
Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks, followed by the minimization, monitoring, and control of the impact or probability of those risks occurring. Risks can come from various sources including uncertainty in international markets, political instability, dangers of project failures, legal liabilities, credit risk, accidents, natural causes and disasters, deliberate attack from an adversary, or events of uncertain or unpredictable root-cause.
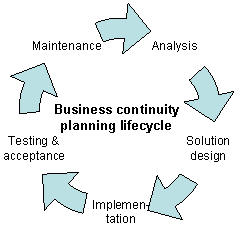
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.

An emergency is an urgent, unexpected, and usually dangerous situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property, or environment and requires immediate action. Most emergencies require urgent intervention to prevent a worsening of the situation, although in some situations, mitigation may not be possible and agencies may only be able to offer palliative care for the aftermath.

Risk assessment determines possible mishaps, their likelihood and consequences, and the tolerances for such events. The results of this process may be expressed in a quantitative or qualitative fashion. Risk assessment is an inherent part of a broader risk management strategy to help reduce any potential risk-related consequences.

Seismic risk or earthquake risk is the potential impact on the built environment and on people's well-being due to future earthquakes. Seismic risk has been defined, for most management purposes, as the potential economic, social and environmental consequences of hazardous events that may occur in a specified period of time. A building located in a region of high seismic hazard is at lower risk if it is built to sound seismic engineering principles. On the other hand, a building located in a region with a history of minor seismicity, in a brick building located on fill subject to liquefaction can be as high or higher risk.
Crisis management is the process by which an organization deals with a disruptive and unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization or its stakeholders. The study of crisis management originated with large-scale industrial and environmental disasters in the 1980s. It is considered to be the most important process in public relations.
Process Safety Managementof Highly Hazardous Chemicals is a regulation promulgated by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). It defines and regulates a process safety management (PSM) program for plants using, storing, manufacturing, handling or carrying out on-site movement of hazardous materials above defined amount thresholds. Companies affected by the regulation usually build a compliant process safety management system and integrate it in their safety management system. Non-U.S. companies frequently choose on a voluntary basis to use the OSHA scheme in their business.

Emergency management is a science and a system charged with creating the framework within which communities reduce vulnerability to hazards and cope with disasters. Emergency management, despite its name, does not actually focus on the management of emergencies; emergencies can be understood as minor events with limited impacts and are managed through the day-to-day functions of a community. Instead, emergency management focuses on the management of disasters, which are events that produce more impacts than a community can handle on its own. The management of disasters tends to require some combination of activity from individuals and households, organizations, local, and/or higher levels of government. Although many different terminologies exist globally, the activities of emergency management can be generally categorized into preparedness, response, mitigation, and recovery, although other terms such as disaster risk reduction and prevention are also common. The outcome of emergency management is to prevent disasters and where this is not possible, to reduce their harmful impacts.
Mitigation is the reduction of something harmful that has occurred or the reduction of its harmful effects. It may refer to measures taken to reduce the harmful effects of hazards that remain in potentia, or to manage harmful incidents that have already occurred. It is a stage or component of emergency management and of risk management. The theory of mitigation is a frequently used element in criminal law and is often used by a judge to try cases such as murder, where a perpetrator is subject to varying degrees of responsibility as a result of one's actions.
An incident is an event that could lead to loss of, or disruption to, an organization's operations, services or functions. Incident management (IcM) is a term describing the activities of an organization to identify, analyze, and correct hazards to prevent a future re-occurrence. These incidents within a structured organization are normally dealt with by either an incident response team (IRT), an incident management team (IMT), or Incident Command System (ICS). Without effective incident management, an incident can disrupt business operations, information security, IT systems, employees, customers, or other vital business functions.
In emergency management, higher learning institutions must frequently adapt broad, varied policies to deal with the unique scope of disasters that can occur in on-campus settings. Hurricanes, earthquakes, tornadoes, and wildfires are among some of the most common natural disasters that possess the capacity for large losses of life and property, with the potential to effectively destroy a university community. Man-made crises also can pose a serious threat to life and property, as was evident in the case of the 2007 Virginia Tech shooting. In order to preemptively reduce or prevent the severity of emergency situations, universities must coordinate and implement policies to effectively eliminate unnecessary risks' and decrease potential losses.
Human factors are the physical or cognitive properties of individuals, or social behavior which is specific to humans, and which influence functioning of technological systems as well as human-environment equilibria. The safety of underwater diving operations can be improved by reducing the frequency of human error and the consequences when it does occur. Human error can be defined as an individual's deviation from acceptable or desirable practice which culminates in undesirable or unexpected results. Human factors include both the non-technical skills that enhance safety and the non-technical factors that contribute to undesirable incidents that put the diver at risk.
[Safety is] An active, adaptive process which involves making sense of the task in the context of the environment to successfully achieve explicit and implied goals, with the expectation that no harm or damage will occur. – G. Lock, 2022
Dive safety is primarily a function of four factors: the environment, equipment, individual diver performance and dive team performance. The water is a harsh and alien environment which can impose severe physical and psychological stress on a diver. The remaining factors must be controlled and coordinated so the diver can overcome the stresses imposed by the underwater environment and work safely. Diving equipment is crucial because it provides life support to the diver, but the majority of dive accidents are caused by individual diver panic and an associated degradation of the individual diver's performance. – M.A. Blumenberg, 1996

Disaster preparedness in museums, galleries, libraries, archives and private collections, involves any actions taken to plan for, prevent, respond or recover from natural disasters and other events that can cause damage or loss to cultural property. 'Disasters' in this context may include large-scale natural events such as earthquakes, flooding or bushfire, as well as human-caused events such as theft and vandalism. Increasingly, anthropogenic climate change is a factor in cultural heritage disaster planning, due to rising sea levels, changes in rainfall patterns, warming average temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events.
Diving safety is the aspect of underwater diving operations and activities concerned with the safety of the participants. The safety of underwater diving depends on four factors: the environment, the equipment, behaviour of the individual diver and performance of the dive team. The underwater environment can impose severe physical and psychological stress on a diver, and is mostly beyond the diver's control. Equipment is used to operate underwater for anything beyond very short periods, and the reliable function of some of the equipment is critical to even short-term survival. Other equipment allows the diver to operate in relative comfort and efficiency, or to remain healthy over the longer term. The performance of the individual diver depends on learned skills, many of which are not intuitive, and the performance of the team depends on competence, communication, attention and common goals.
The civil liability of a recreational diver may include a duty of care to another diver during a dive. Breach of this duty that is a proximate cause of injury or loss to the other diver may lead to civil litigation for damages in compensation for the injury or loss suffered.
Investigation of diving accidents includes investigations into the causes of reportable incidents in professional diving and recreational diving accidents, usually when there is a fatality or litigation for gross negligence.
The operations manual is the documentation by which an organisation provides guidance for members and employees to perform their functions correctly and reasonably efficiently. It documents the approved standard procedures for performing operations safely to produce goods and provide services. Compliance with the operations manual will generally be considered as activity approved by the persons legally responsible for the organisation.
ISO 22300:2021, Security and resilience – Vocabulary, is an international standard developed by ISO/TC 292 Security and resilience. This document defines terms used in security and resilience standards and includes 360 terms and definitions. This edition was published in the beginning of 2021 and replaces the second edition from 2018.

Nuclear power plants pose high risk to public health and safety if radiation is released into surrounding communities and areas. This nuclear emergency level classificationresponse system was firstly developed by the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission to allow effective and urgent responses to ultimately control and minimise any detrimental effects that nuclear chemicals can have. These classifications come in four different categories – Unusual Event, Alert, Site Area Emergency (SAE), as well as General Emergency. Thus, each classification has differing characteristics and purposes, depending on the situation at hand. Every nuclear power plant has a different emergency response action plan, also depending on its structure, location and nature. They were developed by thorough discussion and planning with numerous authoritative parties such as local, state, federal agencies as well as other private and non-profit groups that are in association with emergency services. Today, nuclear emergency plans are continuously being developed over time to be improved for future serious events to keep communities and nuclear power plant working members safe. There is a high emphasis for the need of these emergency responses in case of future events. Thus, nuclear plants can, and have paid up to approximately $78 million to ensure that are required measurements are readily available, and that equipment is sufficient and safe. This is applicable for all nuclear power plants in the United States of America.
A diving emergency or underwater diving emergency is an emergency that involves an underwater diver. The nature of an emergency requires action to be taken to prevent or avoid death, injury, or serious damage to property or the environment. In the case of diving emergencies, the risk is generally of death or injury to the diver, while diving or in the water before or after diving.







