Related Research Articles

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signaling.
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.
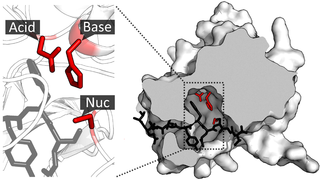
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes. An acid-base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence.
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 2 (ADAM-TS2) also known as procollagen I N-proteinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS2 gene.

Bone morphogenetic protein 1, also known as BMP1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BMP1 gene. There are seven isoforms of the protein created by alternate splicing.
In molecular biology, the Signal Peptide Peptidase (SPP) is a type of protein that specifically cleaves parts of other proteins. It is an intramembrane aspartyl protease with the conserved active site motifs 'YD' and 'GxGD' in adjacent transmembrane domains (TMDs). Its sequences is highly conserved in different vertebrate species. SPP cleaves remnant signal peptides left behind in membrane by the action of signal peptidase and also plays key roles in immune surveillance and the maturation of certain viral proteins.
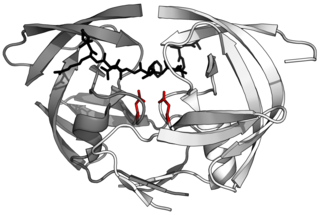
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.

Thermolysin is a thermostable neutral metalloproteinase enzyme produced by the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus thermoproteolyticus. It requires one zinc ion for enzyme activity and four calcium ions for structural stability. Thermolysin specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds containing hydrophobic amino acids. However thermolysin is also widely used for peptide bond formation through the reverse reaction of hydrolysis. Thermolysin is the most stable member of a family of metalloproteinases produced by various Bacillus species. These enzymes are also termed 'neutral' proteinases or thermolysin -like proteinases (TLPs).
Kexin is a prohormone-processing protease, specifically a yeast serine peptidase, found in the budding yeast. It catalyzes the cleavage of -Lys-Arg- and -Arg-Arg- bonds to process yeast alpha-factor pheromone and killer toxin precursors. The human homolog is PCSK4. It is a family of subtilisin-like peptidases. Even though there are a few prokaryote kexin-like peptidases, all kexins are eukaryotes. The enzyme is encoded by the yeast gene KEX2, and usually referred to in the scientific community as Kex2p. It shares structural similarities with the bacterial protease subtilisin. The first mammalian homologue of this protein to be identified was furin. In the mammal, kexin-like peptidases function in creating and regulating many differing proproteins.

Procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCOLCE gene.
The Kazal domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain usually indicative of serine protease inhibitors. However, kazal-like domains are also seen in the extracellular part of agrins, which are not known to be protease inhibitors.
Signal peptidase I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ulp1 peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Rhizopuspepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease.
Procollagen C-endopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Pacifastin is a family of serine proteinase inhibitors found in arthropods. Pacifastin inhibits the serine peptidases trypsin and chymotrypsin.

Glutamic proteases are a group of proteolytic enzymes containing a glutamic acid residue within the active site. This type of protease was first described in 2004 and became the sixth catalytic type of protease. Members of this group of protease had been previously assumed to be an aspartate protease, but structural determination showed it to belong to a novel protease family. The first structure of this group of protease was scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the active site of which contains a catalytic dyad, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), which give rise to the name eqolisin. This group of proteases are found primarily in pathogenic fungi affecting plant and human.
Asparagine peptide lyase are one of the seven groups in which proteases, also termed proteolytic enzymes, peptidases, or proteinases, are classified according to their catalytic residue. The catalytic mechanism of the asparagine peptide lyases involves an asparagine residue acting as nucleophile to perform a nucleophilic elimination reaction, rather than hydrolysis, to catalyse the breaking of a peptide bond.

The sedolisin family of peptidases are a family of serine proteases structurally related to the subtilisin (S8) family. Well-known members of this family include sedolisin ("pseudomonalisin") found in Pseudomonas bacteria, xanthomonalisin ("sedolisin-B"), physarolisin as well as animal tripeptidyl peptidase I. It is also known as sedolysin or serine-carboxyl peptidase. This group of enzymes contains a variation on the catalytic triad: unlike S8 which uses Ser-His-Asp, this group runs on Ser-Glu-Asp, with an additional acidic residue Asp in the oxyanion hole.
References
- ↑ "Procollagen peptidase". 7 October 2019.
- ↑ Lapière CM, Lenaers A, Kohn LD (December 1971). "Procollagen peptidase: an enzyme excising the coordination peptides of procollagen". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 68 (12): 3054–8. Bibcode:1971PNAS...68.3054L. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3054 . PMC 389589 . PMID 5289249.