
Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels.
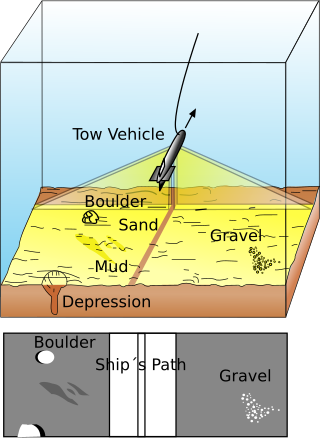
Side-scan sonar is a category of sonar system that is used to efficiently create an image of large areas of the sea floor.

Echo sounding or depth sounding is the use of sonar for ranging, normally to determine the depth of water (bathymetry). It involves transmitting acoustic waves into water and recording the time interval between emission and return of a pulse; the resulting time of flight, along with knowledge of the speed of sound in water, allows determining the distance between sonar and target. This information is then typically used for navigation purposes or in order to obtain depths for charting purposes.

Hydrographic survey is the science of measurement and description of features which affect maritime navigation, marine construction, dredging, offshore wind farms, offshore oil exploration and drilling and related activities. Surveys may also be conducted to determine the route of subsea cables such as telecommunications cables, cables associated with wind farms, and HVDC power cables. Strong emphasis is placed on soundings, shorelines, tides, currents, seabed and submerged obstructions that relate to the previously mentioned activities. The term hydrography is used synonymously to describe maritime cartography, which in the final stages of the hydrographic process uses the raw data collected through hydrographic survey into information usable by the end user.

The Echo class was a class of multi-purpose hydrographic survey ships in commission with the Royal Navy. The ships were primarily tasked with conducting survey work in support of submarine and amphibious operations, however, the class also has a secondary role in mine countermeasures. The two vessels of the class were the most recent additions to the Royal Navy's Hydrographic Squadron. Each ship displaced approximately 3,700 tonnes, and was equipped with a state of the art suite of equipment. The lead ship of the class, HMS Echo, was retired in 2022 and her sister ship in 2023.

HMS Echo was the first of two multi-role hydrographic survey ships commissioned by the Royal Navy. With her sister ship, HMS Enterprise, they formed the Echo class of survey vessels. She was built by Appledore Shipbuilders in Devon in 2002 and was the ninth Royal Navy vessel to carry the name. She was retired from service in 2022.

The Italian Navy is one of the four branches of Italian Armed Forces and was formed in 1946 from what remained of the Regia Marina after World War II. As of August 2014, the Italian Navy had a strength of 30,923 active personnel, with approximately 184 vessels in service, including minor auxiliary vessels. It is considered a multiregional and a blue-water navy.

HMAS Leeuwin is the lead ship of the Leeuwin-class of hydrographic survey vessels operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN).

The Leeuwin class is a two-ship class of hydrographic survey vessels operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). Leeuwin and Melville were ordered from NQEA in 1996, and were commissioned in 2000. The ships are capable of charting waters up to 6,000 metres (20,000 ft) deep, carry three Fantome-class survey boats, and could operate an AS 350B Squirrel helicopter. In addition to surveying duties, since 2001 both vessels have been used to supplement the RAN patrol force. Leeuwin is based at HMAS Cairns, while Melville was decommissioned in August 2024.

A multibeam echosounder (MBES) is a type of sonar that is used to map the seabed. It emits acoustic waves in a fan shape beneath its transceiver. The time it takes for the sound waves to reflect off the seabed and return to the receiver is used to calculate the water depth. Unlike other sonars and echo sounders, MBES uses beamforming to extract directional information from the returning soundwaves, producing a swathe of depth soundings from a single ping.

HMAS Melville is the second ship of the Leeuwin class of hydrographic survey vessels operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). The ship was decommissioned on 8 August 2024.

The Fantome class is a class of eight small survey motor boats (SMBs) operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and DMS Maritime. The four-man boats are designed to operate from the Leeuwin-class survey vessels, with three assigned to each ship, while the seventh and eighth were attached to the RAN Hydrographic School at HMAS Penguin. They are fitted with navigational and survey equipment and are unarmed.

INS Jamuna (J16) is a hydrographic survey ship in the Indian Navy, under the Southern Naval Command. Jamuna is equipped with a helicopter, a Bofors 40 mm gun, four survey motor boats, and two small boats. The ship has the distinction of being associated with relief work in the wake of the Gujarat earthquake, Tsunami 2004, as well as Operation Vijay during the Kargil war. Jamuna was also awarded a Mention in Dispatches.

The Sandhayak-class survey ships are a series of eight vessels built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata and Goa Shipyard, Ltd., Vasco for the Indian Navy. While Sandhayak, Investigator, Nirdeshak, Nirupak were built in GRSE; Sarveshak, Jamuna, Darshak, Sutlej were built by Goa Shipyard. The vessels equipped with four survey motorboats, two small boats and are powered by two diesel engines with a top speed of 16 knots. They have a helicopter deck and are also armed with a Bofors 40 mm/60 gun mount for self-defense.

Alliance (A5345) is a research vessel owned by NATO and operated by the Marina Militare as a NATO research vessel and owned by the CMRE – Centre for Maritime Research and Experimentation, in La Spezia, Italy. Alliance has the status of an auxiliary ship of the Marina Militare.

The Ninfe class of survey vessels consists of two catamaran hulls operated by the Marina Militare Italiana.
GO 11 is a Floating dry dock of the Marina Militare.
USSP is a planned Submarine rescue ship of the Marina Militare, financed with 2017's balance law.
It is expected to replace Italian ship Anteo.
UIOM is a planned ocean-going Hydrographic survey vessel of the Marina Militare to replace Italian ship Ammiraglio Magnaghi (A5303) from 2020

INS Nirdeshak (J19) was the sixth ship of the Sandhayak class of the Indian Navy. The ship operated as a hydrographic survey ship in the Indian Navy, under the Eastern Naval Command. Nirdeshak was equipped to prepare a variety of marine charts and maps for ECDIS system. The ship's secondary role was to conduct humanitarian aid and disaster management operations, wherein the ship could be converted into a hospital ship. The ship was also equipped with an operating theater and associated equipment needed to attend to medical emergencies at sea.


















