
Hornchurch is a suburban town in East London, England, and part of the London Borough of Havering. It is located 15.2 miles (24.5 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross. It comprises a number of shopping streets and a large residential area. It historically formed a large ancient parish in the county of Essex that became the manor and liberty of Havering. The economic history of Hornchurch is underpinned by a shift away from agriculture to other industries with the growing significance of nearby Romford as a market town and centre of administration. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Hornchurch significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming an urban district in 1926 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. It is the location of Queen's Theatre, Havering Sixth Form College and Havering College of Further and Higher Education.
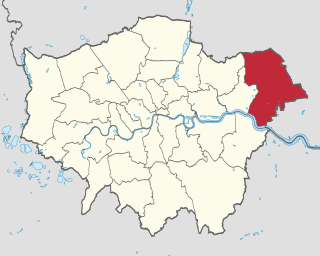
The London Borough of Havering in East London, England, forms part of Outer London. It has a population of 259,552 inhabitants; the principal town is Romford, while other communities are Hornchurch, Upminster, Collier Row and Rainham. The borough is mainly suburban, with large areas of protected open space. Romford is a major retail and night time entertainment centre, and to the south the borough extends into the London Riverside redevelopment area of the Thames Gateway. The name Havering is a reference to the Royal Liberty of Havering which occupied the area for several centuries. The local authority is Havering London Borough Council. It is the easternmost London borough.
The A13 is a major road in England linking Central London with east London and south Essex. Its route is similar to that of the London, Tilbury and Southend line via Rainham, Grays, Tilbury & Stanford-Le-Hope, and runs the entire length of the northern Thames Gateway area, terminating on the Thames Estuary at Shoeburyness. It is a trunk road between London and the Tilbury junction, a primary route between there and Sadlers Hall Farm near South Benfleet, and a non-primary route between there and Shoeburyness.

The River Ingrebourne is a tributary of the River Thames 27 miles (43.3 km) in length. It is considered a strategic waterway in London, forming part of the Blue Ribbon Network. It flows through the London Borough of Havering roughly from north to south, joining the Thames at Rainham.

Wennington is a small village and former civil parish in the London Borough of Havering, within the Metropolitan Green Belt. It is situated 14.8 miles (23.8 km) east of Charing Cross.

East London is a part of London, capital of the United Kingdom, east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames, which comprises the London boroughs of Barking and Dagenham, Hackney, Havering, Newham, Redbridge, Tower Hamlets and Waltham Forest. The East End of London is a subset of East London, consisting of areas close to the ancient City of London. The Eastern (E) Postal District is a different subset of East London; and there is also an "East" sub-region used in the London Plan for planning policy reporting purposes. The 2011 iteration includes seven boroughs north of the Thames, with the addition of three boroughs south of the river.

Crossness is a location in the London Borough of Bexley, close to the southern bank of the River Thames, to the east of Thamesmead, west of Belvedere and north-west of Erith. The place takes its name from Cross Ness, a specific promontory on the southern bank of the River Thames. In maritime terms, the tip of Cross Ness, in the past referred to as 'Leather Bottle Point', marks the boundary between Barking Reach and Halfway Reach. An unmanned lighthouse on Crossness is a navigational aid to shipping.

The London Riverside is a redevelopment area on the north side of the River Thames in East London, England and part of the larger Thames Gateway redevelopment zone. The London Riverside area forms part of the Green Enterprise District, a project to create a low-carbon economy region in Greater London. Land available for redevelopment is owned by GLA Land and Property. From 2004 to 2013 the redevelopment of London Riverside and the Lower Lea Valley was the responsibility of the London Thames Gateway Development Corporation. There is also a London Riverside business improvement district which covers a smaller area.

Hornchurch was a local government district in southwest Essex from 1926 to 1965, formed as an urban district for the civil parish of Hornchurch. It was greatly expanded in 1934 with the addition of Cranham, Great Warley, Rainham, Upminster and Wennington; and in 1935 by gaining North Ockendon. Hornchurch Urban District Council was based at Langtons House in Hornchurch from 1929. The district formed a suburb of London and with a population peaking at 131,014 in 1961, it was one of the largest districts of its type in England. It now forms the greater part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.

South Hornchurch is a locality to the south of Hornchurch in London Borough of Havering, east London. It is a suburban development situated 13.6 miles (21.8 km) east of Charing Cross. The area is a relatively recent addition, compared with the more mature suburbs in Havering. It was built on open farmland and the former site of RAF Hornchurch.

Rainham Marshes is an RSPB nature reserve in the east of London, adjacent to the Thames Estuary in Purfleet, Thurrock and the London Borough of Havering. In 2000, the area of land was bought from the Ministry of Defence, who used it as a test firing range. With no activity for several years, the nature reserve was officially opened to the public in 2006. It has maintained much of its medieval landscape, and is the largest area of wetland on the upper parts of the Thames Estuary.
Frog Island is a peninsula on the north bank of the River Thames in Rainham, London at grid reference TQ515805. It is used for vehicle storage in Ferry Lane Industrial Estate and for the mechanical biological treatment works building of the East London Waste Authority.
There are various formal and informal subdivisions of London Borough of Barking and Dagenham

Coldharbour is an area of the London Borough of Havering by the River Thames and southwest of the Rainham Marshes Nature Reserve. It is the location of Coldharbour Point, where there has been a lighthouse since 1885. This point is adjacent to the town of Erith in Bexley, across the Thames. The nearest accessible settlement on land is the town of Rainham, which is connected by Coldharbour Lane; the village of Wennington is also nearby but not accessible by road. The area around the point is mainly industrial land known as the Freightmaster Estate depot. The London Loop passes through Coldharbour on its way east to Purfleet in Thurrock.

Rainham is a suburb of East London, England, in the London Borough of Havering. Rainham is 13.6 miles (21.9 km) east of Charing Cross and is surrounded by a residential area, which has grown from the historic village, to the north and a commercial area, fronting the River Thames, to the south.
Public transport in the London Borough of Havering, in east London, England, is a mix of National Rail, London Underground, London Overground and Crossrail and London Buses services. Rail services are primarily radial to central London with bus services providing most of the orbital connections. The public transport authority is Transport for London and the local authority is Havering London Borough Council.

Rainham Hall is a Grade II* listed Georgian house, owned by the National Trust, in Rainham, in the London Borough of Havering. Built in 1729 for Captain John Harle, the house was transferred to the National Trust in 1949; let to a number of private tenants, it remained closed to the public until late 2015. Of note is that Rainham Hall recently appeared as a location in the 2019 BBC production A Christmas Carol.
The Belvedere Crossing is a proposed River Thames crossing in East London, running between Rainham in the London Borough of Havering and Belvedere/Thamesmead in the London Borough of Bexley. The proposed site is just downstream of the location for the Gallions Reach Crossing, and the two crossings are being developed in conjunction with each other by Transport for London.

Pope's Urn, on Champion's Wharf at Twickenham riverside in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, is a contemporary piece of public art inspired by the poetry of 18th-century Twickenham resident Alexander Pope, who is buried in the parish church that overlooks the wharf. It consists of a stylised urn on a pedestal, both made in corten steel and standing just over eight-foot high, surrounded by wooden benches inscribed with aphorisms written by Pope. It was commissioned to celebrate the 2015 Rugby World Cup, for which Twickenham Stadium was one of the venues, and was opened in a ceremony on 21 September 2015.















