
The Miami are a Native American nation originally speaking the Miami–Illinois language, one of the Algonquian languages. Among the peoples known as the Great Lakes tribes, they occupied territory that is now identified as north-central Indiana, southwest Michigan, and western Ohio. The Miami were historically made up of several prominent subgroups, including the Piankeshaw, Wea, Pepikokia, Kilatika, Mengakonkia, and Atchakangouen. In modern times, Miami is used more specifically to refer to the Atchakangouen. By 1846, most of the Miami had been forcefully displaced to Indian Territory. The Miami Tribe of Oklahoma are the federally recognized tribe of Miami Indians in the United States. The Miami Nation of Indiana, a nonprofit organization of self-identified descendants of Miamis who were exempted from removal, have unsuccessfully sought separate recognition.

Wabash is a city in Noble Township, Wabash County, in the U.S. state of Indiana. The population was 10,666 at the 2010 census. The city is situated along the Wabash River in the county seat of Wabash County.

The Chief Jean Baptiste de Richardville House was built near Fort Wayne, Indiana, in 1827. Subsidized by the U.S. federal government through the 1826 Treaty of Mississinewas, it is believed to be one of only three treaty houses built east of the Mississippi River. It was designated a National Historic Landmark on March 2, 2012.

The Fort Wayne Old City Hall Building in downtown Fort Wayne, Indiana operates as a museum known as The History Center, and has served as headquarters for the Allen County–Fort Wayne Historical Society since 1980. The Richardsonian Romanesque style sandstone building was designed by the architectural firm Wing & Mahurin and built in 1893. It served as a functioning city hall for the city until 1971 when local officials moved to the City-County Building.

The Wabash and Erie Canal was a shipping canal that linked the Great Lakes to the Ohio River via an artificial waterway. The canal provided traders with access from the Great Lakes all the way to the Gulf of Mexico. Over 460 miles long, it was the longest canal ever built in North America.

Jean Baptiste de Richardville, also known as Pinšiwa or Peshewa in the Miami-Illinois language or John Richardville in English, was the last akima 'civil chief' of the Miami people. He began his career in the 1790s as a fur trader who controlled an important portage connecting the Maumee River to the Little River in what became the present-day state of Indiana. Richardville emerged a principal chief in 1816 and remained a leader of the Miamis until his death in 1841. He was a signatory to the Treaty of Greenville (1795), as well as several later treaties between the U.S. government and the Miami people, most notably the Treaty of Fort Wayne (1803), the Treaty of Fort Wayne (1809), the Treaty of Saint Mary's (1818), the Treaty of Mississinewas (1826), the treaty signed at the Forks of the Wabash (1838), and the Treaty of the Wabash (1840).
The Treaty of Mississinewas or the Treaty of Mississinewa also called Treaty of the Wabash is an 1826 treaty between the United States and the Miami and Potawatomi Tribes regarding purchase of Indian lands in Indiana and Michigan. The signing was held at the mouth of the Mississinewa River on the Wabash, hence the name.

Fort Miami (Miamis) was a British fort built in spring 1794 on the Maumee River in what was at the time territory claimed by the United States, and designated by the federal government as the Northwest Territory. The fort was located at the eastern edge of present-day Maumee, Ohio, southwest of Toledo. The British built the fort to forestall a putative assault on Fort Detroit by Gen. "Mad" Anthony Wayne's army, then advancing northward in southwestern Ohio.

The Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception in Fort Wayne, Indiana, is the primary cathedral of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Fort Wayne-South Bend, headed by Most Rev. Kevin C. Rhoades. The parish was established in 1836, making it the oldest in Fort Wayne. The church was erected in 1860.
Allen Hamilton (1798–1864) was a founding father of Fort Wayne in Allen County, Indiana.

The Little River is a 22.6-mile-long (36.4 km) stream in Allen and Huntington counties in northeastern Indiana. A tributary of the Wabash River, it is sometimes called the "Little Wabash", which may cause it to be confused with the Little Wabash River of Illinois. The river drains an area of 287.9 square miles (746 km2).

Papakeecha was the most influential Miami chief in the region around Lake Wawasee, in what is now Kosciusko County, Indiana, United States leading his people from 1820 until 1837. Lake Papakeechie was named after him.

Red Clay State Historic Park is a state park located in southern Bradley County, Tennessee, United States. The park preserves the Red Clay Council Grounds, which were the site of the last capital of the Cherokee Nation in the eastern United States from 1832 to 1838 before the enforcement of the Indian Removal Act of 1830. This act resulted in a forced migration of most of the Cherokee people to present-day Oklahoma known as the Cherokee removal. At the council grounds, the Cherokee made multiple unsuccessful pleas to the U.S. government to be allowed to remain in their ancestral homeland. The site is considered sacred to the Cherokees, and includes the Blue Hole Spring, a large hydrological spring. It is also listed as an interpretive center along the Trail of Tears National Historic Trail.
Huntington Township is one of twelve townships in Huntington County, Indiana. As of the 2020 census, its population was 20,326, making it the most populous township in the county.

Francis La Fontaine, or Toohpia was the last principal chief of the unified Miami tribe, and oversaw the split into the Western and Eastern Miami tribes.

Francis Godfroy was a chief of the Miami people. He negotiated treaties with between his tribe and the United States.
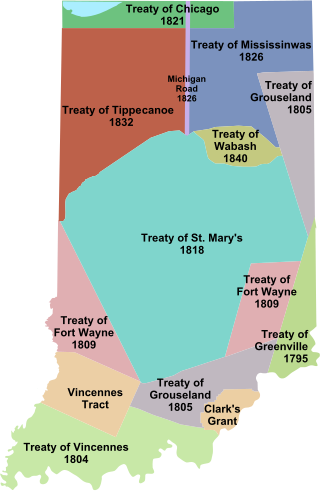
The Treaty of the Wabash was an agreement between the United States government and Native American Miami tribes in Indiana on November 28, 1840.




















