Names
In English
The first known written use of the English adjective Tibetian is from in 1747; the first known use of the modern form, Tibetan, was in 1822. The first known written use of the proper noun was in 1827, as Thibet. [1] The western name, “Tibet” is, however, much older: it was recorded in the 13th century by Giovanni da Pian del Carpine and William Rubruck, as Tebet. William Rubruck (1253) records Tebet as the name of a people, situated beyond the Tangut , and were distinctive for their customs and traditions. [2] The name Tebet appears to be a loan from an Iranian or Turkic language, perhaps Sogdian. [3] In 17th-century Modern Latin, Tibet is known as Tibetum (also Thibetum, Tibet, Thobbat, Tubet). [4] The ultimate origin of the name, however, remains unclear. Suggestions include derivation from Tibetan, Turkic or Chinese.
The proposed Tibetan etymology derives the term from Stod-bod (pronounced Tö-bhöt) "High/Upper Tibet" from the autonym Bod. [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] Andreas Gruschke's study of the Tibetan Amdo Province says,
At the beginning of the Tang dynasty's rule of China, Tibetans were called Tubo, a term that seems to be derived from tu phod or stod pod (upper Tibet). The archaic Tibetan dialects of Amdo have retained the articulation of the medieval Tibetan language; as such the pronunciation is Töwöd, as in Mongolian tongue. Thus, the term was handed down as Tübüt in Turkish diction, Tibbat in Arabic and passed on as Tibet in Western languages. [10]
The proposed Turkic etymology adduces töbäd 'the heights' (plural of töbän). Behr (1994) cites Bazin and Hamilton (1991) [11] to the effect that the four variant 土/吐-番/蕃 characters used to write Tu-fan/bo (Middle Chinese *Tʰɔʰ-buan < Old Chinese *Thaˤ-pjan) "Tibet" suggest "a purely phonetic transcription" of an underlying *Töpün "The Heights, Peaks" "Tibet" etymology from Old Turkic töpä/töpü "peak; height". [12] He further hypothesizes that the final -t in Tibet names derives from "an Altaic collective plural which results in *Töpät, thus perfectly matching Turkic Töpüt 'Tibet'", which is attested in the Old Turkic Orkhon inscriptions.
Proposed Chinese etymology compares Tǔfān/Tǔbō. [13] The premise of the Chinese name being the primary origin of the name hinges its having had -t final in Middle Chinese, e.g., Eric Partridge's hypothetical Tu-pat. [14] Stein (1922) assumes that Tufan has the same origin as Tibet, but not that the latter is adopted from Chinese: Instead, the Chinese name would have arisen "by assimilation with the name of the T'u-fa, a Turco-Mongol race, who must originally have been called something like Tuppat", also reflected in Sogdian and Turkic texts as Tüpüt. [3]
In Tibetan
The Standard or Central Tibetan endonym for Tibet, Bod (Tibetan : བོད་), is pronounced [pʰøʔ] , transliterated Bhö or Phö.
Rolf Stein (1922) explains,
The name Tibetans give their country, Bod (now pronounced Pö in the Central dialect, as we have seen), was closely rendered and preserved by their Indian neighbours to the south, as Bhoṭa, Bhauṭa or Bauṭa. It has even been suggested that this name is to be found in Ptolemy and the Periplus Maris Erythraei , a first-century Greek narrative, where the river Bautisos and a people called the Bautai are mentioned in connexion with a region of Central Asia. But we have no knowledge of the existence of Tibetans at that time. [3]
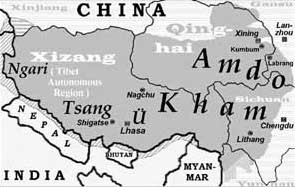
Christopher Beckwith agrees that Ptolemy's geographic reference to the "Bautai – i.e., the "Bauts"" was "the first mention in either Western or Eastern historical sources of the native ethnonym of Tibet". He compares the 4th-century historian Ammianus Marcellinus describing the Bautai living "on the slopes of high mountains to the south" of Serica with contemporaneous Chinese sources recording a Qiang people called the Fa 發, anciently "pronounced something like Puat" and "undoubtedly intended to represent Baut, the name that became pronounced by seventh-century Tibetans as Bod (and now, in the modern Lhasa dialect, rather like the French peu)." [15] Bod originally named the Central Tibetan region Ü-Tsang or Dbus-gtsang.
This first mention of the name Bod, the usual name for Tibet in the later Tibetan historical sources, is significant in that it is used to refer to a conquered region. In other words, the ancient name Bod originally referred only to a part of the Tibetan Plateau, a part which, together with Rtsaṅ (Tsang, in Tibetan now spelled Gtsaṅ), has come to be called Dbus-gtsaṅ (Central Tibet). [16]
In Chinese

The oldest Chinese language name for "Tibet" is 吐蕃, transliterated either pinyin Tǔbō, Wade–Giles T'u-po or pinyin Tǔfān, Wade–Giles T'u-fan. Chinese 藏 Zàng ("Tsang") is a loan from Tibetan གཙང (gtsang), the name of the southwestern part of the Tibetan Plateau. Modern Xizang (Chinese :西藏; pinyin :Xīzàng; Wade–Giles :Hsi-tsang) "Western Tsang" now specifies the "Tibet Autonomous Region".
吐蕃 Tufan/Tubo is first recorded in the Old Book of Tang (dated 945 CE) describing the Tibetan King Namri Songtsen (Gnam-ri-slon-rtsan) sent two emissaries to Emperor Yang of Sui in 608 and 609. [17]
The Tubo vs. Tufan transliteration of 吐蕃 is based on historical spellings involving four different characters:
- the first character is written either tǔ 土 "earth; soil; land" or tǔ 吐 "spit out; vomit"
- the second character is written either fān 番 "times, occurrences; foreign" or fān 蕃 "hedge, screen; frontier; foreign country" (usually pronounced fán 蕃 "luxuriant; flourishing").
The latter two fān Chinese characters are used interchangeably for "foreign" words, e.g., fānqié 番茄 or 蕃茄 (lit. "foreign eggplant") "tomato". Fán is sometimes translated as "barbarian" meaning "non-Chinese; foreign". [18]
For the character 蕃, pre-modern Chinese dictionaries indicate only the pronunciation fán. According to Paul Pelliot, the pronunciation tǔbō was suggested by Abel Rémusat in the early 19th century, based on pronunciations of similar characters, and adopted uncritically by other European scholars. [19]
Contemporary Chinese dictionaries disagree whether 吐蕃 "Tibet" is pronounced "Tǔbō" or Tǔfān – a question complicated by the homophonous slur tǔfān 土番 (lit. "dirt barbarians", possibly "agricultural barbarians" [20] ) "barbarians; natives; aborigines". [21] The Hanyu Da Cidian cites the first recorded Chinese usages of Tǔfān 土番 "ancient name for Tibet" in the 7th century (Li Tai 李泰) and tǔfān 土番 "natives (derogatory)" in the 19th century (Bi Fucheng 薜福成). [22] Sinological linguists are engaged in ongoing debates whether 吐蕃 is "properly" pronounced Tubo or Tufan. For example, Sino-Platonic Papers has been the venue for disputation among Victor H. Mair, [23] [24] [25] Edwin G. Pulleyblank, [26] and W. South Coblin . [27]
The Chinese neologism Tǔbó 圖博 (written with tǔ 圖 "drawing; map" and bó 博 "abundant; plentiful") avoids the problematic Tǔfān pronunciation, and is used by authorities such as the Central Tibetan Administration.
Stein discusses the fan pronunciation of "Tibet".
The Chinese, well informed on the Tibetans as they were from the seventh century onwards, rendered Bod as Fan (at that time pronounced something like B'i̭wan). Was this because the Tibetans sometimes said 'Bon' instead of 'Bod', or because 'fan' in Chinese was a common term for 'barbarians'? We do not know. But before long, on the testimony of a Tibetan ambassador, the Chinese started using the form T'u-fan, by assimilation with the name of the T'u-fa, a Turco-Mongol race, who must originally have been called something like Tuppat. At the same period, Turkic and Sogdian texts mention a people called 'Tüpüt', situated roughly in the north-east of modern Tibet. This is the form that Moslem writers have used since the ninth century (Tübbet, Tibbat, etc.). Through them it reached the medieval European explorers (Piano-Carpini, Rubruck, Marco Polo, Francesco della Penna). [3]
This Fan 蕃 pronunciation of "B'i̭wan" illustrates the difference between modern Chinese pronunciation and the Middle Chinese spoken during the Sui dynasty (581-618 CE) and Tang dynasty (618-907 CE) period when "Tibet" was first recorded. Reconstructed Middle Chinese pronunciations of Tǔbō and Tǔfān "Tibet" are: t'uopuâ and t'uop'i̭wɐn (Bernhard Karlgren), [28] thwopwâ and thwobjwɐn (Axel Schuessler), [29] tʰɔ'pa and tʰɔ'puan (Edwin G. Pulleyblank "Early Middle"), [30] or thux-pat and thux-pjon (William H. Baxter). [31]
Xizang 西藏 is the present-day Chinese name for "Tibet". This compound of xi 西 "west" and zàng 藏 "storage place; treasure vault; (Buddhist/Daoist) canon (e.g., Daozang )" is a phonetic transliteration of Ü-Tsang , the traditional province in western and central Tibet.
Zang 藏 was used to transcribe the Tsang people as early as the Yuan dynasty (1279–1368 CE), and "Xizang" was coined under the Qing dynasty Jiaqing Emperor (r. 1796–1820 CE). Zang abbreviates "Tibet" in words such as Zàngwén 藏文 "Tibetan language" and Zàngzú 藏族 "Tibetan people".
The People's Republic of China government equates Xīzàng with the Xīzàng Zìzhìqū 西藏自治区 "Tibet Autonomous Region, TAR". The English borrowing Xizang from Chinese can be used to differentiate the modern "TAR" from the historical "Tibet".
In Sanskrit
भोट (Bhot) is the name used by ancient India for Bod (Tibetan : བོད་).