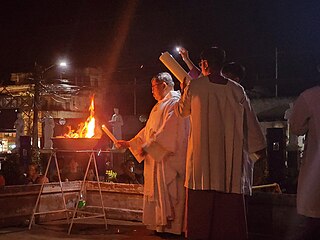The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical days and seasons that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be observed, and which portions of scripture are to be read.

The Tridentine Mass, also known as the Traditional Latin Mass or the Traditional Rite, is the liturgy in the Roman Missal of the Catholic Church codified in 1570 and published thereafter with amendments up to 1962. Celebrated almost exclusively in Ecclesiastical Latin, it was the most widely used Eucharistic liturgy in the world from its issuance in 1570 until the introduction of the Mass of Paul VI.

Septuagesima is the name for the ninth Sunday before Easter, the third before Ash Wednesday. The term is sometimes applied to the seventy days starting on Septuagesima Sunday and ending on the Saturday after Easter. Alternatively, the term is sometimes applied also to the period sometimes called pre-Lent that begins on this day and ends on Shrove Tuesday, the day before Ash Wednesday, when Lent begins.

The Paschal Triduum or Easter Triduum, Holy Triduum, or the Three Days, is the period of three days that begins with the liturgy on the evening of Maundy Thursday, reaches its high point in the Easter Vigil, and closes with evening prayer on Easter Sunday. It is a moveable observance recalling the Passion, Crucifixion, Death, burial, and Resurrection of Jesus, as portrayed in the canonical Gospels.

Passion Sunday is the fifth Sunday in Lent, marking the beginning of Passiontide. In 1969, the Roman Catholic Church removed Passiontide from the liturgical year of the Novus Ordo, but it is still observed in the Extraordinary Form, the Personal Ordinariates, and by some Anglicans and Lutherans.
The Octave of Easter is the eight-day period, or octave, that begins on Easter Sunday and ends with Second Sunday of Easter. It marks the beginning of Eastertide. The first seven of these eight days are also collectively known as Easter Week.

The gradual is a certain chant or hymn in liturgical Christian worship. It is practiced in the Catholic Mass, Lutheran Divine Service, Anglican service and other traditions. It gets its name from the Latin gradus because it was once chanted on the step of the ambo or altar. It is customarily placed after a reading of scripture.

Eastertide or Paschaltide is a festal season in the liturgical year of Christianity that focuses on celebrating the Resurrection of Jesus Christ. Preceded by Lent, it begins on Easter Sunday, which initiates Easter Week in Western Christianity, and Bright Week in Eastern Christianity.

A missal is a liturgical book containing instructions and texts necessary for the celebration of Mass throughout the liturgical year. Versions differ across liturgical tradition, period, and purpose, with some missals intended to enable a priest to celebrate Mass publicly and others for private and lay use. The texts of the most common Eucharistic liturgy in the world, the Catholic Church's Mass of Paul VI of the Roman Rite, are contained in the 1970 edition of the Roman Missal.
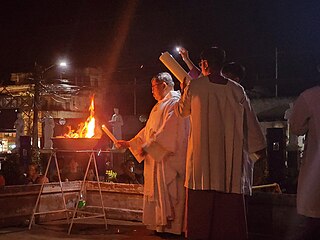
The Easter Vigil, also called the Paschal Vigil, the Great Vigil of Easter, or Holy Saturday in the Easter Vigil on the Holy Night of Easter is a liturgy held in traditional Christian churches as the first official celebration of the Resurrection of Jesus. Historically, it is during this liturgy that people are baptized and that adult catechumens are received into full communion with the Church. It is held in the hours of darkness between sunset on Holy Saturday and sunrise on Easter Day – most commonly in the evening of Holy Saturday or midnight – and is the first celebration of Easter, days traditionally being considered to begin at sunset.

The Roman Rite is the most common ritual family for performing the ecclesiastical services of the Latin Church, the largest of the sui iuris particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. The Roman Rite governs rites such as the Roman Mass and the Liturgy of the Hours as well as the manner in which sacraments and blessings are performed.

Passiontide is a name for the last two weeks of Lent, beginning on the Fifth Sunday of Lent, long celebrated as Passion Sunday, and continuing through Lazarus Saturday. It commemorates the suffering of Christ. The second week of Passiontide is Holy Week, ending on Holy Saturday.

Asperges is the rite of sprinkling a congregation with holy water. The name comes from the first word in the 9th verse of Psalm 51 in the Latin translation which is sung during the traditional form of the rite except during Eastertide. The 51st Psalm is also one of the antiphons that may be sung in the rite under the Mass of Paul VI.

Weinen, Klagen, Sorgen, Zagen, BWV 12, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it in Weimar for Jubilate, the third Sunday after Easter, and led the first performance on 22 April 1714 in the Schlosskirche, the court chapel of the Schloss in Weimar.

The Mass of the Lord's Supper, also known as A Service of Worship for Maundy Thursday, is a Holy Week service celebrated on the evening of Maundy Thursday. It inaugurates the Easter Triduum, and commemorates the Last Supper of Jesus with his disciples, more explicitly than other celebrations of the Mass.
The Church of the Ascension is an Anglo-Catholic parish in the Episcopal Diocese of Chicago. Founded in 1857 as a mission of St. James Church, it is now located on North La Salle Drive on Chicago's Near North Side. The church became a part of the Anglo-Catholic movement in 1869. The principal service on Sunday is the Solemn High Mass celebrated at 11 a.m., according to Rite II in the Episcopal Church's Book of Common Prayer (1979). This Mass is celebrated at the High Altar, and includes three sacred ministers, many acolytes, incense, and music provided by a professional choir. The mass includes processions and other devotions on certain feasts and holy days.
The Fifth Sunday of Easter is the fifth Sunday of the Easter season, being four weeks after the Christian celebration of Easter Sunday. In Western Christianity, this day is also known as the Fourth Sunday after Easter or Cantate Sunday. Eastern Christianity also calls this day the "Fifth Sunday," but typically using an Eastern synonym for Easter; for example, Fifth Sunday of Holy Pascha or Fifth Sunday of the Resurrection. In the Byzantine Rite, this day is also known as the Sunday of the Samaritan Woman.
The ranking of liturgical days in the Roman Rite is a regulation for the liturgy of the Roman Catholic church. It determines for each liturgical day which observance has priority when liturgical dates and times coincide, which texts are used for the celebration of the Holy Mass and the Liturgy of the hours and which liturgical color is assigned to the day or celebration.
The Second Sunday of Easter is the eighth day of the Christian season of Eastertide, and the seventh after Easter Sunday. It is known by various names, including Divine Mercy Sunday, the Octave Day of Easter, White Sunday, Quasimodo Sunday, Bright Sunday and Low Sunday. In Eastern Christianity, it is known as Antipascha, New Sunday, and Thomas Sunday.
The Third Sunday of Easter or Third Sunday of Eastertide is the third Sunday of the Easter season, being the day that occurs two weeks after the Christian celebration of Easter Sunday. It is also known as Good Shepherd Sunday.