
Iron is a chemical element with symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust.

An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion.

Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

The mineral pyrite, or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula FeS2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.

Aqua regia is a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, optimally in a molar ratio of 1:3. Aqua regia is a fuming liquid. Freshly prepared aqua regia is colorless, but it turns yellow, orange or red within seconds due to the formation of nitrosyl chloride and nitrogen dioxide. It was named by alchemists because it can dissolve the noble metals gold and platinum, though not all metals.

Redox is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state.

The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula SO2−4. Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid.

Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturally as the mineral magnetite. As the mineral known as hematite, Fe2O3 is the main source of iron for the steel industry. Fe2O3 is readily attacked by acids. Iron(III) oxide is often called rust, and to some extent this label is useful, because rust shares several properties and has a similar composition; however, in chemistry, rust is considered an ill-defined material, described as Hydrous ferric oxide.
The pedosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. The pedosphere is the skin of the Earth and only develops when there is a dynamic interaction between the atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere and the hydrosphere. The pedosphere is the foundation of terrestrial life on Earth.

Iron(II,III) oxide is the chemical compound with formula Fe3O4. It occurs in nature as the mineral magnetite. It is one of a number of iron oxides, the others being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare, and iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3) which also occurs naturally as the mineral hematite. It contains both Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions and is sometimes formulated as FeO ∙ Fe2O3. This iron oxide is encountered in the laboratory as a black powder. It exhibits permanent magnetism and is ferrimagnetic, but is sometimes incorrectly described as ferromagnetic. Its most extensive use is as a black pigment. For this purpose, it is synthesized rather than being extracted from the naturally occurring mineral as the particle size and shape can be varied by the method of production.
Fenton's reagent is a solution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with ferrous iron (typically iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4) as a catalyst that is used to oxidize contaminants or waste waters as part of an advanced oxidation process. Fenton's reagent can be used to destroy organic compounds such as trichloroethylene (TCE) and tetrachloroethylene (perchloroethylene, PCE). It was developed in the 1890s by Henry John Horstman Fenton as an analytical reagent.
Iron–sulfur proteins are proteins characterized by the presence of iron–sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers in variable oxidation states. Iron–sulfur clusters are found in a variety of metalloproteins, such as the ferredoxins, as well as NADH dehydrogenase, hydrogenases, coenzyme Q – cytochrome c reductase, succinate – coenzyme Q reductase and nitrogenase. Iron–sulfur clusters are best known for their role in the oxidation-reduction reactions of electron transport in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Both Complex I and Complex II of oxidative phosphorylation have multiple Fe–S clusters. They have many other functions including catalysis as illustrated by aconitase, generation of radicals as illustrated by SAM-dependent enzymes, and as sulfur donors in the biosynthesis of lipoic acid and biotin. Additionally, some Fe–S proteins regulate gene expression. Fe–S proteins are vulnerable to attack by biogenic nitric oxide, forming dinitrosyl iron complexes. In most Fe–S proteins, the terminal ligands on Fe are thiolate, but exceptions exist.
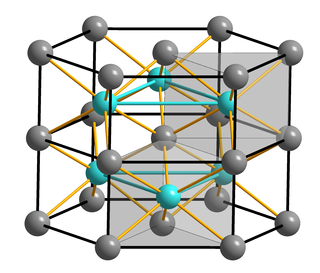
Iron(II) sulfide or ferrous sulfide is one of a family chemical compounds and minerals with the approximate formula FeS. Iron sulfides are often iron-deficient non-stoichiometric. All are black, water-insoluble solids.

Iron(II) hydroxide or ferrous hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Fe(OH)2. It is produced when iron(II) salts, from a compound such as iron(II) sulfate, are treated with hydroxide ions. Iron(II) hydroxide is a white solid, but even traces of oxygen impart a greenish tinge. The air-oxidised solid is sometimes known as "green rust".
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry is a systematic method of naming inorganic chemical compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. Ideally, every inorganic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous formula can be determined. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry.

Pentetic acid or diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid consisting of a diethylenetriamine backbone with five carboxymethyl groups. The molecule can be viewed as an expanded version of EDTA and is used similarly. It is a white solid with limited solubility in water.
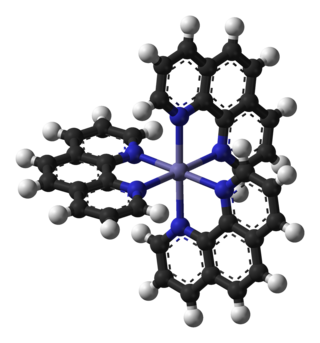
Ferroin is the chemical compound with the formula [Fe(o-phen)3]SO4, where o-phen is an abbreviation for 1,10-phenanthroline, a bidentate ligand. The term "ferroin" is used loosely and includes salts of other anions such as chloride.
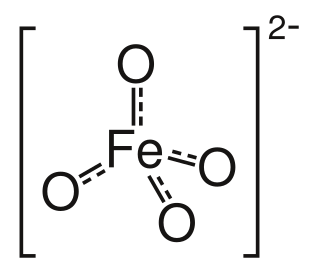
High-valent iron commonly denotes compounds and intermediates in which iron is found in a formal oxidation state > 3 that show a number of bonds > 6 with a coordination number ≤ 6. The term is rather uncommon for hepta-coordinate compounds of iron. It has to be distinguished from the terms hypervalent and hypercoordinate, as high-valent iron compounds neither necessarily violate the 18-electron rule nor necessarily show coordination numbers > 6. The ferrate(VI) ion [FeO4]2− was the first structure in this class synthesized. The synthetic compounds discussed below contain highly oxidized iron in general, as the concepts are closely related.
A tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with four fluorines in its formula.
Potassium ferrooxalate, also known as potassium bisoxalatoferrate(II), is a salt with the formula K
2[Fe(C
2O
4)
2], sometimes abbreviated K
2FeOx
2. The ferrooxalate anion [Fe(C
2O
4)
2]2−
is a transition metal complex, consisting of an atom of iron in the +2 oxidation state bound to two bidentate oxalate ions C
2O2−
4. The anion charge is balanced by two cations of potassium K+
.














