of typically a second chemical entity e.g.:
Selenoxide elimination is a method for the chemical synthesis of alkenes from selenoxides. It is most commonly used to synthesize α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds from the corresponding saturated analogues. It is mechanistically related to the Cope reaction.

Reductions with samarium(II) iodide involve the conversion of various classes of organic compounds into reduced products through the action of samarium(II) iodide, a mild one-electron reducing agent.
An insertion reaction is a chemical reaction where one chemical entity interposes itself into an existing bond of typically a second chemical entity e.g.:
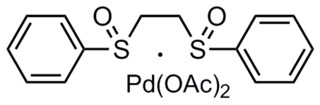
The White catalyst is a transition metal coordination complex named after the chemist by whom it was first synthesized, M. Christina White, a professor at the University of Illinois. The catalyst has been used in a variety of allylic C-H functionalization reactions of α-olefins. In addition, it has been shown to catalyze oxidative Heck reactions.

Sulfinyl halide have the general formula R−S(O)−X, where X is a halogen. They are intermediate in oxidation level between sulfenyl halides, R−S−X, and sulfonyl halides, R−SO2−X. The best known examples are sulfinyl chlorides, thermolabile, moisture-sensitive compounds, which are useful intermediates for preparation of other sufinyl derivatives such as sulfinamides, sulfinates, sulfoxides, and thiosulfinates. Unlike the sulfur atom in sulfonyl halides and sulfenyl halides, the sulfur atom in sulfinyl halides is chiral, as shown for methanesulfinyl chloride.
In organic chemistry, the Davis oxidation or Davis' oxaziridine oxidation refers to oxidations involving the use of the Davis reagent or other similar oxaziridine reagents. This reaction mainly refers to the generation of α-hydroxy carbonyl compounds (acyloins) from ketones or esters. The reaction is carried out in a basic environment to generate the corresponding enolate from the ketone or ester. This reaction has been shown to work for amides.




























