Related Research Articles
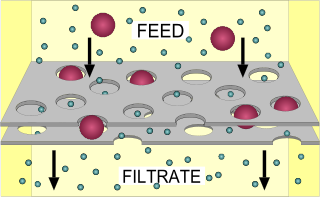
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms.

Paint is any pigmented liquid, liquefiable, or solid mastic composition that, after application to a substrate in a thin layer, converts to a solid film. It is most commonly used to protect, color, or provide texture. Paint can be made in many colors—and in many different types. Paint is typically stored, sold, and applied as a liquid, but most types dry into a solid. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based and each has distinct characteristics. For one, it is illegal in most municipalities to discard oil-based paint down household drains or sewers. Clean-up solvents are also different for water-based paint than they are for oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted Usually, the object being painted must be over 10 °C (50 °F), although some manufacturers of external paints/primers claim they can be applied when temperatures are as low as 2 °C (35 °F).

Spall are fragments of a material that are broken off a larger solid body. It can be produced by a variety of mechanisms, including as a result of projectile impact, corrosion, weathering, cavitation, or excessive rolling pressure. Spalling and spallation both describe the process of surface failure in which spall is shed.

Anti-fouling paint is a specialized category of coatings applied as the outer (outboard) layer to the hull of a ship or boat, to slow the growth of and facilitate detachment of subaquatic organisms that attach to the hull and can affect a vessel's performance and durability. It falls into a category of commercially available underwater hull paints, also known as bottom paints.

Biofouling or biological fouling is the accumulation of microorganisms, plants, algae, or small animals where it is not wanted on surfaces such as ship and submarine hulls, devices such as water inlets, pipework, grates, ponds, and rivers that cause degradation to the primary purpose of that item. Such accumulation is referred to as epibiosis when the host surface is another organism and the relationship is not parasitic. Since biofouling can occur almost anywhere water is present, biofouling poses risks to a wide variety of objects such as boat hulls and equipment, medical devices and membranes, as well as to entire industries, such as paper manufacturing, food processing, underwater construction, and desalination plants.

A car wash, carwash, or auto wash is a facility used to clean the exterior, and in some cases the interior of cars. Car washes can be self-service, full-service, or fully automated.

A primer or undercoat is a preparatory coating put on materials before painting. Priming ensures better adhesion of paint to the surface, increases paint durability, and provides additional protection for the material being painted.

Pressure washing or power washing is the use of high-pressure water spray to remove loose paint, mold, grime, dust, mud, and dirt from surfaces and objects such as buildings, vehicles and concrete surfaces. The volume of a mechanical pressure washer is expressed in gallons or liters per minute, often designed into the pump and not variable. The pressure, expressed in pounds per square inch, pascals, or bar, is designed into the pump but can be varied by adjusting the unloader valve. Machines that produce pressures from 750 to 30,000 psi or more are available.

Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted material on solid surfaces. The fouling materials can consist of either living organisms (biofouling) or a non-living substance. Fouling is usually distinguished from other surface-growth phenomena in that it occurs on a surface of a component, system, or plant performing a defined and useful function and that the fouling process impedes or interferes with this function.

Thermal spraying techniques are coating processes in which melted materials are sprayed onto a surface. The "feedstock" is heated by electrical or chemical means.

Hydrodemolition is a concrete removal technique which utilizes high-pressure water, often containing an abrasive material, to remove deteriorated and sound concrete as well as asphalt and grout. This process provides an excellent bonding surface for repair material and new coating applications. First developed in Europe in the 1980s, this technology has become widely accepted for concrete removal and surface preparation throughout Europe and North America.
Plasma activation is a method of surface modification employing plasma processing, which improves surface adhesion properties of many materials including metals, glass, ceramics, a broad range of polymers and textiles and even natural materials such as wood and seeds. Plasma functionalization also refers to the introduction of functional groups on the surface of exposed materials. It is widely used in industrial processes to prepare surfaces for bonding, gluing, coating and painting. Plasma processing achieves this effect through a combination of reduction of metal oxides, ultra-fine surface cleaning from organic contaminants, modification of the surface topography and deposition of functional chemical groups. Importantly, the plasma activation can be performed at atmospheric pressure using air or typical industrial gases including hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen. Thus, the surface functionalization is achieved without expensive vacuum equipment or wet chemistry, which positively affects its costs, safety and environmental impact. Fast processing speeds further facilitate numerous industrial applications.

Parts cleaning is essential to many industrial processes, as a prelude to surface finishing or to protect sensitive components. Electroplating is particularly a sensitive to part cleanliness, since molecular layers of oil can prevent the coating adhesion. ASTM B322 is a standard guide for cleaning metals prior to electroplating. Cleaning processes include solvent cleaning, hot alkaline detergent cleaning, electro-cleaning, and acid etch. The most common industrial test for cleanliness is the water-break test, in which the surface is thoroughly rinsed and vertically held. A quantitative measurement for this parameter is the contact angle. Hydrophobic contaminants such as oils cause the water to bead and break up, allowing the water to drain rapidly. Perfectly clean metal surfaces are hydrophilic and will keep an unbroken sheet of water that does not bead up or drain off. ASTM F22 describes a version of this test. This test does not detect hydrophilic contaminants, but the electroplating process can displace these easily since the solutions are water-based. Surfactants such as soap reduce the sensitivity of the test, so these must be thoroughly rinsed off.
Swimming pool sanitation is the process of ensuring healthy conditions in swimming pools. Proper sanitation is needed to maintain the visual clarity of water and to prevent the transmission of infectious waterborne diseases.

Sandblasting, sometimes known as abrasive blasting, is the operation of forcibly propelling a stream of abrasive material against a surface under high pressure to smooth a rough surface, roughen a smooth surface, shape a surface or remove surface contaminants. A pressurised fluid, typically compressed air, or a centrifugal wheel is used to propel the blasting material. The first abrasive blasting process was patented by Benjamin Chew Tilghman on 18 October 1870.
An anti-graffiti coating is a coating that prevents graffiti paint from bonding to surfaces.

A spray is a dynamic collection of drops dispersed in a gas. The process of forming a spray is known as atomization. A spray nozzle is the device used to generate a spray. The two main uses of sprays are to distribute material over a cross-section and to generate liquid surface area. There are thousands of applications in which sprays allow material to be used most efficiently. The spray characteristics required must be understood in order to select the most appropriate technology, optimal device and size.

Carbon dioxide cleaning (CO2 cleaning) comprises a family of methods for parts cleaning and sterilization, using carbon dioxide in its various phases. Due to being non-destructive, non-abrasive, and residue-free, it is often preferred for use on delicate surfaces. CO2 cleaning has found application in the aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical, and other industries. Carbon dioxide snow cleaning has been used to remove particles and organic residues from metals, polymers, ceramics, glasses, and other materials, and from surfaces including hard drives and optical surfaces.
Ice blasting is a form of non-abrasive blasting where frozen water particles are combined with compressed air and propelled towards a surface for cleaning purposes. Ice is one of several different media commonly used for blast cleaning. Another common method of non-abrasive blasting is dry ice blasting, which uses solid carbon dioxide as a blast media. Other forms of abrasive blasting use mediums such as sand, plastic beads, and baking soda.

Ships husbandry or ship husbandry is all aspects of maintenance, cleaning, and general upkeep of the hull, rigging, and equipment of a ship. It may also be used to refer to aspects of maintenance which are not specifically covered by the technical departments. The term is used in both naval and merchant shipping, but naval vessel husbandry may also be used for specific reference to naval vessels.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Morrisey, Donald; Woods, Chris (November 2015). In-water cleaning technologies: Review of information. MPI Technical Paper No: 2015/38 Prepared for Ministry for Primary Industries (Report). Wellington, New Zealand: Ministry for Primary Industries. ISBN 978-1-77665-128-3. ISSN 2253-3923 – via www.researchgate.net.
- ↑ Jameson, Grant. New Commercial Air Diving Manual. Durban, South Africa: Professional Diving Centre.