SCADA is a control system architecture comprising computers, networked data communications and graphical user interfaces for high-level supervision of machines and processes. It also covers sensors and other devices, such as programmable logic controllers, which interface with process plant or machinery.

A remote terminal unit (RTU) is a microprocessor-controlled electronic device that interfaces objects in the physical world to a distributed control system or SCADA system by transmitting telemetry data to a master system, and by using messages from the master supervisory system to control connected objects. Other terms that may be used for RTU are remote telemetry unit and remote telecontrol unit.
Open Platform Communications (OPC) is a series of standards and specifications for industrial telecommunication. They are based on Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) for process control. An industrial automation task force developed the original standard in 1996 under the name OLE for Process Control. OPC specifies the communication of real-time plant data between control devices from different manufacturers.
Digital storage media command and control (DSM-CC) is a toolkit for developing control channels associated with MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 streams. It is defined in part 6 of the MPEG-2 standard and uses a client/server model connected via an underlying network.
In electrical engineering and power system automation, the International Electrotechnical Commission 60870 standards define systems used for telecontrol. Such systems are used for controlling electric power transmission grids and other geographically widespread control systems. By use of standardized protocols, equipment from many different suppliers can be made to interoperate. IEC standard 60870 has six parts, defining general information related to the standard, operating conditions, electrical interfaces, performance requirements, and data transmission protocols. The 60870 standards are developed by IEC Technical Committee 57.

IEC 62056 is a set of standards for electricity metering data exchange by International Electrotechnical Commission. The IEC 62056 standards are the international standard versions of the DLMS/COSEM specification.
IEC 61850 is an international standard defining communication protocols for intelligent electronic devices at electrical substations. It is a part of the International Electrotechnical Commission's (IEC) Technical Committee 57 reference architecture for electric power systems. The abstract data models defined in IEC 61850 can be mapped to a number of protocols. Current mappings in the standard are to Manufacturing Message Specification (MMS), GOOSE [see section 3, Terms and definitions, term 3.65 on page 14], SV or SMV, and soon to web services. In the previous version of the standard, GOOSE stood for "Generic Object Oriented Substation Event", but this old definition is still very common in IEC 61850 documentation. These protocols can run over TCP/IP networks or substation LANs using high speed switched Ethernet to obtain the necessary response times below four milliseconds for protective relaying.
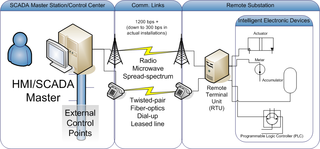
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.
The Common Information Model (CIM) is an electric power transmission and distribution standard developed by the electric power industry. It aims to allow application software to exchange information about an electrical network. It has been officially adopted by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
OPC Unified Architecture is a cross-platform, open-source, IEC62541 standard for data exchange from sensors to cloud applications developed by the OPC Foundation. Distinguishing characteristics are:
International standard IEC 61400-25 provides uniform information exchange for monitoring and control of wind power plants. This addresses the issue of proprietary communication systems utilizing a wide variety of protocols, labels, semantics, etc., thus enabling one to exchange information with different wind power plants independently of a vendor. It is a subset of IEC 61400; a set of standards for designing wind turbines.
M-Bus or Meter-Bus is a European standard for the remote reading of water, gas or electricity meters. M-Bus is also usable for other types of consumption meters, such as heating systems or water meters. The M-Bus interface is made for communication on two wires, making it cost-effective. A radio variant of M-Bus Wireless M-Bus is also specified in EN 13757–4.
IEC 61334, known as Distribution automation using distribution line carrier systems, is a standard for low-speed reliable power line communications by electricity meters, water meters and SCADA. It is also known as spread frequency-shift keying (S-FSK) and was formerly known as IEC 1334 before IEC's most recent renumbering. It is actually a series of standards describing the researched physical environment of power lines, a well-adapted physical layer, a workable low-power media access layer, and a management interface. Related standards use the physical layer, but not the higher layers.
IEC 62351 is a standard developed by WG15 of IEC TC57. This is developed for handling the security of TC 57 series of protocols including IEC 60870-5 series, IEC 60870-6 series, IEC 61850 series, IEC 61970 series & IEC 61968 series. The different security objectives include authentication of data transfer through digital signatures, ensuring only authenticated access, prevention of eavesdropping, prevention of playback and spoofing, and intrusion detection.
IEC 60870 part 5 is one of the IEC 60870 set of standards which define systems used for telecontrol in electrical engineering and power system automation applications. Part 5 provides a communication profile for sending basic telecontrol messages between two systems, which uses permanent directly connected data circuits between the systems. The IEC Technical Committee 57 have developed a protocol standard for telecontrol, teleprotection, and associated telecommunications for electric power systems. The result of this work is IEC 60870-5. Five documents specify the base IEC 60870-5:
A distribution management system (DMS) is a collection of applications designed to monitor and control the electric power distribution networks efficiently and reliably. It acts as a decision support system to assist the control room and field operating personnel with the monitoring and control of the electric distribution system. Improving the reliability and quality of service in terms of reducing power outages, minimizing outage time, maintaining acceptable frequency and voltage levels are the key deliverables of a DMS. Given the complexity of distribution grids, such systems may involve communication and coordination across multiple components. For example, the control of active loads may require a complex chain of communication through different components as described in US patent 11747849B2
The Open Smart Grid Protocol (OSGP) is a family of specifications published by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) used in conjunction with the ISO/IEC 14908 control networking standard for smart grid applications. OSGP is optimized to provide reliable and efficient delivery of command and control information for smart meters, direct load control modules, solar panels, gateways, and other smart grid devices. With over 5 million OSGP based smart meters and devices deployed worldwide it is one of the most widely used smart meter and smart grid device networking standards.
VHPready is an open industry standard for the control of decentralised power generation plants, consumers and energy storage systems via a central control centre. The uniform use of this standard enables the flexible connection of decentralized power plants to virtual power plants and Smart Grid applications.
TRAME was the name of the second computer network in the world similar to the internet to be used in an electric utility. Like the internet, the base technology was packet switching; it was developed by the electric utility ENHER in Barcelona. It was deployed by the same utility, first in Catalonia and Aragón, Spain, and later in other places. Its development started in 1974 and the first routers, called nodes at that time, were deployed by 1978. The network was in operation until 2016 with successive technological software and hardware updates.


