
Cranham is a residential area of east London, and part of the London Borough of Havering. It is located 17.5 miles (28 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross and comprises an extensive built-up area to the north and a low density conservation area to the south surrounded by open land. It was historically a rural village in the county of Essex and formed an ancient parish. It is peripheral to London, forming the eastern edge of the urban sprawl. The economic history of Cranham is characterised by a shift from agriculture to housing development. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Cranham significantly increased in population, becoming part of Hornchurch Urban District in 1934 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. The 2011 Census population of Cranham was included in Upminster.

Harold Wood is a suburban neighbourhood in East London in the London Borough of Havering. It is situated 16.5 miles (26.6 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross. Harold Wood was part of the ancient parish of Hornchurch, which became the Liberty of Havering. Most of the current area of Harold Wood became part of Hornchurch Urban District in 1926. It is near to the Greater London boundary with Essex.

Hornchurch is a suburban town in East London in the London Borough of Havering. It is located 15.2 miles (24.5 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross. It comprises a number of shopping streets and a large residential area. It historically formed a large ancient parish in the county of Essex that became the manor and liberty of Havering. The economic history of Hornchurch is underpinned by a shift away from agriculture to other industries with the growing significance of nearby Romford as a market town and centre of administration. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Hornchurch significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming an urban district in 1926 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. It is the location of Queen's Theatre, Havering Sixth Form College and Havering College of Further and Higher Education.

Romford is a large town in East London, England, 14 miles (23 km) northeast of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Havering, the town is one of the major metropolitan centres of Greater London identified in the London Plan.

Upminster is a suburban town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Havering. Located 16.5 miles (26.6 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, it is one of the locally important district centres identified in the London Plan.
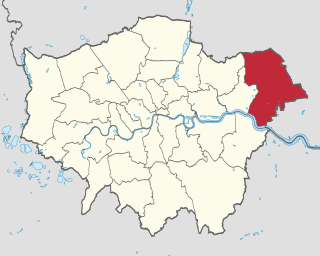
The London Borough of Havering in East London, England, forms part of Outer London. It has a population of 259,552 inhabitants; the principal town is Romford, while other communities include Hornchurch, Upminster, Collier Row and Rainham. The borough is mainly suburban, with large areas of protected open space. Romford is a major retail and night time entertainment centre, and to the south the borough extends into the London Riverside redevelopment area of the Thames Gateway. The name Havering is a reference to the Royal Liberty of Havering which occupied the area for several centuries. The local authority is Havering London Borough Council. It is the easternmost London borough.

Emerson Park is a suburban neighbourhood in the London Borough of Havering, east London. The neighbourhood developed as two large housing estates built on the 550 acres (2.2 km2) estate of Nelmes manor in the parish of Hornchurch. Emerson Park estate to the south started construction in 1895 and Great Nelmes estate to the north was begun in 1901. It is located north of the Romford–Upminster line and a station opened at Emerson Park in 1909. The mansion of Nelmes survived until it was demolished in 1967 to avoid preservation by the Civic Amenities Act and was replaced with a small housing estate called The Witherings. Emerson Park is located 15 miles (24.1 km) northeast of Charing Cross in Central London.

Harold Hill is a suburban area in the London Borough of Havering, East London. 16.6 miles (26.7 km) northeast of Charing Cross. It is a district centre in the London Plan. The name refers to King Harold II, who held the manor of Havering-atte-Bower, and who was killed at the Battle of Hastings in 1066. The suburb is peripheral to London, forming an eastern edge of the urban sprawl.

William Derham FRS was an English clergyman, natural theologian, natural philosopher and scientist. He produced the earliest reasonably accurate measurement of the speed of sound.

Upminster is an interchange station serving the town of Upminster in the London Borough of Havering, Greater London. It is on the London, Tilbury and Southend line (LTSR), 15 miles 20 chains (24.5 km) down the line from London Fenchurch Street; it is the eastern terminus of the District line on the London Underground; and it is the eastern terminus of the Liberty line on the London Overground network. Upminster is the easternmost station on the London Underground network as well as the easternmost National Rail station in London.

Upminster Bridge is a London Underground station in the Upminster Bridge neighbourhood of Upminster in the London Borough of Havering, east London. It is on the District line between Hornchurch to the west and Upminster to the east. It is 1.2 kilometres (0.75 mi) along the line from the eastern terminus at Upminster and 33 kilometres (21 mi) to Earl's Court in central London where the line divides into numerous branches. The station was opened on 17 December 1934 by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway on the local electrified tracks between Upminster and Barking that were constructed in 1932. The main station building, on Upminster Road, is of a distinctive polygonal design by William Henry Hamlyn. It has relatively low usage for a suburban station, with approximately 1.15 million passenger entries/exits in 2017.

Hornchurch is a London Underground station serving the town of Hornchurch in the London Borough of Havering, east London. It is on the District line between Elm Park to the west and Upminster Bridge to the east. It is 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) along the line from the eastern terminus at Upminster and 31.7 kilometres (19.7 mi) to Earl's Court in central London where the line divides into numerous branches.

Emerson Park is a London Overground station in the Emerson Park neighbourhood of Hornchurch in the London Borough of Havering, east London. The station is on the Liberty line and is the only intermediate station on that single-track line, located between Romford and Upminster. The station was opened in 1909 by the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway on a branch line which had connected Romford with Upminster and Grays since 1893. The station entrance is on Butts Green Road, with minimal station buildings other than a canopy over the single platform. Emerson Park is one of the least used stations in London and the least used London Overground station.

Upminster Bridge is a crossing of the River Ingrebourne carrying the A124 road between the suburbs of Hornchurch and Upminster in northeast London, England. The bridge is known to have existed since at least 1375 and the current brick bridge was opened in 1892, replacing a series of wooden bridges. It gave its name to the nearby Upminster Bridge tube station, which opened in 1934, and has also been applied to the neighbourhood around the station in the London Borough of Havering.

Havering, also known as Havering-atte-Bower, was a royal manor and ancient liberty whose area now forms part of, and gives its name to, the London Borough of Havering in Greater London. The manor was in the possession of the Crown from the 11th to the 19th centuries and was the location of Havering Palace from the 13th to the late 17th century. It occupied the same area as the ancient parish of Hornchurch which was divided into the three chapelries of Havering, Hornchurch and Romford.

East London is the northeastern part of London, England, east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames as it begins to widen. East London developed as London's docklands and the primary industrial centre. The expansion of railways in the 19th century encouraged the eastward expansion of the East End of London and a proliferation of new suburbs. The industrial lands of East London are today an area of regeneration, which are well advanced in places such as Canary Wharf and ongoing elsewhere.

Hornchurch was a local government district in southwest Essex from 1926 to 1965, formed as an urban district for the civil parish of Hornchurch. It was greatly expanded in 1934 with the addition of Cranham, Great Warley, Rainham, Upminster and Wennington; and in 1936 by gaining North Ockendon. Hornchurch Urban District Council was based at Langtons House in Hornchurch from 1929. The district formed a suburb of London and with a population peaking at 131,014 in 1961, it was one of the largest districts of its type in England. It now forms the greater part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.

South Hornchurch is a locality to the south of Hornchurch in London Borough of Havering, east London. It is a suburban development situated 13.6 miles (21.8 km) east of Charing Cross. The area is a relatively recent addition, compared with the more mature suburbs in Havering. It was built on open farmland and the former site of RAF Hornchurch.

Rainham is a suburb of East London, England, in the London Borough of Havering. Historically an ancient parish in the county of Essex, Rainham is 13.6 miles (21.9 km) east of Charing Cross and is surrounded by a residential area, which has grown from the historic village, to the north and a commercial area, fronting the River Thames, to the south. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Rainham significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming part of Hornchurch Urban District in 1934, and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. The economic history of Rainham is underpinned by a shift from agriculture to industry and manufacture and is now in a period of regeneration, coming within the London Riverside section of the Thames Gateway redevelopment area.






















