
Upminster Windmill is a Grade II* listed smock mill located in Upminster in the London Borough of Havering, England. It was formerly known as Abraham's Mill and was in Essex when built. It has been restored and is a museum open to the public at selected times.

Outwood Windmill is a Grade I listed post mill in Outwood, Surrey. Built in 1665 by Thomas Budgen, a miller from Nutfield in Surrey, it is Britain's oldest working windmill.

Caston Tower Windmill is a grade II* listed tower mill at Caston, Norfolk, England which is under restoration. The mill is also a scheduled monument.
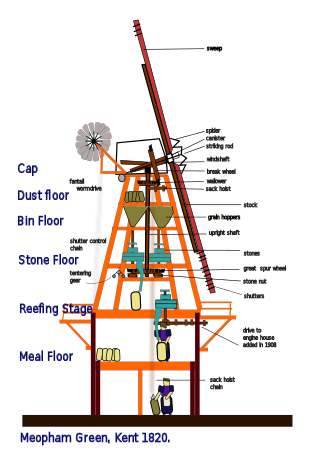
This glossary of mill machinery covers the major pieces of machinery to be found in windmills, watermills and horse mills. It does not cover machinery found in modern factories.

Shiremark Mill, also known as Kingsfold Mill or Capel Mill was a listed Smock mill at Capel, Surrey, England, which was burnt down in 1972.

Aythorpe Roding Windmill is a Grade II* listed Post mill at Aythorpe Roding, Essex, England which has been restored to working order.

Bocking Windmill or Bocking Churchstreet Windmill is a grade I listed post mill at Bocking, Essex, England which has been restored.

Fryerning Mill is a grade II* listed post mill at Mill Green, Fryerning, Essex, which has been restored.

Mountnessing Windmill is a grade II* listed post mill at Mountnessing, Essex, England. Built in 1807, it was most recently restored to working order in 1983.

Ramsey Windmill is a grade II* listed post mill at Ramsey, Essex, England which has been restored.

Baker Street Mill is a grade II listed smock mill at Baker Street, Orsett, Essex, England which has been part adapted to residential use on its lower two floors only.

Terling Windmill is a grade II listed Smock mill at Terling, Essex, England, which has been converted to residential use.

South Ockendon Windmill was a Smock mill at South Ockendon, Essex, England which collapsed on 2 November 1977.
Church End Mill is a grade II listed Tower mill at Great Dunmow, Essex, England which has been converted to residential use.

Stansted Mountfitchet Windmill is a grade II* listed Tower mill at Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England which is also a Scheduled Ancient Monument. It has been restored and can turn by wind.

Stock Windmill is a grade II* listed tower mill at Stock, Essex, which has been restored.

Gainsford End Mill is a grade II listed tower mill at Gainsford End, near Toppesfield, Essex, England, which has been converted to a residence.

Thelnetham Windmill, also known as Button's Mill is a Grade II* listed tower mill constructed of brick. The windmill is located at Thelnetham, Suffolk, England. It was built in the early nineteenth century to grind wheat into flour. Thelnetham windmill worked by wind power until 1924, latterly on two sails, after which it became derelict.

Buxhall Mill is a tower mill at Buxhall, Suffolk, England which has been converted to residential accommodation.
Kenninghall Road Mill is a Grade II listed tower mill at East Harling, Norfolk, England which has been converted to residential accommodation.




















