A file manager or file browser is a computer program that provides a user interface to manage files and folders. The most common operations performed on files or groups of files include creating, opening, renaming, copying, moving, deleting and searching for files, as well as modifying file attributes, properties and file permissions. Folders and files may be displayed in a hierarchical tree based on their directory structure.

A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard.
AppleScript is a scripting language created by Apple Inc. that facilitates automated control of Mac applications. First introduced in System 7, it is currently included in macOS in a package of automation tools. The term AppleScript may refer to the scripting language, to a script written in the language, or to the macOS Open Scripting Architecture that underlies the language.

The Finder is the default file manager and graphical user interface shell used on all Macintosh operating systems. Described in its "About" window as "The Macintosh Desktop Experience", it is responsible for the launching of other applications, and for the overall user management of files, disks, and network volumes. It was introduced with the Macintosh 128K—the first Macintosh computer—and also exists as part of GS/OS on the Apple IIGS. It was rewritten completely with the release of Mac OS X in 2001.
In computing, a window is a graphical control element. It consists of a visual area containing some of the graphical user interface of the program it belongs to and is framed by a window decoration. It usually has a rectangular shape that can overlap with the area of other windows. It displays the output of and may allow input to one or more processes.
The Dock is a prominent feature of the graphical user interface of macOS. It is used to launch applications and to switch between running applications. The Dock is also a prominent feature of macOS's predecessor NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP operating systems. The earliest known implementations of a dock are found in operating systems such as RISC OS and NeXTSTEP. iOS has its own version of the Dock for the iPhone and iPod Touch, as does iPadOS for the iPad.
In computing, the desktop metaphor is an interface metaphor which is a set of unifying concepts used by graphical user interfaces to help users interact more easily with the computer. The desktop metaphor treats the computer monitor as if it is the top of the user's desk, upon which objects such as documents and folders of documents can be placed. A document can be opened into a window, which represents a paper copy of the document placed on the desktop. Small applications called desk accessories are also available, such as a desk calculator or notepad, etc.

File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application and default desktop environment that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems, as well as user interface elements such as the taskbar and desktop.

Mission Control is a feature of the macOS operating system. Dashboard, Exposé, and Spaces were combined and renamed Mission Control in 2011 with the release of Mac OS X 10.7 Lion. Exposé was first previewed on June 23, 2003, at the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference as a feature of the then forthcoming Mac OS X 10.3 Panther.

Aqua is the graphical user interface, design language and visual theme of Apple's macOS and iOS operating systems. It was originally based on the theme of water, with droplet-like components and a liberal use of reflection effects and translucency. Its goal is to "incorporate color, depth, translucence, and complex textures into a visually appealing interface" in macOS applications. At its introduction, Steve Jobs noted that "... it's liquid, one of the design goals was when you saw it you wanted to lick it".
A graphical widget in a graphical user interface is an element of interaction, such as a button or a scroll bar. Controls are software components that a computer user interacts with through direct manipulation to read or edit information about an application. User interface libraries such as Windows Presentation Foundation, Qt, GTK, and Cocoa, contain a collection of controls and the logic to render these.

The FOX toolkit is an open-source, cross-platform widget toolkit, i.e. a library of basic elements for building a graphical user interface (GUI). FOX stands for Free Objects for X.

System Settings is an application included with macOS. It allows users to modify various system settings, which are divided into separate Preference Panes. The System Settings application was introduced in the first version of Mac OS X to replace the control panels found in earlier versions of the Mac operating system.

Control Panel is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides the ability to view and change system settings. It consists of a set of applets that include adding or removing hardware and software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking settings. Additional applets are provided by third parties, such as audio and video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools.
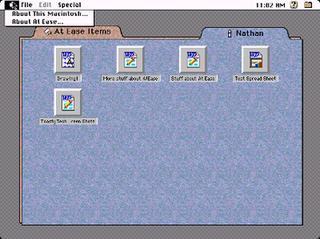
At Ease was an alternative to the Macintosh desktop developed by Apple Computer in the early 1990s for the classic Mac OS. It provided a simple environment for new Macintosh users and young children to help them to work without supervision. At Ease replaces the Finder desktop, providing a simple tabbed panel-oriented graphical user interface in which applications and documents are represented by icons on large buttons. Aside from its security features, its interface and basic functionality is very similar to the Packard Bell Navigator.
On the classic Mac OS, extensions were small pieces of code that extended the system's functionality. They were run initially at start-up time, and operated by a variety of mechanisms, including trap patching and other code modifying techniques. Initially an Apple developer hack, extensions became the standard way to provide a modular operating system. Large amounts of important system services such as the TCP/IP network stacks and USB and FireWire support were optional components implemented as extensions. The phrase "system extension" later came to encompass faceless background applications as well.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of notable file managers.
The Start menu is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, providing a means of opening programs and performing other functions in the Windows shell. The Start menu, and the Taskbar on which it appears, were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard.

In computing, the trash, also known by other names such as trash bin, dustbin, wastebasket, and similar names, is a graphical user interface desktop metaphor for temporary storage for files set aside by the user for deletion, but which are not yet permanently erased. This lifts the burden from the user of having to be highly careful while selecting files for deletion, since a trash bin provides a grace period to reverse unwanted deletions. The concept and name is part of Mac operating systems; a similar implementation is called the Recycle Bin in Microsoft Windows, and other operating systems use other names, sometimes ending with "-bin".













