Articles related to anatomy include:

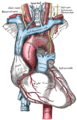
The brachiocephalic artery,brachiocephalic trunk, or innominate artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm, head, and neck.

The left and right brachiocephalic veins are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein.

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

The jugular veins are veins that take deoxygenated blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
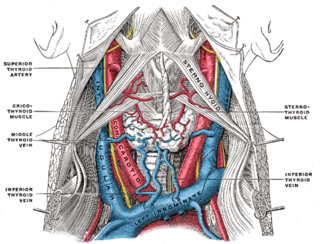
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.

In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.

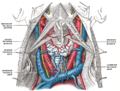
The superior thoracic aperture, also known as the thoracic outlet, or thoracic inlet refers to the opening at the top of the thoracic cavity. It is also clinically referred to as the thoracic outlet, in the case of thoracic outlet syndrome. A lower thoracic opening is the inferior thoracic aperture.

The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spinal nerve 1 that run with the hypoglossal nerve to reach this muscle. The thyrohyoid muscle depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx during swallowing. By controlling the position and shape of the larynx, it aids in making sound.

The superior hypogastric plexus is a plexus of nerves situated on the vertebral bodies anterior to the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta. It bifurcates to form the left and the right hypogastric nerve. The SHP is the continuation of the abdominal aortic plexus.

The inferior mesenteric vein begins in the rectum as the superior rectal vein, which has its origin in the hemorrhoidal plexus, and through this plexus communicates with the middle and inferior hemorrhoidal veins.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The inferior cervical ganglion is one of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia. It situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib, on the medial side of the costocervical artery.
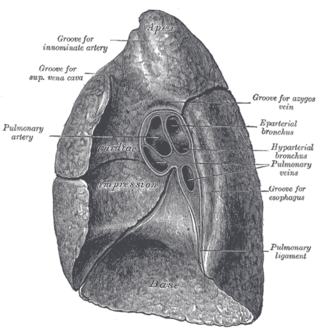
The root of the lung is a group of structures that emerge at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression of the lung. It is nearer to the back than the front. The root of the lung is connected by the structures that form it to the heart and the trachea. The rib cage is separated from the lung by a two-layered membranous coating, the pleura. The hilum is the large triangular depression where the connection between the parietal pleura and the visceral pleura is made, and this marks the meeting point between the mediastinum and the pleural cavities.

The superior cardiac nerve arises by two or more branches from the superior cervical ganglion, and occasionally receives a filament from the trunk between the first and second cervical ganglia. It runs down the neck behind the common carotid artery, and in front of the Longus colli muscle; and crosses in front of the inferior thyroid artery, and recurrent nerve. The course of the nerves on the two sides then differs.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

In anatomy, the venae cavae are two large veins that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the right atrium. They are located slightly off-center, toward the right side of the body.