Related Research Articles
HD 101930, also known as Gliese 3683, is an orange hued star with an orbiting exoplanet located in the southern constellation Centaurus. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.21, making it faintly visible in binoculars but not to the naked eye. The system is located relatively close at a distance of 98 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 18.4 km/s. It has a relatively large proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere with an angular velocity of 0.320″·yr−1.
HD 190984, also known as HIP 99496, is a star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Pavo, the peacock. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.76, making it readily visible in small telescopes, but not to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements from the Gaia spacecraft, the object is estimated to be 486 light years away from the Solar System. It appears to be receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 20.3 km/s.

Kepler-10, formerly known as KOI-72, is a Sun-like star in the constellation of Draco that lies 607 light-years from Earth. Kepler-10 was targeted by NASA's Kepler space telescope, as it was seen as the first star identified by the Kepler mission that could be a possible host to a small, transiting exoplanet. The star is slightly less massive, slightly larger, and slightly cooler than the Sun; at an estimated 11.9 billion years in age, Kepler-10 is 2.3 times the age of the Sun.
Kepler-22 is a Sun-like star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, the swan, that is orbited by 1 planet found to be unequivocally within the star's habitable zone. It is located at the celestial coordinates: Right Ascension 19h 16m 52.2s, Declination +47° 53′ 3.9″. With an apparent visual magnitude of 11.7, this star is too faint to be seen with the naked eye. It can be viewed with a telescope having an aperture of at least 4 in (10 cm). The estimated distance to Kepler-22 is 644 light-years.
Kepler-70, also known as KIC 5807616 and KOI-55, is a star about 3,600 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus, with an apparent visual magnitude of 14.87. This is too faint to be seen with the naked eye; viewing it requires a telescope with an aperture of 40 cm (20 in) or more. A subdwarf B star, Kepler-70 passed through the red giant stage some 18.4 million years ago. In its present-day state, it is fusing helium in its core. Once it runs out of helium it will contract to form a white dwarf. It has a relatively small radius of about 0.2 times the Sun's radius; white dwarfs are generally much smaller. The star may be host to a planetary system with two planets, although later research indicates that this is not in fact the case.
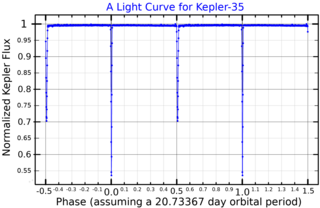
Kepler-35 is a binary star system in the constellation of Cygnus. These stars, called Kepler-35A and Kepler-35B have masses of 89% and 81% solar masses respectively, and both are assumed to be of spectral class G. They are separated by 0.176 AU, and complete an eccentric orbit around a common center of mass every 20.73 days.

Kepler-37, also known as UGA-1785, is a G-type main-sequence star located in the constellation Lyra 209 light-years from Earth. It is host to exoplanets Kepler-37b, Kepler-37c, Kepler-37d and possibly Kepler-37e, all of which orbit very close to it. Kepler-37 has a mass about 80.3 percent of the Sun's and a radius about 77 percent as large. It has a temperature similar to that of the Sun, but a bit cooler at 5,357 K. It has about half the metallicity of the Sun. With an age of roughly 6 billion years, it is slightly older than the Sun, but is still a main-sequence star. Until January 2015, Kepler-37 was the smallest star to be measured via asteroseismology.
Kepler-68 is a Sun-like main sequence star located 471 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus. It is known to have at least four planets orbiting around it. The third planet has a mass similar to Jupiter but orbits within the habitable zone.

Kepler-37b is an exoplanet orbiting the star Kepler-37 in the constellation Lyra. As of February 2013, it is the smallest planet discovered around a main-sequence star, with a radius slightly greater than that of the Moon and slightly smaller than that of Mercury. The measurements do not constrain its mass, but masses above a few times that of the Moon give unphysically high densities.
Kepler-37c is an exoplanet discovered by the Kepler space telescope in February 2013. With an orbital period of 21 days, it is located 209 light-years away, in the constellation Lyra.
Kepler-102 is a star 353 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra. Kepler-102 is less luminous than the Sun. The star system does not contain any observable amount of dust. Kepler-102 is suspected to be orbited by a binary consisting of two red dwarf stars, at projected separations of 591 and 627 AU.

Kepler-78 is a 12th magnitude star 407 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus. Initially classified as an eclipsing binary with orbital period 0.710015 days, it was later re-classified as a single star with significant interaction between star magnetosphere and close-in planet. The radius of the star is of about 74% of the Sun, and the effective temperature is about 5100 K.

KOI-256 is a double star located in the constellation Cygnus approximately 575 light-years (176 pc) from Earth. While observations by the Kepler spacecraft suggested the system contained a gas giant exoplanet orbiting a red dwarf, later studies determined that KOI-256 was a binary system composed of the red dwarf orbiting a white dwarf.
HIP 41378 is a star located 346 light-years away in the constellation of Cancer. The star has an apparent magnitude of 8.92. This F-type main sequence dwarf has a mass of 1.15 M☉ and a radius of 1.25 R☉. It has a surface temperature of about 6,251 K.

HD 179070, also known as Kepler-21, is a star with a closely orbiting exoplanet in the northern constellation of Lyra. At an apparent visual magnitude of 8.25 this was the brightest star observed by the Kepler spacecraft to host a validated planet until the discovery of an exoplanet orbiting HD 212657 in 2018. This system is located at a distance of 354 light-years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −18.2 km/s.
HD 7449 is a binary star system about 126 light-years way. The primary star, HD 7449 A, is a main-sequence star belonging to the spectral class F9.5. It is younger than the Sun. The primary star is slightly depleted of heavy elements, having 80% of solar abundance.
Gliese 328, also known as BD+02 2098, is a M-type main-sequence star located 66.9 light-years away in the constellation Hydra. Its surface temperature is 3989 K. Gliese 328 is depleted in heavy elements compared to the Sun, with a metallicity Fe/H index of −0.13. The age of the star is unknown. Gliese 328 exhibits an activity cycle similar to that of the Sun, with a period around 2000 d.

Kepler-93b (KOI-69b) is a hot, dense transiting Super-Earth exoplanet located approximately 313 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra, orbiting the G-type star Kepler-93. Its discovery was announced in February 2014 by American astronomer Geoffrey Marcy and his team. In July 2014, its radius was determined with a mere 1.3% margin of error, the most precise measurement ever made for an exoplanet's radius at the time.
HD 21693 is a star in the constellation Reticulum. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 7.94, therefore it is not visible to the naked eye. From its parallax measured by the Gaia spacecraft, it is located at a distance of 108.6 light-years (33.3 parsecs) from Earth.
References
- ↑ Barclay, T.; Rowe, J. F.; Lissauer, J. J.; Huber, D.; Fressin, F.; Howell, S. B.; Bryson, S. T.; Chaplin, W. J.; Désert, J. M. (2013-02-20). "A sub-Mercury-sized exoplanet". Nature . 494 (7438): 452–4. arXiv: 1305.5587 . Bibcode:2013Natur.494..452B. doi:10.1038/nature11914. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 23426260. S2CID 205232792.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Bonomo, A. S.; Dumusque, X.; et al. (April 2023). "Cold Jupiters and improved masses in 38 Kepler and K2 small-planet systems from 3661 high-precision HARPS-N radial velocities. No excess of cold Jupiters in small-planet systems". Astronomy & Astrophysics . arXiv: 2304.05773 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346211. S2CID 258078829.
- 1 2 3 4 Rajpaul, V. M.; Buchhave, L. A.; Lacedelli, G.; Rice, K.; Mortier, A.; Malavolta, L.; Aigrain, S.; Borsato, L.; Mayo, A. W.; Charbonneau, D.; Damasso, M.; Dumusque, X.; Ghedina, A.; Latham, D. W.; López-Morales, M.; Magazzù, A.; Micela, G.; Molinari, E.; Pepe, F.; Piotto, G.; Poretti, E.; Rowther, S.; Sozzetti, A.; Udry, S.; Watson, C. A. (2021), "A HARPS-N mass for the elusive Kepler-37d: A case study in disentangling stellar activity and planetary signals", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 507 (2): 1847–1868, arXiv: 2107.13900 , doi: 10.1093/mnras/stab2192
- 1 2 Black, Charles. "NASA's Kepler discovers small planet system". SEN TV LIMITED. Archived from the original on 23 February 2013. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- ↑ Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv: 2208.00211 . Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 . S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Harwood, William. "Kepler telescope spots smallest exoplanet yet". Spaceflight Now Inc. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- ↑ "Tompkins County Strategic Tourism Planning Board" (PDF). Tompkins County NY. April 15, 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 27, 2016. Retrieved March 5, 2016.
- ↑ "Kepler-37d".
- ↑ Fraser Cain (16 September 2008). "How Old is the Sun?". Universe Today . Retrieved 19 February 2011.
- ↑ Fraser Cain (15 September 2008). "Temperature of the Sun". Universe Today. Retrieved 19 February 2011.



