
A context menu is a menu in a graphical user interface (GUI) that appears upon user interaction, such as a right-click mouse operation. A context menu offers a limited set of choices that are available in the current state, or context, of the operating system or application to which the menu belongs. Usually the available choices are actions related to the selected object. From a technical point of view, such a context menu is a graphical control element.

A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard.

The history of the graphical user interface, understood as the use of graphic icons and a pointing device to control a computer, covers a five-decade span of incremental refinements, built on some constant core principles. Several vendors have created their own windowing systems based on independent code, but with basic elements in common that define the WIMP "window, icon, menu and pointing device" paradigm.

A pointing device is a human interface device that allows a user to input spatial data to a computer. CAD systems and graphical user interfaces (GUI) allow the user to control and provide data to the computer using physical gestures by moving a hand-held mouse or similar device across the surface of the physical desktop and activating switches on the mouse. Movements of the pointing device are echoed on the screen by movements of the pointer and other visual changes. Common gestures are point and click and drag and drop.
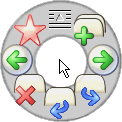
In user interface design, a pie menu or radial menu is a circular context menu where selection depends on direction. It is a graphical control element. A pie menu is made of several "pie slices" around an inactive center and works best with stylus input, and well with a mouse. Pie slices are drawn with a hole in the middle for an easy way to exit the menu.
In computing, a window is a graphical control element. It consists of a visual area containing some of the graphical user interface of the program it belongs to and is framed by a window decoration. It usually has a rectangular shape that can overlap with the area of other windows. It displays the output of and may allow input to one or more processes.
In computing, an icon is a pictogram or ideogram displayed on a computer screen in order to help the user navigate a computer system. The icon itself is a quickly comprehensible symbol of a software tool, function, or a data file, accessible on the system and is more like a traffic sign than a detailed illustration of the actual entity it represents. It can serve as an electronic hyperlink or file shortcut to access the program or data. The user can activate an icon using a mouse, pointer, finger, or voice commands. Their placement on the screen, also in relation to other icons, may provide further information to the user about their usage. In activating an icon, the user can move directly into and out of the identified function without knowing anything further about the location or requirements of the file or code.

In computer graphical user interfaces, drag and drop is a pointing device gesture in which the user selects a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, it can be used to invoke many kinds of actions, or create various types of associations between two abstract objects.
Point and click are one of the actions of a computer user moving a pointer to a certain location on a screen (pointing) and then pressing a button on a mouse or other pointing device (click). An example of point and click is in hypermedia, where users click on hyperlinks to navigate from document to document. User interfaces, for example graphical user interfaces, are sometimes described as "point-and-click interfaces", often to suggest that they are very easy to use, requiring that the user simply point to indicate their wishes. Describing software this way implies that the interface can be controlled solely through a pointing device with little or no input from the keyboard, as with many graphical user interfaces.
The taskbar is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, displaying and facilitating switching between running programs. The taskbar and the associated Start Menu were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on Great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard.

In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an early form of human–computer interaction, before the advent of bitmapped displays and modern conventional graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Like modern GUIs, they can use the entire screen area and may accept mouse and other inputs. They may also use color and often structure the display using box-drawing characters such as ┌ and ╣. The modern context of use is usually a terminal emulator.

In human–computer interaction, WIMP stands for "windows, icons, menus, pointer", denoting a style of interaction using these elements of the user interface. Other expansions are sometimes used, such as substituting "mouse" and "mice" for menus, or "pull-down menu" and "pointing" for pointer.
A graphical widget in a graphical user interface is an element of interaction, such as a button or a scroll bar. Controls are software components that a computer user interacts with through direct manipulation to read or edit information about an application. User interface libraries such as Windows Presentation Foundation, Qt, GTK, and Cocoa, contain a collection of controls and the logic to render these.

A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They work in conjunction with the underlying graphical system that provides required functionality—support for graphics hardware, pointing devices, and a keyboard—and are often written and created using a widget toolkit.
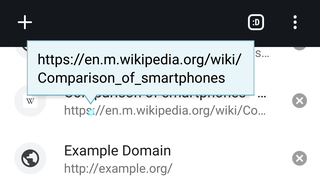
The tooltip, also known as infotip or hint, is a common graphical user interface (GUI) element in which, when hovering over a screen element or component, a text box displays information about that element, such as a description of a button's function, what an abbreviation stands for, or the exact absolute time stamp over a relative time. In common practice, the tooltip is displayed continuously as long as the user hovers over the element or the text box provided by the tool. It is sometimes possible for the mouse to hover within the text box provided to activate a nested tooltip, and this can continue to any depth, often with multiple text boxes overlapped.
In human–computer interaction, a cursor is an indicator used to show the current position on a computer monitor or other display device that will respond to input.
The Windows shell is the graphical user interface for the Microsoft Windows operating system. Its readily identifiable elements consist of the desktop, the taskbar, the Start menu, the task switcher and the AutoPlay feature. On some versions of Windows, it also includes Flip 3D and the charms. In Windows 10, the Windows Shell Experience Host interface drives visuals like the Start Menu, Action Center, Taskbar, and Task View/Timeline. However, the Windows shell also implements a shell namespace that enables computer programs running on Windows to access the computer's resources via the hierarchy of shell objects. "Desktop" is the top object of the hierarchy; below it there are a number of files and folders stored on the disk, as well as a number of special folders whose contents are either virtual or dynamically created. Recycle Bin, Libraries, Control Panel, This PC and Network are examples of such shell objects.

Workbench is the desktop environment and graphical file manager of AmigaOS developed by Commodore International for their Amiga line of computers. Workbench provides the user with a graphical interface to work with file systems and launch applications. It uses a workbench metaphor for representing file system organisation.

A mouse button is an electric switch on a computer mouse which can be pressed (“clicked”) to select or interact with an element of a graphical user interface. Mouse buttons are most commonly implemented as miniature snap-action switches.
A software widget is a relatively simple and easy-to-use software application or component made for one or more different software platforms.













