Related Research Articles
A management system is a set of policies, processes and procedures used by an organization to ensure that it can fulfill the tasks required to achieve its objectives. These objectives cover many aspects of the organization's operations. For instance, a quality management system enables organizations to improve their quality performance, an environmental management system enables organizations to improve their environmental performance, and an occupational health and safety management system enables organizations to improve their occupational health and safety performance, can be run in an integrated management system.
ISO/IEC 20000 is the international standard for IT service management. It was developed in 2005 by ISO/IEC JTC1/SC7 and revised in 2011 and 2018. It was originally based on the earlier BS 15000 that was developed by BSI Group.
Information security standards are techniques generally outlined in published materials that attempt to protect a user's or organization's cyber environment. This environment includes users themselves, networks, devices, all software, processes, information in storage or transit, applications, services, and systems that can be connected directly or indirectly to networks.

The Global Reporting Initiative is an international independent standards organization that helps businesses, governments, and other organizations understand and communicate their impacts on issues such as climate change, human rights, and corruption.
Environment, health and safety (EHS) is an interdisciplinary field focused on the study and implementation of practical aspects environmental protection and safeguard of people's health and safety, especially in an occupational context. It is what organizations must do to make sure that their activities do not cause harm. Commonly, quality - quality assurance and quality control - is adjoined to form HSQE or equivalent initialisms.

ISO 22000 is a food safety management system by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) which is outcome focused, providing requirements for any organization in the food industry with objective to help to improve overall performance in food safety. These standards are intended to ensure safety in the global food supply chain. The standards involve the overall guidelines for food safety management and also focuses on traceability in the feed and food chain.
ISO 13485Medical devices -- Quality management systems -- Requirements for regulatory purposes is a voluntary standard, published by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for the first time in 1996, and contains a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices. The latest version of this standard supersedes earlier documents such as EN 46001 and EN 46002 (1996), the previously published ISO 13485, and ISO 13488.

The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies standards certification services for business and personnel.
ISO 55000 is an international standard covering management of assets of any kind. Before it, a Publicly Available Specification (PAS 55) was published by the British Standards Institution in 2004 for physical assets. The ISO 55000 series of Asset Management standards was launched in January 2014.
An occupational safety management system (OSMS) is a management system designed to manage occupational safety and health risks in the workplace. If the system contains elements of management of longer-term health impacts and occupational disease, it may be referred to as a occupational safety and health management system (OSHMS) or occupational health and safety management system (OHSMS).

The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is the National Standards Body of India under Department of Consumer affairs, Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Government of India. It is established by the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 2016 which came into effect on 12 October 2017. The Minister in charge of the Ministry or Department having administrative control of the BIS is the ex-officio President of the BIS. BIS has 500 plus scientific officers working as Certification Officers, Member secretaries of technical committees and lab OIC's.

British Approvals Service for Cables is an independent accredited certification body headquartered in Milton Keynes, United Kingdom. Here, the organization's dedicated testing laboratory also operates which is believed to be the largest of its type in Europe. BASEC was established in 1971 and principally provides product certification services for all types of cable and wire, ancillary products and management systems within the cable industry. The organization maintains operations throughout the world including Africa, Middle East, America, Asia and Europe.

The Canadian Welding Bureau is a certification and registration organization for companies involved in the welding of steel structures. Welders in Canada are required to be retested every two years by the Canadian Welding Bureau. The CWB Group was formed in 1947 to administer the then, new W47.1 welding standard for structural steel. The CWB has today expanded its scope well beyond the original structural steel roots and is accredited by the Standards Council of Canada as a Certification Body for the administration of CSA Standards including W47.1, W47.2, W55.3, W186, W178.1 and W48 to industries across Canada and internationally for:
The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is a private organization that works as a "coalition of action" from the Consumer Goods Forum (CGF) and brings together retailers and brand owners (manufacturers) from across the CGF membership. The GFSI operates under multi-stakeholder governance, with the objective to create "an extended food safety community to oversee food safety standards for businesses and help provide access to safe food for people everywhere". GFSI's work in benchmarking and harmonization aims to foster mutual acceptance of GFSI-recognized certification programs across the industry, with the ambition to enable a "once certified, accepted everywhere" approach.
Nigel Howard Croft is a globally recognized authority on quality management and conformity assessment. He retired as Chairman of the ISO Joint Technical Coordination Group for Management System Standards in December 2023 after serving a three-year term, having been appointed by ISO's Technical Management Board in December 2020. During his tenure, he coordinated the deployment of the ISO London Declaration on Climate Action into all ISO Management System Standards, requiring organizations that implement these standards to determine the extent to which climate change can affect their results and the ways in which their activities can have a impact on climate change. This can then lead to the implementation of risk-based adaptation and mitigation strategies. Dr Croft was previously Chair of the ISO Technical Committee TC 176/SC 2 from February 2010 until December 2018, with overall responsibility for the ISO 9001 standard, used worldwide as a basis for certification of quality management systems, and the ISO 9004 guidelines standard aimed at improving organisational performance, among others. In 2019 and 2020 he led the revision of "Annex SL" of the ISO Directives, that forms the basis for over 40 management system standards including those on environmental management, Occupational Health and Safety, Information Security, Anti-bribery, Food Safety, Artificial Intelligence and many more.

Occupational safety and health (OSH) or occupational health and safety (OHS) is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. OSH is related to the fields of occupational medicine and occupational hygiene and aligns with workplace health promotion initiatives. OSH also protects all the general public who may be affected by the occupational environment.

Reykjavik Geothermal Ltd (RG) is a geothermal development company that specifically identifies and targets high quality geothermal resources in combination with underserved power markets.
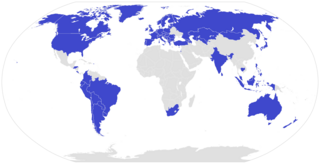
ISO 45001 is an international standard for occupational health and safety management systems. It was developed in March 2018 by International Organization for Standardization. The goal of the standard is the reduction of occupational injuries and diseases, including promoting and protecting physical and mental health. The standard was designed to fit into an integrated management system.
The Canadian Registered Safety Professional (CRSP)/ Professionnel en sécurité agréé du Canada (PSAC) is a certification offered by the Board of Canadian Registered Safety Professionals for an Occupational Health and Safety professional. The CRSP/PSAC is accredited in Canada to ISO 17024 by the Standards Council of Canada.
References
- 1 2 "International Labour Office Report, Page 2, Footnote 3" (PDF). International Labour Office. International Labour Organization. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 February 2018. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 "What is OHSAS 18001?". 18000 Store. Standards Stores. Archived from the original on 28 June 2017. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ↑ "ISO 45001". www.iso.org. ISO official website. Retrieved 25 September 2018.
- ↑ "Let the migration begin". ISO. Retrieved 2018-03-13.
- ↑ "ILO OSH 2001". International Labour Office. International Labour Organization. Archived from the original on 1 March 2007. Retrieved 1 March 2007.
