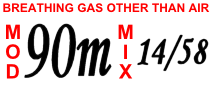
Narcosis while diving is a reversible alteration in consciousness that occurs while diving at depth. It is caused by the anesthetic effect of certain gases at high pressure. The Greek word νάρκωσις (narkōsis), "the act of making numb", is derived from νάρκη (narkē), "numbness, torpor", a term used by Homer and Hippocrates. Narcosis produces a state similar to drunkenness, or nitrous oxide inhalation. It can occur during shallow dives, but does not usually become noticeable at depths less than 30 meters (100 ft).
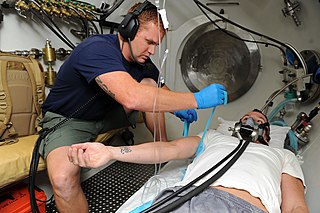
Decompression sickness is a medical condition caused by dissolved gases emerging from solution as bubbles inside the body tissues during decompression. DCS most commonly occurs during or soon after a decompression ascent from underwater diving, but can also result from other causes of depressurisation, such as emerging from a caisson, decompression from saturation, flying in an unpressurised aircraft at high altitude, and extravehicular activity from spacecraft. DCS and arterial gas embolism are collectively referred to as decompression illness.

Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas.
In-water recompression (IWR) or underwater oxygen treatment is the emergency treatment of decompression sickness (DCS) by returning the diver underwater to help the gas bubbles in the tissues, which are causing the symptoms, to resolve. It is a procedure that exposes the diver to significant risk which should be compared with the risk associated with the available options and balanced against the probable benefits. Some authorities recommend that it is only to be used when the time to travel to the nearest recompression chamber is too long to save the victim's life, others take a more pragmatic approach, and accept that in some circumstances IWR is the best available option. The risks may not be justified for case of mild symptoms likely to resolve spontaneously, or for cases where the diver is likely to be unsafe in the water, but in-water recompression may be justified in cases where severe outcomes are likely if not recompressed, if conducted by a competent and suitably equipped team.

Diving medicine, also called undersea and hyperbaric medicine (UHB), is the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of conditions caused by humans entering the undersea environment. It includes the effects on the body of pressure on gases, the diagnosis and treatment of conditions caused by marine hazards and how relationships of a diver's fitness to dive affect a diver's safety. Diving medical practitioners are also expected to be competent in the examination of divers and potential divers to determine fitness to dive.
Diving disorders, or diving related medical conditions, are conditions associated with underwater diving, and include both conditions unique to underwater diving, and those that also occur during other activities. This second group further divides into conditions caused by exposure to ambient pressures significantly different from surface atmospheric pressure, and a range of conditions caused by general environment and equipment associated with diving activities.
Rubicon Foundation, Inc. is a non-profit organization devoted to contributing to the interdependent dynamic between research, exploration, science and education. The foundation, started in 2002, is located in Durham, North Carolina and is primarily supported by donations and grants. Funding has included the Office of Naval Research from 2008 to 2010. Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher has provided pro bono services to assist in copyright searches and support.
The Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) is an organization based in the US which supports research on matters of hyperbaric medicine and physiology, and provides a certificate of added qualification for physicians with an unrestricted license to practice medicine and for limited licensed practitioners, at the completion of the Program for Advanced Training in Hyperbaric Medicine. They support an extensive library and are a primary source of information for diving and hyperbaric medicine physiology worldwide.
Peter B. Bennett was the founder and a president and CEO of the Divers Alert Network (DAN), a non-profit organization devoted to assisting scuba divers in need. He was a professor of anesthesiology at Duke University Medical Center, and was the Senior Director of the Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Environmental Physiology at Duke. Bennett is recognized as a leading authority on the effects of high pressure on human physiology.

American Nitrox Divers International was founded by Ed Betts and Dick Rutkowski in 1988.
In physiology, isobaric counterdiffusion (ICD) is the diffusion of different gases into and out of tissues while under a constant ambient pressure, after a change of gas composition, and the physiological effects of this phenomenon. The term inert gas counterdiffusion is sometimes used as a synonym, but can also be applied to situations where the ambient pressure changes. It has relevance in mixed gas diving and anesthesiology.

Colonel William Paul Fife USAF (Ret) was a United States Air Force officer that first proved the feasibility for U.S. Air Force Security Service airborne Communications Intelligence (COMINT) collection and Fife is considered the "Father of Airborne Intercept". Fife was also a hyperbaric medicine specialist who was known for his pioneering research on pressurized environments ranging from high altitude to underwater habitats. Fife was a Professor Emeritus at Texas A&M University.

Capt. Charles Wesley Shilling USN (ret.) was an American physician who was known as a leader in the field of undersea and hyperbaric medicine, research, and education. Shilling was widely recognized as an expert on deep sea diving, naval medicine, radiation biology, and submarine capabilities. In 1939, he was Senior Medical Officer in the rescue of the submarine U.S.S. Squalus.
Hyperbaric nursing is a nursing specialty involved in the care of patients receiving hyperbaric oxygen therapy. The National Board of Diving and Hyperbaric Medical Technology offers certification in hyperbaric nursing as a Certified Hyperbaric Registered Nurse (CHRN). The professional nursing organization for hyperbaric nursing is the Baromedical Nurses Association.

Robert William Hamilton Jr., known as Bill, was an American physiologist known for his work in hyperbaric physiology.

Eugene Weston Hobbs II, known as Gene Hobbs is an American technical diver and founding board member of the non-profit Rubicon Foundation. Hobbs has served as medical officer for the Woodville Karst Plain Project since 2004 and was named the 2010 Divers Alert Network/ Rolex Diver of the year. Hobbs was a hyperbaric technologist and simulation coordinator at Duke Medical Center before taking a position as the Director of Simulation for the University of North Carolina School of Medicine and Clinical Instructor in the Department of Pediatrics. As of 2018, Hobbs is the business manager for the UNC Health Care Department of Neurosurgery.

Neal Pollock is a Canadian academic and diver. Born in Edmonton, Canada he completed a bachelor's degree in zoology; the first three years at University of Alberta and the final year at the University of British Columbia. After completing a master's degree he then served as diving officer at University of British Columbia for almost five years. He then moved to Florida and completed a doctorate in exercise physiology/environmental physiology at Florida State University.
Brian Andrew Hills, born 19 March 1934 in Cardiff, Wales, died 13 January 2006 in Brisbane, Queensland, was a physiologist who worked on decompression theory.