Related Research Articles
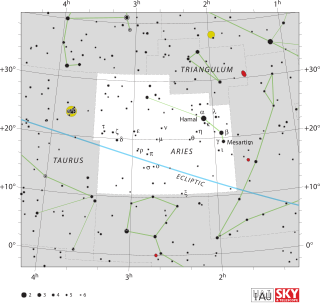
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram. Its old astronomical symbol is (♈︎). It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation ranking 39th in overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees.

Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux.
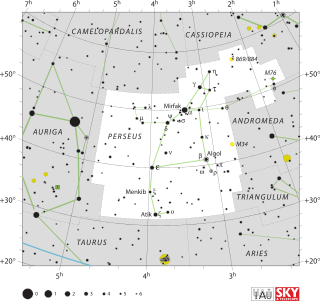
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as Perseus et Caput Medusae; however, this never came into popular usage.
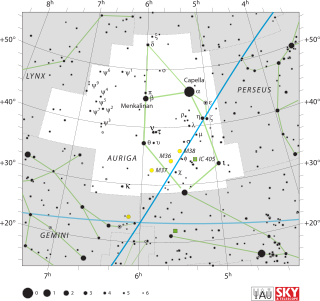
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as −34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra.

R Doradus is a red giant variable star in the far-southern constellation Dorado, close to the border with Reticulum. Its distance from Earth is 178 light-years. Having a uniform disk diameter of 57±5 mas, it is thought to be the extrasolar star with the largest apparent size as viewed from Earth.
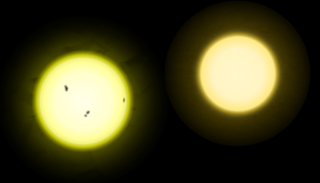
Solar-type stars, solar analogs, and solar twins are stars that are particularly similar to the Sun. The stellar classification is a hierarchy with solar twin being most like the Sun followed by solar analog and then solar-type. Observations of these stars are important for understanding better the properties of the Sun in relation to other stars and the habitability of planets.

SIMBAD is an astronomical database of objects beyond the Solar System. It is maintained by the Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS), France.

Sigma Arae is the Bayer designation for a star in the southern constellation of Ara. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.575. The distance to this star, based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.62 mas, is around 380 light-years.
Andromeda IX is a dwarf spheroidal satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy. It was discovered in 2004 by resolved stellar photometry from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), by Zucker et al. (2004). At the time of its discovery, it was the galaxy with the lowest known surface brightness, ΣV ≃ 26.8mags arcsec−2 and the faintest galaxy known from its intrinsic absolute brightness.

NGC 2440 is a planetary nebula, one of many in our galaxy. Its central star, HD 62166, is possibly the hottest known white dwarf, about 400,000°F(200,000°C). The nebula is situated in the constellation Puppis.
Theta Lyrae is a star in a trinary star system, in the constellation Lyra, approximately 760 light years away from Earth. Theta Lyrae is an orange bright giant star of the spectral type K0II, which means that it possesses a surface temperature of about 5,000 K, and is many times bigger and brighter, yet cooler, than the Sun.

Tau Cygni, Latinised from τ Cygni, is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus, approximately 69 light years away from Earth. This visual binary system has a period of 49.6 years.

Abell 39 is a low surface brightness planetary nebula in the constellation of Hercules. It is the 39th entry in George Abell's 1966 Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae of 86 old planetary nebulae which either Abell or Albert George Wilson discovered before August 1955 as part of the National Geographic Society - Palomar Observatory Sky Survey. It is estimated to be about 3,800 light-years from earth and thus 2,600 light-years above the Galactic plane. It is almost perfectly spherical and also one of the largest known spheres with a radius of about 1.4 light-years.

Sidus Ludoviciana, also known as HD 116798, is an 8th-magnitude giant star in the asterism of the Big Dipper in the constellation Ursa Major, halfway between Mizar and Alcor. It was discovered on 2 December 1722 by Johann Georg Liebknecht, who mistook it for a planet and named it after Louis V, Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt. A line-of-sight companion with Mizar and Alcor, it is roughly four times more distant. It has the spectral type A8/F0 III. That spectral class suggests it is a giant star, but evolutionary models place it on the main sequence.

NGC 681 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation of Cetus, located approximately 66.5 million light-years from Earth.

NGC 972 is a dusty spiral galaxy in the northern constellation of Aries, located at an approximate distance of 49.8 Mly from the Milky Way. It was discovered in 1784 by William Herschel. The galactic features suggest it may have undergone a merger with a gas-rich companion, giving it asymmetrical arms, plus starburst activity in the nucleus and an off-planar nuclear ring. The inner 3.6 kpc of the galaxy is undergoing star formation at the rate of 2.1–2.7 M☉·yr−1, but it lacks a nuclear bulge.

NGC 676 is a lenticular Seyfert 2 galaxy in the constellation Pisces. Its velocity with respect to the cosmic microwave background is 1217 ± 20 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 58.6 ± 4.2 Mly (17.96 ± 1.29 Mpc). In addition, two non redshift measurements give a distance of 61.0 ± 2.6 Mly (18.7 ± 0.8 Mpc). The galaxy was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel on 30 September 1786.
Kepler-737 is an M-type main-sequence red dwarf located 671 light-years away on the border of the constellation Cygnus.
References
- 1 2 "Simbad Query Result". Simbad. Retrieved October 17, 2007.