Related Research Articles

Papua New Guinea is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, it shares its only land border with Indonesia to the west and it is directly adjacent to Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).
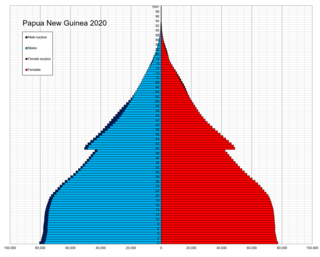
The indigenous population of Papua New Guinea is one of the most heterogeneous in the world. Papua New Guinea has several thousand separate communities, most with only a few hundred people. Divided by language, customs, and tradition, some of these communities have engaged in endemic warfare with their neighbors for centuries. It is the second most populous nation in Oceania, with a total population estimated variously as being between 9.5 and 10.1 million inhabitants.

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.

The Papuan languages are the non-Austronesian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands in Indonesia, Solomon Islands, and East Timor by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship.
The Border or Upper Tami languages are an independent family of Papuan languages in Malcolm Ross's version of the Trans–New Guinea proposal.
The Yuat languages are an independent family of five Papuan languages spoken along the Yuat River in East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. They are an independent family in the classification of Malcolm Ross, but are included in Stephen Wurm's Sepik–Ramu proposal. However, Foley and Ross could find no lexical or morphological evidence that they are related to the Sepik or Ramu languages.
The Kol language is a language spoken in eastern New Britain island, Papua New Guinea. There are about 4000 speakers in Pomio District of East New Britain Province, mostly on the southern side of New Britain island.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 840 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ."
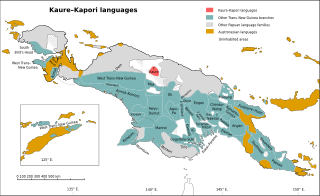
The Kaure–Kosare or Nawa River languages are a small family spoken along the Nawa River in West Papua, near the northern border with Papua New Guinea. The languages are Kaure and Kosare.
The Timor–Alor–Pantar (TAP) languages are a family of languages spoken in Timor, Kisar, and the Alor archipelago in Southern Indonesia. It is the westernmost Papuan language family, and one of two such outlier families in east Nusantara.

The Teberan languages are a well established family of Papuan languages that Stephen Wurm (1975) grouped with the Pawaia language as a branch of the Trans–New Guinea phylum.
The Kwalean or Humene–Uare languages are a small family of Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea. They are classified within the Southeast Papuan branch of Trans–New Guinea.

The Southeast Papuan or Papuan Peninsula languages are a group of half a dozen small families of Papuan languages in the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea that are part of the Trans–New Guinea (TNG) phylum.
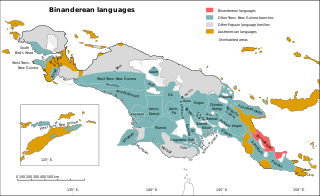
The Greater Binanderean or Guhu-Oro languages are a language family spoken along the northeast coast of the Papuan Peninsula – the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea – and appear to be a recent expansion from the north. They were classified as a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages by Stephen Wurm (1975) and Malcolm Ross (2005), but removed by Timothy Usher (2020). The Binandere family proper is transparently valid; Ross connected it to the Guhu-Semane isolate based on pronominal evidence, and this has been confirmed by Smallhorn (2011). Proto-Binanderean has been reconstructed in Smallhorn (2011).
The Demta–Sentani languages form a language family of coastal Indonesian Papua near the Papua New Guinea border.

The Tama languages are a small family of three clusters of closely related languages of northern Papua New Guinea, spoken just to the south of Nuku town in eastern Sandaun Province. They are classified as subgroup of the Sepik languages. Tama is the word for 'man' in the languages that make up this group.
Rigo District is a district of Central Province in Papua New Guinea. It is one of the four administrative districts that make up the province.
Deraa.k.a.Mangguar and Kamberataro (Komberatoro) is a Senagi language of Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. In Papua New Guinea, it is primarily spoken in Kamberataro village, Amanab Rural LLG, Sandaun Province.
Papua New Guinean Sign Language (PNGSL) is a sign language originating from Papua New Guinea. The standardised form of PNGSL was made an official language of Papua New Guinea in 2015.
Proto-Trans–New Guinea is the reconstructed proto-language ancestral to the Trans–New Guinea languages. Reconstructions have been proposed by Malcolm Ross and Andrew Pawley.