
Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya. It is the namesake member of the papain-like protease family.
Gluten exorphins are a group of opioid peptides formed during the digestion of the gluten protein. These peptides work as external regulators for gastrointestinal movement and hormonal release. The breakdown of gliadin, a polymer of wheat proteins, creates amino acids that stop the gluten epitopes from entering the immune system to activate inflammatory reactions. During this process, gluten does not fully break down, thus increasing the presence of gluten exorphins. Because of this, researchers think this is what might lead to various diseases.
An exopeptidase is any peptidase that catalyzes the cleavage of the terminal peptide bond; the process releases a single amino acid, dipeptide or a tripeptide from the peptide chain. Depending on whether the amino acid is released from the amino or the carboxy terminal, an exopeptidase is further classified as an aminopeptidase or a carboxypeptidase, respectively. Thus, an aminopeptidase, an enzyme in the brush border of the small intestine, will cleave a single amino acid from the amino terminal, whereas carboxypeptidase, which is a digestive enzyme present in pancreatic juice, will cleave a single amino acid from the carboxylic end of the peptide.
Neurophysin I is a carrier protein with a size of 10 KDa and contains 90 to 97 amino acids. It is a cleavage product of preprooxyphysin. It is a neurohypophysial hormone that is transported in vesicles with oxytocin, the other cleavage product, along axons, from magnocellular neurons of the hypothalamus to the posterior lobe of the pituitary. Although it is stored in neurosecretory granules with oxytocin and released with oxytocin, its biological action is unclear.
A tetrapeptide is a peptide, classified as an oligopeptide, since it only consists of four amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Many tetrapeptides are pharmacologically active, often showing affinity and specificity for a variety of receptors in protein-protein signaling. Present in nature are both linear and cyclic tetrapeptides (CTPs), the latter of which mimics protein reverse turns which are often present on the surface of proteins and druggable targets. Tetrapeptides may be cyclized by a fourth peptide bond or other covalent bonds.
omega-Grammotoxin SIA (ω-grammotoxin SIA) is a protein toxin that inhibits P, Q, and N voltage-gated calcium channels (Ca2+ channels) in neurons.

Slotoxin is a peptide from Centruroides noxius Hoffmann scorpion venom. It belongs to the short scorpion toxin superfamily.

Grammotoxin is a toxin in the venom of the tarantula Grammostola spatulata. It is a protein toxin that inhibits P-, Q- and N-type voltage-gated calcium channels in neurons. Grammotoxin is also known as omega-grammotoxin SIA.

Neurophysin II is a carrier protein with a size of 19,687.3 Da and is made up of a dimer of two virtually identical chains of amino acids. Neurophysin II is a cleavage product of the AVP gene. It is a neurohypophysial hormone that is transported in vesicles with vasopressin, the other cleavage product, along axons, from magnocellular neurons of the hypothalamus to the posterior lobe of the pituitary. Although it is stored in neurosecretory granules with vasopressin and released with vasopressin into the bloodstream, its biological action is unclear. Neurophysin II is also known as a stimulator of prolactin secretion.
Tazarotene-induced gene-1 (TIG1) is a protein which has been implicated as a putative tumor suppressor. It is structurally similar to the protein latexin, which has also been shown to demonstrate some tumor suppression activity. TIG1 is thought to be a transmembrane protein, and its mechanism of tumor suppression is largely unknown.
Big dynorphin is an endogenous opioid peptide of the dynorphin family that is composed of both dynorphin A and dynorphin B. Big dynorphin has the amino acid sequence: Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys-Trp-Asp-Asn-Gln-Lys-Arg-Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Gln-Phe-Lys-Val-Val-Thr. It has nociceptive and anxiolytic-like properties, as well as effects on memory in mice.
Salmon calcitonin (sCT) is the type of calcitonin hormone found in salmon.
Taspoglutide is a former experimental drug, a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist, that was under investigation for treatment of type 2 diabetes and being codeveloped by Ipsen and Roche.
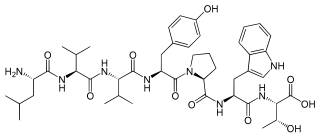
Spinorphin is an endogenous, non-classical opioid peptide of the hemorphin family first isolated from the bovine spinal cord (hence the prefix spin-) and acts as a regulator of the enkephalinases, a class of enzymes that break down endogenous the enkephalin peptides. It does so by inhibiting the enzymes aminopeptidase N (APN), dipeptidyl peptidase III (DPP3), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), and neutral endopeptidase (NEP). Spinorphin is a heptapeptide and has the amino acid sequence Leu-Val-Val-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Thr (LVVYPWT). It has been observed to possess antinociceptive, antiallodynic, and anti-inflammatory properties. The mechanism of action of spinorphin has not been fully elucidated (i.e., how it acts to inhibit the enkephalinases), but it has been found to act as an antagonist of the P2X3 receptor, and as a weak partial agonist/antagonist of the FP1 receptor.

Tynorphin is a synthetic opioid peptide which is a potent and competitive inhibitor of the enkephalinase class of enzymes which break down the endogenous enkephalin peptides. It specifically inactivates dipeptidyl aminopeptidase III (DPP3) with very high efficacy, but also inhibits neutral endopeptidase (NEP), aminopeptidase N (APN), and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to a lesser extent. It has a pentapeptide structure with the amino acid sequence Val-Val-Tyr-Pro-Trp (VVYPW).
Leumorphin, also known as dynorphin B1–29, is a naturally occurring endogenous opioid peptide. Derived as a proteolytic cleavage product of residues 226-254 of prodynorphin, leumorphin is a nonacosapeptide and has the sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Gln-Phe-Lys-Val-Val-Thr-Arg-Ser-Gln-Glu-Asp-Pro-Asn-Ala-Tyr-Ser-Gly-Glu-Leu-Phe-Asp-Ala. It can be further reduced to dynorphin B and dynorphin B-14 by pitrilysin metallopeptidase 1, an enzyme of the endopeptidase family. Leumorphin behaves as a potent and selective κ-opioid receptor agonist, similarly to other endogenous opioid peptide derivatives of prodynorphin.
Modified GRF (1-29) often abbreviated as mod GRF (1-29), originally known as tetrasubstituted GRF (1-29), is a term used to identify a 29 amino acid peptide analogue of growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), a releasing hormone of growth hormone (GH). It is a modified version of the shortest fully functional fragment of GHRH, often referred to as growth hormone releasing factor (1-29), and also known by its standardized name, sermorelin.
An endopeptidase inhibitor is a drug that inhibits one or more endopeptidase enzymes. Endopeptidases are one of two types of proteases, the other being exopeptidases. Endopeptidases cleave peptide bonds of non-terminal amino acids, whereas exopeptidases break terminal bonds, resulting in the release of a single amino acid or dipeptide from the peptide chain.
An exopeptidase inhibitor is a drug that inhibits one or more exopeptidase enzymes. Exopeptidases are one of two types of proteases, the other being endopeptidases. Exopeptidases cleave peptide bonds of terminal amino acids, resulting in the release of a single amino acid or dipeptide from the peptide chain, whereas endoeptidases break non-terminal bonds.
DKK-SP1 is one of the many neurotoxins present in the scorpion Mesobuthus martensii. This toxin inhibits the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.8.






