Related Research Articles
The following is a glossary of diabetes which explains terms connected with diabetes.

Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of consciousness. A person's breath may develop a specific "fruity" smell. The onset of symptoms is usually rapid. People without a previous diagnosis of diabetes may develop DKA as the first obvious symptom.

Clinical chemistry is a division in medical laboratory sciences focusing on qualitative tests of important compounds, referred to as analytes or markers, in bodily fluids and tissues using analytical techniques and specialized instruments. This interdisciplinary field includes knowledge from medicine, biology, chemistry, biomedical engineering, informatics, and an applied form of biochemistry.

Ketosis is a metabolic state characterized by elevated levels of ketone bodies in the blood or urine. Physiological ketosis is a normal response to low glucose availability. In physiological ketosis, ketones in the blood are elevated above baseline levels, but the body's acid–base homeostasis is maintained. This contrasts with ketoacidosis, an uncontrolled production of ketones that occurs in pathologic states and causes a metabolic acidosis, which is a medical emergency. Ketoacidosis is most commonly the result of complete insulin deficiency in type 1 diabetes or late-stage type 2 diabetes. Ketone levels can be measured in blood, urine or breath and are generally between 0.5 and 3.0 millimolar (mM) in physiological ketosis, while ketoacidosis may cause blood concentrations greater than 10 mM.

Diabetic coma is a life-threatening but reversible form of coma found in people with diabetes mellitus.
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be absent, mild or severe. Mild symptoms include a decreased ability to think, headaches, nausea, and poor balance. Severe symptoms include confusion, seizures, and coma; death can ensue.

Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly, often due to high intensity exercise over a short period. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some of the muscle breakdown products, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and can cause acute kidney injury.

The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.

Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.
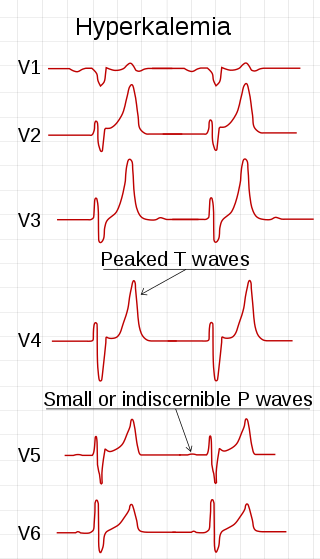
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5 mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Hyperkalemia can cause an abnormal heart rhythm which can result in cardiac arrest and death.

Alcoholic ketoacidosis (AKA) is a specific group of symptoms and metabolic state related to alcohol use. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, vomiting, agitation, a fast respiratory rate, and a specific "fruity" smell. Consciousness is generally normal. Complications may include sudden death.

Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid–base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by consuming too little or too much electrolyte as well as excreting too little or too much electrolyte. Examples of electrolytes include calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium.

Glycosuria is the excretion of glucose into the urine. Ordinarily, urine contains no glucose because the kidneys are able to reabsorb all of the filtered glucose from the tubular fluid back into the bloodstream. Glycosuria is nearly always caused by an elevated blood sugar level, most commonly due to untreated diabetes. Rarely, glycosuria is due to an intrinsic problem with glucose reabsorption within the kidneys, producing a condition termed renal glycosuria. Glycosuria leads to excessive water loss into the urine with resultant dehydration, a process called osmotic diuresis.
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and nystagmus. Complications may include seizures or cardiac arrest such as from torsade de pointes. Those with low magnesium often have low potassium.

Ketonuria is a medical condition in which ketone bodies are present in the urine.
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), also known as hyperosmolar non-ketotic state (HONK), is a complication of diabetes mellitus in which high blood sugar results in high osmolarity without significant ketoacidosis. Symptoms include signs of dehydration, weakness, leg cramps, vision problems, and an altered level of consciousness. Onset is typically over days to weeks. Complications may include seizures, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, mesenteric artery occlusion, or rhabdomyolysis.

A urine test strip or dipstick is a basic diagnostic tool used to determine pathological changes in a patient's urine in standard urinalysis.
Complications of diabetes are secondary diseases that are a result of elevated blood glucose levels that occur in diabetic patients. These complications can be divided into two types: acute and chronic. Acute complications are complications that develop rapidly and can be exemplified as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), lactic acidosis (LA), and hypoglycemia. Chronic complications develop over time and are generally classified in two categories: microvascular and macrovascular. Microvascular complications include neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy; while cardiovascular disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease are included in the macrovascular complications.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the beta cells of the endocrine pancreas either stop producing insulin or can no longer produce it in enough quantity for the body's needs. The disease can affect humans as well as animals such as dogs.
Post-mortem chemistry, also called necrochemistry or death chemistry, is a subdiscipline of chemistry in which the chemical structures, reactions, processes and parameters of a dead organism is investigated. Post-mortem chemistry plays a significant role in forensic pathology. Biochemical analyses of vitreous humor, cerebrospinal fluid, blood and urine is important in determining the cause of death or in elucidating forensic cases.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome
- 1 2 "Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS) - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Edition". MSD Manual Professional Edition. Retrieved 2018-09-25.