VBScript is an Active Scripting language developed by Microsoft that is modeled on Visual Basic. It allows Microsoft Windows system administrators to generate powerful tools for managing computers with error handling, subroutines, and other advanced programming constructs. It can give the user complete control over many aspects of their computing environment.
In computing and telecommunication, an escape character is a character which invokes an alternative interpretation on subsequent characters in a character sequence. An escape character is a particular case of metacharacters. Generally, the judgment of whether something is an escape character or not depends on context.
In human–computer interaction and user interface design, cut, copy and paste are related commands that offer an interprocess communication technique for transferring data through a computer's user interface. The cut command removes the selected data from its original position, while the copy command creates a duplicate; in both cases the selected data is kept in a temporary storage device called the clipboard. The data in the clipboard is later inserted in the position where the paste command is issued. The data is available to any application supporting the feature, thus allowing easy data transfer between applications.

Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET) is a multi-paradigm, object-oriented programming language, implemented on the .NET Framework. Microsoft launched VB.NET in 2002 as the successor to its original Visual Basic language. Although the ".NET" portion of the name was dropped in 2005, this article uses "Visual Basic [.NET]" to refer to all Visual Basic languages released since 2002, in order to distinguish between them and the classic Visual Basic. Along with Visual C#, it is one of the two main languages targeting the .NET framework.
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97. The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.
Extensible Application Markup Language is a declarative XML-based language developed by Microsoft that is used for initializing structured values and objects. It is available under Microsoft's Open Specification Promise. The acronym originally stood for Extensible Avalon Markup Language, Avalon being the code-name for Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF).
A control element in a graphical user interface is an element of interaction, such as a button or a scroll bar. Controls are software components that a computer user interacts with through direct manipulation to read or edit information about an application. User interface libraries such as Windows Presentation Foundation, GTK+, and Cocoa, contain a collection of controls and the logic to render these.
Windows Forms (WinForms) is a graphical (GUI) class library included as a part of Microsoft .NET Framework or Mono Framework, providing a platform to write rich client applications for desktop, laptop, and tablet PCs. While it is seen as a replacement for the earlier and more complex C++ based Microsoft Foundation Class Library, it does not offer a comparable paradigm and only acts as a platform for the user interface tier in a multi-tier solution.
A double-click is the act of pressing a computer mouse button twice quickly without moving the mouse. Double-clicking allows two different actions to be associated with the same mouse button. It was developed by Bill Atkinson of Apple Computer for their Lisa project. Often, single-clicking selects an object, while a double-click executes the function associated with that object. Following a link in a web browser is accomplished with only a single click, requiring the use of a second mouse button, "click and hold" delay, or modifier key to gain access to actions other than following the link. On touchscreens, the double-click is called "double-tap"; it's not used as much as double-click, but typically it functions as a zoom feature.

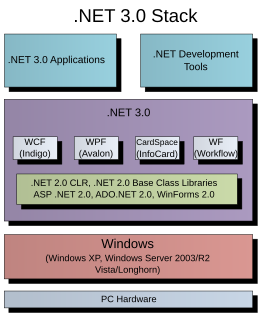
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) is a graphical subsystem by Microsoft for rendering user interfaces in Windows-based applications. WPF, previously known as "Avalon", was initially released as part of .NET Framework 3.0 in 2006. WPF uses DirectX and attempts to provide a consistent programming model for building applications. It separates the user interface from business logic, and resembles similar XML-oriented object models, such as those implemented in XUL and SVG.
Microsoft WinHelp is a proprietary format for online help files that can be displayed by the Microsoft Help browser winhelp.exe or winhlp32.exe. The file format is based on Rich Text Format (RTF). It remained a popular Help platform from Windows 3.0 platform through Windows XP. WinHelp was removed in Windows Vista purportedly to discourage software developers from using the obsolete format and encourage use of newer help formats.
Microsoft Active Accessibility (MSAA) is an Application Programming Interface (API) for user interface accessibility. MSAA was introduced as a platform add-on to Microsoft Windows 95 in 1997. MSAA is designed to help Assistive Technology (AT) products interact with standard and custom user interface (UI) elements of an application, as well as to access, identify, and manipulate an application's UI elements. AT products work with MSAA enabled applications in order to provide better access for individuals who have physical or cognitive difficulties, impairments, or disabilities. Some examples of AT products are screen readers for users with limited sight, on screen keyboards for users with limited physical access, or narrators for users with limited hearing. MSAA can also be used for automated testing tools, and computer-based training applications.

Windows Aero is a design language introduced in the Windows Vista operating system. The changes made in the Aero interface affected many elements of the Windows interface, including the incorporation of a new look, along with changes in interface guidelines reflecting appearance, layout, and the phrasing and tone of instructions and other text in applications.

Windows XP visual styles are customizations of the graphical user interface of Windows XP. "Luna", "Royale", "Zune", and "Embedded" are codenames of the official visual styles designed for Windows XP by Microsoft. Since Windows XP, themes include the choice of visual styles as well. By default, "Luna" is preinstalled on Windows XP Home and Professional editions, "Royale" is preinstalled on Windows XP Media Center Edition and "Embedded" is preinstalled Windows Embedded Standard 2009 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009. In addition to the preinstalled visual styles, Microsoft has released additional ones for download. Third parties have also released visual styles, though these require modification of core Windows components to work. Visual styles are compatible with all Windows XP editions.
An HTML Application (HTA) is a Microsoft Windows program whose source code consists of HTML, Dynamic HTML, and one or more scripting languages supported by Internet Explorer, such as VBScript or JScript. The HTML is used to generate the user interface, and the scripting language is used for the program logic. An HTA executes without the constraints of the internet browser security model; in fact, it executes as a "fully trusted" application.

Windows Speech Recognition (WSR) is a speech recognition component developed by Microsoft for the Windows Vista operating system that enables the use of voice commands to control the desktop user interface; dictate text in electronic documents and email; navigate websites; perform keyboard shortcuts; and to operate the mouse cursor. It also supports the creation of custom macros to perform additional tasks.

Microsoft Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft. It is used to develop computer programs, as well as websites, web apps, web services and mobile apps. Visual Studio uses Microsoft software development platforms such as Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation, Windows Store and Microsoft Silverlight. It can produce both native code and managed code.
The Text Object Model (TOM) is a Microsoft Windows API that provides developers with object-based rich text manipulation interfaces. It is implemented through COM, and can be accessed through Microsoft Word or additionally through the RichEdit controls that normally ship with Windows.
typeof, alternately also typeOf, and TypeOf, is an operator provided by several programming languages to determine the data type of a variable. This is useful when constructing programs that must accept multiple types of data without explicitly specifying the type.









