Related Research Articles

Chhattisgarh is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Pradesh to the northwest, Maharashtra to the southwest, Jharkhand to the northeast, Odisha to the east, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana to the south. Formerly a part of Madhya Pradesh, it was granted statehood on 1 November 2000 with Raipur as the designated state capital.
Ho is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken primarily in India by about 2.2 million people per the 2001 census. It is spoken by the Ho, Munda, Kolha and Kol tribal communities of Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal and Assam and is written using Warang Citi script. Devanagari, Latin and Odia script are also used, although native speakers are said to prefer Warang Chiti, invented by Lako Bodra.

Kurukh, also Kurux, Oraon or Uranw, is a North Dravidian language spoken by the Kurukh (Oraon) and Kisan people of East India. It is spoken by about two million people in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Assam, Bihar and Tripura, as well as by 65,000 in northern Bangladesh, 28,600 of a dialect called Uranw in Nepal and about 5,000 in Bhutan. The most closely related language to Kurukh is Malto; together with Brahui, all three languages form the North Dravidian branch of the Dravidian language family. It is marked as being in a "vulnerable" state in UNESCO's list of endangered languages. The Kisan dialect has 206,100 speakers as of 2011.

Jharsuguda is a district in Odisha, India with Jharsuguda town as its headquarters. This region is rich in coal and other mineral reserves. Of late, many small and medium scale iron and steel units have been set up in the vicinity of Jharsuguda town, giving impetus to the industrial growth of the district.

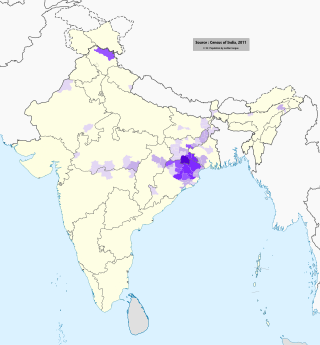
The Kharia language is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family, that is primarily spoken by the Kharia people of eastern India.

Jashpur District is a district of the central Indian state of Chhattisgarh bordering Jharkhand and Odisha. Jashpur Nagar is the administrative headquarters of the district. The district was formerly a princely state before Independence. Highly mountainous and forested, Jashpur is known for its natural environment.

Raigarh is a city in northern Chhattisgarh known as the 'Cultural capital of Chhattisgarh'; Raigarh is famous for its dance form “Kathak” and classical music; Raigarh is also known as Sanskritidhani.

Korba District is an administrative district of Chhattisgarh state in central India. The headquarter of this district is Korba. It is the Largest District in the state.

Surguja district is a district of the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. The district is one of the oldest districts of Chhattisgarh. The headquarters of the district is Ambikapur.
Kodaku people are an indigenous people who live in India. They live in the hills and forest of Chhotanagpur, the bordering area of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh. Their mother tongue, a Munda language, is also called Kodaku. Some Kodaku people speak Korwa as their mother tongue. They also speak Sadri, Chhattisgarhi, or Kurukh as their second language. The Kodaku people are mainly concentrated in the northeastern area of Surguja district in Chhattishgarh, southern parts of Palamau, Gadhwa in Jharkhand and the southeastern region of Sonabhadra district of Uttar Pradesh. Kodaku people are now included in Scheduled Tribes by government of India.

The Korwa people are a Munda, a Scheduled Tribe ethnic group of India. They live mainly on the border between Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand. A small number of Korwa are also found in the Mirzapur district of Uttar Pradesh.

Nagpuri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Bihar. It is primarily spoken in the west and central Chota Nagpur plateau region. It is sometimes considered a dialect of Bhojpuri.
Mundari (Munɖari) is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken by the Munda tribes in eastern Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal and northern Rangpur Division of Bangladesh. It is closely related to Santali. Mundari Bani, a script specifically to write Mundari, was invented by Rohidas Singh Nag. It has also been written in the Devanagari, Odia, Bengali, and Latin writing systems.
Asuri is an Austroasiatic language spoken by the Asur people, part of the Munda branch. Asuri has many Dravidian loanwords due to contact with Kurukh.
Most of the languages of Bihar, the third most populous state of India, belong to the Bihari subgroup of the Indo-Aryan family. Chief among them are Bhojpuri, spoken in the west of the state, Maithili in the north, Magahi in center around capital Patna and in the south of the state. Maithili has official recognition under the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. The official language of Bihar is Modern Standard Hindi, with Standard Urdu serving as a second official language in 15 districts.

Bhumij is an Austroasiatic language belonging to the Munda subfamily, related to Ho, Mundari, and Santali, primarily spoken by Bhumij peoples in the Indian states Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. As per the 2011 census, only 27,506 people out of 911,349 Bhumij people spoke Bhumij as their mother tongue, as most Bhumijas have shifted to one of the regional dominant languages. Thus the language is considered an extremely endangered language.
Lodhi is a Munda language, or dialect cluster, of India. Kharia Thar is only spoken by one quarter of ethnic Lodhi in Orissa. However, while admitting that Lodhi is related to Sora, a Munda language, Ethnologue classifies it as Indic (Bengali–Assamese), and it is considered a variety of Hindi in the Indian census. It may be that there are both Munda and Indic varieties subsumed under the name Lodhi.
Turi is an endangered Munda language of India that is closely related to Mundari. It is spoken by only half a percent of ethnic Turi, the rest having shifted to Sadri in Jharkhand, Mundari in West Bengal, and Odia in Odisha. The Turi are classified as a Scheduled Caste in Jharkhand.

Balrampur-Ramanujganj district is a district in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. It came into existence on 17 January 2012 and was formerly part of Surguja district. Balrampur-Ramanujganj district is the northernmost district of Chhattisgarh. Its seat is Balrampur.
Surgujia is an Indo-Aryan language variety spoken in Chhattisgarh. It belongs to the Eastern Hindi group. It is considered as a dialect of Chattisgarhi language.
References
- ↑ "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues - 2011". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2018-07-07.
- Anderson, Gregory D.S (ed). 2008. The Munda languages. Routledge Language Family Series 3.New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-32890-X.
- Bahl, Kali Charan. 1962. Korwa Lexicon. m.s., 148pp.
- Singh, Bageshwar and Ajit K. Danda. 1986. The Kodaku of Surguja. Calcutta: Anthropological Survey of India.