Related Research Articles

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signaling.

Pepsin A is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aspergillopepsin I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
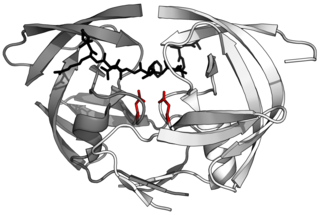
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.
The mannose receptor is a C-type lectin primarily present on the surface of macrophages, immature dendritic cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, but is also expressed on the surface of skin cells such as human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes. It is the first member of a family of endocytic receptors that includes Endo180 (CD280), M-type PLA2R, and DEC-205 (CD205).
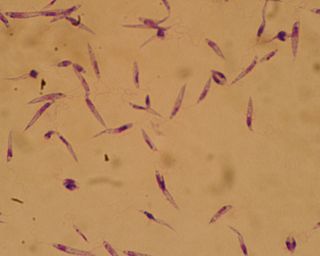
Leishmania major is a species of parasite found in the genus Leishmania, and is associated with the disease zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis. L. major is an intracellular pathogen which infects the macrophages and dendritic cells of the immune system. Though Leishmania species are found on every continent aside from Antarctica, Leishmania major is found only in the Eastern Hemisphere, specifically in Northern Africa, the Middle East, Northwestern China, and Northwestern India.
Kexin is a prohormone-processing protease, specifically a yeast serine peptidase, found in the budding yeast. It catalyzes the cleavage of -Lys-Arg- and -Arg-Arg- bonds to process yeast alpha-factor pheromone and killer toxin precursors. The human homolog is PCSK4. It is a family of subtilisin-like peptidases. Even though there are a few prokaryote kexin-like peptidases, all kexins are eukaryotes. The enzyme is encoded by the yeast gene KEX2, and usually referred to in the scientific community as Kex2p. It shares structural similarities with the bacterial protease subtilisin. The first mammalian homologue of this protein to be identified was furin. In the mammal, kexin-like peptidases function in creating and regulating many differing proproteins.

Fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP-alpha) also known as prolyl endopeptidase FAP is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FAP gene.
Nepenthesin is an aspartic protease of plant origin that has so far been identified in the pitcher secretions of Nepenthes and in the leaves of Drosera peltata. It is similar to pepsin, but differs in that it also cleaves on either side of Asp residues and at Lys┼Arg. While more pH and temperature stable than porcine pepsin A, it is considerably less stable in urea or guanidine hydrochloride. It is the only known protein with such a stability profile.
Lysyl endopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Peptidase Do is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pestivirus NS3 polyprotein peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Gingipain R is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Rhizopuspepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Endothiapepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Mucorpepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease.
Serralysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Magnolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The PA clan is the largest group of proteases with common ancestry as identified by structural homology. Members have a chymotrypsin-like fold and similar proteolysis mechanisms but can have identity of <10%. The clan contains both cysteine and serine proteases. PA clan proteases can be found in plants, animals, fungi, eubacteria, archaea and viruses.
References
- ↑ Button LL, McMaster WR (February 1988). "Molecular cloning of the major surface antigen of leishmania". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 167 (2): 724–9. doi:10.1084/jem.167.2.724. PMC 2188825 . PMID 3346625.
- ↑ Bouvier J, Bordier C, Vogel H, Reichelt R, Etges R (December 1989). "Characterization of the promastigote surface protease of Leishmania as a membrane-bound zinc endopeptidase". Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology. 37 (2): 235–45. doi:10.1016/0166-6851(89)90155-2. PMID 2608099.
- ↑ Chaudhuri G, Chaudhuri M, Pan A, Chang KP (May 1989). "Surface acid proteinase (gp63) of Leishmania mexicana. A metalloenzyme capable of protecting liposome-encapsulated proteins from phagolysosomal degradation by macrophages". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 264 (13): 7483–9. PMID 2708373.
- ↑ Bouvier J, Schneider P, Etges R, Bordier C (October 1990). "Peptide substrate specificity of the membrane-bound metalloprotease of Leishmania". Biochemistry. 29 (43): 10113–9. doi:10.1021/bi00495a015. PMID 2271643.