This is a list of properties and districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Connecticut. There are more than 1,500 listed sites in Connecticut. All 8 counties in Connecticut have listings on the National Register.

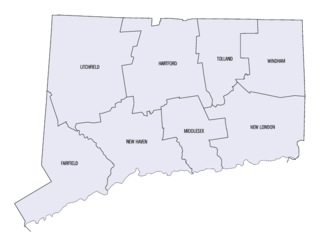
This is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map.

The Arcola Carnegie Public Library is a Carnegie library located at 407 E. Main St. in Arcola, Illinois. The library was built in 1905 through a $10,000 grant from the Carnegie Foundation. Architect Paul O. Moratz designed the library in the Classical Revival style. The building's front entrance is situated within a Classical gabled portico supported by stone pilasters. The hipped roof of the building features an ornamental cornice along its edge and a cupola at its peak. The building still serves as Arcola's public library and houses a collection of over 18,000 books.

The Sacramento City Library, also known as Central Branch, is part of the Sacramento Public Library system, and faces I Street in Sacramento, California near Sacramento City Hall.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Columbiana County, Ohio.

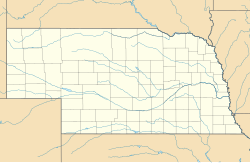
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Clay County, Nebraska.

The Fort Fairfield Public Library, located at 339 Main Street, is the public library of Fort Fairfield, Maine, United State. Fort Fairfield had a private library as early as 1880. It became a town-supported library in 1894 with a circulation of 300 books. In 1911 the town received a grant of $10,000 from Andrew Carnegie - making it one of the seventeen Carnegie libraries in the state of Maine. The building was designed by Lewiston architect Harry Coombs, and built by R.J. Noyes of Augusta. The Fort Fairfield Public Library was completed and officially opened on September 9, 1913.

The Carnegie Library in Boulder, Colorado is a building from 1906. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979. The building is now known as the Carnegie Library for Local History, and is a branch of the Boulder Public Library. The library contains an area of 4,000 square feet (370 m2).

The Carnegie Library in Anaheim, California is a Carnegie Library building built in 1908. The Classical Revival style building was designed by John C. Austin, and opened in 1909.

The Carnegie Library in Newton, Kansas is a building from 1903. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.

The Carnegie Library of Albany is a Carnegie library in Albany, Missouri, listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It was designed by Edmond J. Eckel and opened in 1906.

Fairfield Public Library is located in Fairfield, Iowa, United States. A library association was founded by a group of local men in 1853, and funded by dues from its members. It was housed in several different buildings for the first 40 years. U.S. Senator James F. Wilson from Fairfield was instrumental in obtaining a grant from Andrew Carnegie for a building of its own. The grant for $40,000 was accepted on January 15, 1892. It was the first Carnegie Library outside of Western Pennsylvania and the first of 101 built in Iowa. It was also one the few libraries Carnegie funded without stipulations concerning its use, public support, or design. The building was designed in the Richardsonian Romanesque style by Kansas City architect C. Stafford. It was officially opened on Friday, September 29, 1893, and it was dedicated on November 28 of the same year. The association continued to run the library until 1899 when voters approved a referendum to support it with taxes. The building has been altered in the ensuing years, and it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983. The library moved to a new building in 1996, and the historic building is now home to the Jefferson County Service Center of Indian Hills Community College.

The Architecture of Henry K. Holsman Historic Campus District, also known as the Maharishi International University, is a nationally recognized historic district located in Fairfield, Iowa, United States. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983. At the time of its nomination it included five contributing buildings that were built from 1903 to 1915 on the campus of Parsons College. They were designed in the Collegiate Gothic style by Iowa-born and Chicago-based architect Henry K. Holsman. It also includes Ewing Hall, which is an older building on the campus, and individually listed on the National Register. The buildings were built after the destruction by fire of Ankeny Hall in 1902. Foster Hall (1903), Fairfield Hall (1903), and the Carnegie Library (1907) have elements of the Beaux-Arts style. Barhydt Chapel and the Parsons Bible School were completed in 1912. Parsons Hall was completed in 1915.

Hawthorne Branch Library No. 2, also known as Hawthorne Education Annex, is a historic Carnegie library building located in Indianapolis, Marion County, Indiana. Built in 1909-1911, with funds provided by the Carnegie Foundation, it is a one-story, rectangular, Classical Revival style brick and limestone building on a raised basement. It has a truncated hipped roof and features a slightly projecting pavilion housing a round arch. It was renovated in 1955, after its closure as a library, and again in 1999.

Indianapolis Public Library Branch No. 6, also known as Spades Park Library (Carnegie), is a historic Carnegie library located in Indianapolis, Indiana. It was built in 1911-1912, and is a two-story, "L"-shaped, Italian Renaissance style masonry building on a raised basement. It has a terra cotta tile hipped roof, decorative brickwork, limestone accents, and elements of American Craftsman and Arts and Crafts style decorative elements. It was one of five libraries constructed from the $120,000 the Carnegie Foundation gave the City of Indianapolis in 1909 to be used towards the construction of six branch libraries. The library remains in operation as the Spades Park Branch of the Indianapolis Public Library.

The Carnegie Public Library at 314 McLeod St. in Big Timber, Montana is a Carnegie library which was built in 1913. It has also been known as Big Timber Carnegie Library. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2002.

The Woman's Club of Olympia was founded in Olympia, Washington in 1883. It one of the one of the oldest woman's club on the West Coast. Founding members included Mehitable Elder, Pamela Case Hale, Mary Hartsock, Janet Moore, Phebe Moore, Mary Shelton, Ella Stork, Abbie Howard Hunt Stuart, and Sarah E. Whitney. Its first president, Mrs. A.H.H. Stewart, a college graduate and a veteran of the Women's Club in Boston, was a "driving force" in the club's organization and was known as the "Mother of Women's Clubs" for having founded other clubs, too.

The Sterling Public Library, at 210 S. 4th St. in Sterling, Colorado, was built in 1918. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2001.

The Schuyler Carnegie Library is a historic building in Schuyler, Nebraska. It was built as a Carnegie library by P.H. Wind & Sons in 1911, and designed in the Tudor Revival style by the architectural firm Fisher & Lawrie. It was a library until 1975, and it housed the Schuyler / Colfax County Historical Society Museum from 1977 to 1998. It has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since November 29, 2001.
Richard W. Grant (1862-1939), often known as R. W. Grant, was an architect based in Beatrice, Nebraska. He designed about 70 schools and at least four Carnegie libraries. A number of his works are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP).