Related Research Articles

The International Electrotechnical Commission is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology". IEC standards cover a vast range of technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology, and marine energy, as well as many others. The IEC also manages four global conformity assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its international standards.

An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.

EU Directive 92/75/EC (1992) established an energy consumption labelling scheme. The directive was implemented by several other directives thus most white goods, light bulb packaging and cars must have an EU Energy Label clearly displayed when offered for sale or rent. The energy efficiency of the appliance is rated in terms of a set of energy efficiency classes from A to G on the label, A being the most energy efficient, G the least efficient. The labels also give other useful information to the customer as they choose between various models. The information should also be given in catalogues and included by internet retailers on their websites.
Internet Explorer 4 is the fourth version of the Internet Explorer graphical web browser.
Internet Explorer 2 is the second version of the Internet Explorer graphical web browser.
IEC 60364Electrical Installations for Buildings is the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)'s international standard on electrical installations of buildings. This standard is an attempt to harmonize national wiring standards in an IEC standard and is published in the European Union by CENELEC as "HD 60364". The latest versions of many European wiring regulations follow the section structure of IEC 60364 very closely, but contain additional language to cater for historic national practice and to simplify field use and determination of compliance by electricians and inspectors. National codes and site guides are meant to attain the common objectives of IEC 60364, and provide rules in a form that allows for guidance of persons installing and inspecting electrical systems.
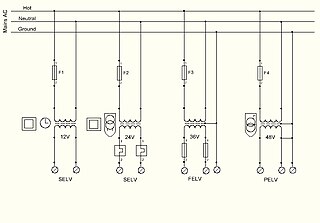
Extra-low voltage (ELV) is an electricity supply voltage and is a part of the low-voltage band in a range which carries a low risk of dangerous electrical shock. There are various standards that define extra-low voltage. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the UK IET define an ELV device or circuit as one in which the electrical potential between two conductors or between an electrical conductor and Earth (ground) does not exceed 120 volts (V) for ripple-free direct current (DC) or 50 VRMS for alternating current (AC).
European Standards, sometimes called Euronorm, are technical standards which have been ratified by one of the three European Standards Organizations (ESO): European Committee for Standardization (CEN), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC), or European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). All ENs are designed and created by all standards organizations and interested parties through a transparent, open, and consensual process.
IEC 61508 is an international standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) consisting of methods on how to apply, design, deploy and maintain automatic protection systems called safety-related systems. It is titled Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems.
In electrical engineering, low voltage is a relative term, the definition varying by context. Different definitions are used in electric power transmission and distribution, compared with electronics design. Electrical safety codes define "low voltage" circuits that are exempt from the protection required at higher voltages. These definitions vary by country and specific codes or regulations.

SAE J1772, also known as a J plug or Type 1 connector after its international standard, IEC 62196 Type 1, is a North American standard for electrical connectors for electric vehicles maintained by SAE International under the formal title "SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler".

A fractional-horsepower motor (FHP) is an electric motor with a rated output power of less than one horsepower (745.7 W). There is no defined minimum output, however, it is generally accepted that a motor with a frame size of less than 35mm square can be referred to as a 'micro-motor'.
Premium efficiency, when used in reference to specific types of Electric Motors, is a class of motor efficiency.
The Ecodesign Directive of the European Union establishes a framework to set mandatory ecological requirements for energy-using and energy-related products sold in all 27 member states. Its scope currently covers more than 40 product groups, which are responsible for around 40% of all EU greenhouse gas emissions.

The common external power supply was a European Commission (EC) specification for a universal charger for smartphones sold within the European Union. The specification included the use of a USB Micro-B connector and adherence to the USB Battery Charging Specification.
The European Pump Manufacturers Association, mostly known as Europump, is the European association for pump manufacturers.

A high efficiency glandless circulating pump is a component of a heating and air conditioning system that allows the system to perform with increased efficiency while significantly reducing the system's electrical usage.
Ecomechatronics is an engineering approach to developing and applying mechatronical technology in order to reduce the ecological impact and total cost of ownership of machines. It builds upon the integrative approach of mechatronics, but not with the aim of only improving the functionality of a machine. Mechatronics is the multidisciplinary field of science and engineering that merges mechanics, electronics, control theory, and computer science to improve and optimize product design and manufacturing. In ecomechatronics, additionally, functionality should go hand in hand with an efficient use and limited impact on resources. Machine improvements are targeted in 3 key areas: energy efficiency, performance and user comfort.
The International Electrotechnical Vocabulary (IEV) is managed list of terms and definitions organized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which is grouped in classes. It serves to promote the global unification of terminology in the field of electrotechnology, electronics and telecommunications. It is developed by the IEC Technical Committee 1 (Terminology), and published as both the IEC 60050 series of standards and online as the Electropedia. The Electropedia database contains English and French definitions for more than 22 000 concepts, and provides terms in up to 18 other languages.

Heatball is a brand name for an incandescent lamp. The brand was used as part of a scheme by Siegfried Rotthäuser, a mechanical engineer from Essen in Germany, to stimulate discussion of EU Regulation 244/2009. This Regulation forbade the importation or sale of light sources with energy efficiency worse than 'Class C' after September 2012 as part of the phase-out of incandescent light bulbs.
References
- ↑ International Electrotechnical Commission: TC2 rotating machinery work programme homepage
- ↑ Commission Regulation (EC) No 640/2009: implementing Directive 2005/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to ecodesign requirements for electric motors, PDF, 22 July 2009
- ↑ Commission Regulation (EU) No 1781/2019: laying down ecodesign requirements for electric motors and variable speed drives pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, amending Regulation (EC) No 641/2009 with regard to ecodesign requirements for glandless standalone circulators and glandless circulators integrated in products and repealing Commission Regulation (EC) No 640/2009, PDF, 1 October 2019