
Metropolitan counties are a subdivision of England which were originally used for local government. There are six metropolitan counties: Greater Manchester, Merseyside, South Yorkshire, Tyne and Wear, West Midlands and West Yorkshire.
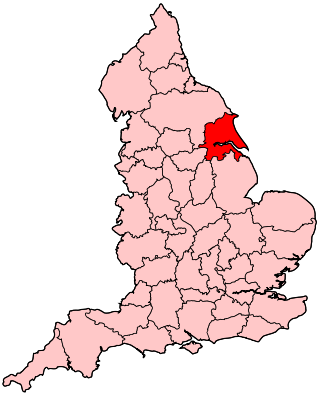
Humberside was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East Riding of Yorkshire, West Riding of Yorkshire, and the northern part of Lindsey, Lincolnshire. The county council's headquarters was County Hall at Beverley, inherited from East Riding County Council. Its largest settlement and only city was Kingston upon Hull. Other notable towns included Goole, Beverley, Scunthorpe, Grimsby, Cleethorpes and Bridlington. The county stretched from Wold Newton at its northern tip to a different Wold Newton at its southernmost point.

The North Riding of Yorkshire was a subdivision of Yorkshire, England, alongside York, the East Riding and West Riding. The riding's highest point was at Mickle Fell at 2,585 ft (788 m).
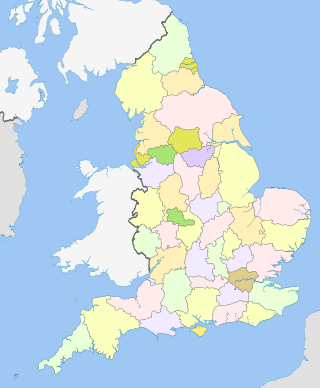
The counties of England are divisions of England. Counties have been used as administrative areas in England since Anglo-Saxon times. There are two main legal definitions of the counties in modern usage: the 84 counties for the purposes of local government, and the 48 counties for the purposes of lieutenancy, also termed the ceremonial counties.

The Parts of Lindsey are a traditional division of Lincolnshire, England, covering the northern part of the county. The Isle of Axholme, which is on the west side of the River Trent, has normally formed part of it. The district's name originated from the Kingdom of Lindsey of Anglo-Saxon times, whose territories were merged with that of Stamford to form Lincolnshire.

The Borough of Scarborough was a non-metropolitan district with borough status in North Yorkshire, England. In addition to the town of Scarborough, it covered a large stretch of the coast of Yorkshire, including Whitby and Filey. It bordered Redcar and Cleveland to the north, the Ryedale and Hambleton districts to the west and the East Riding of Yorkshire to the south.

Glanford was, from 1974 to 1996, a local government district with borough status in the non-metropolitan county of Humberside, England.

The Local Government Act 1972 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74.
A non-metropolitan county, or colloquially, shire county, is a subdivision of England used for local government.

The unitary authorities of England are a type of local authority responsible for all local government services in an area. They combine the functions of a non-metropolitan county council and a non-metropolitan district council, which elsewhere in England provide two tiers of local government.

The Local Government Commission for England was the body responsible for reviewing the structure of local government in England from 1992 to 2002. It was established under the Local Government Act 1992, replacing the Local Government Boundary Commission for England. The Commission could be ordered by the Secretary of State to undertake "structural reviews" in specified areas and recommend the creation of unitary authorities in the two-tier shire counties of England. The Commission, chaired by John Banham, conducted a review of all the non-metropolitan counties of England from 1993 to 1994, making various recommendations on their future.
The history of local government in England is one of gradual change and evolution since the Middle Ages. England has never possessed a formal written constitution, with the result that modern administration is based on precedent, and is derived from administrative powers granted to older systems, such as that of the shires.

Cleveland was a non-metropolitan county located in North East England which existed between 1974 and 1996. Cleveland was a two-tier county and had four boroughs: Hartlepool, Stockton-on-Tees, Middlesbrough and Langbaurgh-on-Tees. The county town was Middlesbrough, where Cleveland County Council met. The county was named after the historic area of Cleveland, Yorkshire. Its area is now split between the counties of North Yorkshire and County Durham.

North Yorkshire Council is the unitary authority which governs the non-metropolitan county of North Yorkshire, within the larger ceremonial county of North Yorkshire, in England. North Yorkshire was a two-tier non-metropolitan county from 1974 to 2023, when North Yorkshire Council was a county council called North Yorkshire County Council. On 1 April 2023 the seven lower-tier districts of the county were abolished and their functions taken over by the new unitary authority.
The East Riding of Yorkshire is a local government district with unitary authority status, and is a ceremonial county of England. It is named after the historic East Riding of Yorkshire which was one of three ridings alongside the North Riding and West Riding, which were constituent parts a Yorkshire ceremonial and administrative county until 1974. From 1974 to 1996 the area of the modern East Riding of Yorkshire constituted the northern part of Humberside.

Combined authorities and combined county authorities are a type of local government institution in England.

City of York Council is the local authority for York, in Yorkshire, England. York has had a city council from medieval times, which has been reformed on numerous occasions. Since 1996 the council has been a unitary authority, performing both district-level and county-level functions. It is composed of 47 councillors and has been under Labour majority control since 2023. The council is based at West Offices on Station Rise.
Structural changes to local government in England took place between 2019 and 2023. Some of these changes continue the trend of new unitary authorities being created from other types of local government districts, which was a policy of Communities Secretary Robert Jenrick from 2019.





















