
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.
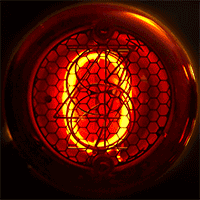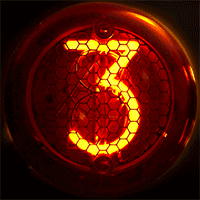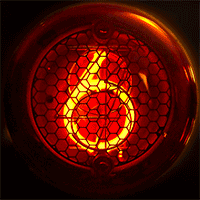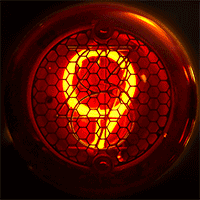
A Nixie tube, or cold cathode display, is an electronic device used for displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.

A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a filament. A cathode may be considered "cold" if it emits more electrons than can be supplied by thermionic emission alone. It is used in gas-discharge lamps, such as neon lamps, discharge tubes, and some types of vacuum tube. The other type of cathode is a hot cathode, which is heated by electric current passing through a filament. A cold cathode does not necessarily operate at a low temperature: it is often heated to its operating temperature by other methods, such as the current passing from the cathode into the gas.

The ANITA Mark VII and ANITA Mark VIII calculators were launched simultaneously in late 1961 as the world's first all-electronic desktop calculators. Designed and built by the Bell Punch Co. in Britain, and marketed through its Sumlock Comptometer division, they used vacuum tubes and cold-cathode switching tubes in their logic circuits and nixie tubes for their numerical displays.

A neon lamp is a miniature gas-discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes. When sufficient voltage is applied and sufficient current is supplied between the electrodes, the lamp produces an orange glow discharge. The glowing portion in the lamp is a thin region near the cathode; the larger and much longer neon signs are also glow discharges, but they use the positive column which is not present in the ordinary neon lamp. Neon glow lamps were widely used as indicator lamps in the displays of electronic instruments and appliances. They are still sometimes used for their electrical simplicity in high-voltage circuits.

A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a display device once commonly used on consumer electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens.

A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays.

Daniel McFarlan Moore was an American electrical engineer and inventor. He developed a novel light source, the "Moore lamp", and a business that produced them in the early 1900s. The Moore lamp was the first commercially viable light-source based on gas discharges instead of incandescence; it was the predecessor to contemporary neon lighting and fluorescent lighting. In his later career Moore developed a miniature neon lamp that was extensively used in electronic displays, as well as vacuum tubes that were used in early television systems.

An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance. Discrete circuits are made of individual electronic components that only perform one function each as packaged, which are known as discrete components, although strictly the term discrete component refers to such a component with semiconductor material such as individual transistors.

Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode at each end, filled with one of a number of gases at low pressure. A high potential of several thousand volts applied to the electrodes ionizes the gas in the tube, causing it to emit colored light. The color of the light depends on the gas in the tube. Neon lights were named for neon, a noble gas which gives off a popular orange light, but other gases and chemicals called phosphors are used to produce other colors, such as hydrogen (purple-red), helium, carbon dioxide (white), and mercury (blue). Neon tubes can be fabricated in curving artistic shapes, to form letters or pictures. They are mainly used to make dramatic, multicolored glowing signage for advertising, called neon signs, which were popular from the 1920s to 1960s and again in the 1980s.

A digital clock displays the time digitally, as opposed to an analogue clock.

Light tubes are structures that transmit or distribute natural or artificial light for the purpose of illumination and are examples of optical waveguides.
Electrically operated display devices have developed from electromechanical systems for display of text, up to all-electronic devices capable of full-motion 3D color graphic displays. Electromagnetic devices, using a solenoid coil to control a visible flag or flap, were the earliest type, and were used for text displays such as stock market prices and arrival/departure display times. The cathode ray tube was the workhorse of text and video display technology for several decades until being displaced by plasma, liquid crystal (LCD), and solid-state devices such as thin-film transistors (TFTs), LEDs and OLEDs. With the advent of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), integrated circuit (IC) chips, microprocessors, and microelectronic devices, many more individual picture elements ("pixels") could be incorporated into one display device, allowing graphic displays and video.
A text display is an electronic alphanumeric display device that is mainly or only capable of showing text, or extremely limited graphic characters. This includes electromechanical split-flap displays, vane displays, and flip-disc displays; all-electronic liquid-crystal displays, incandescent eggcrate displays, LED displays, and vacuum fluorescent displays; and even electric nixie tubes.

A red dot sight is a common classification for a non-magnifying reflector sight that provides an illuminated red dot to the user as a point of aim. A standard design uses a red light-emitting diode (LED) at the focus of collimating optics, which generates a dot-style illuminated reticle that stays in alignment with the firearm the sight is attached to, regardless of eye position.

A reflector sight or reflex sight is an optical sight that allows the user to look through a partially reflecting glass element and see an illuminated projection of an aiming point or some other image superimposed on the field of view. These sights work on the simple optical principle that anything at the focus of a lens or curved mirror will appear to be sitting in front of the viewer at infinity. Reflector sights employ some form of "reflector" to allow the viewer to see the infinity image and the field of view at the same time, either by bouncing the image created by lens off a slanted glass plate, or by using a mostly clear curved glass reflector that images the reticle while the viewer looks through the reflector. Since the reticle is at infinity, it stays in alignment with the device to which the sight is attached regardless of the viewer's eye position, removing most of the parallax and other sighting errors found in simple sighting devices.

A timeline of United States inventions (1890–1945) encompasses the innovative advancements of the United States within a historical context, dating from the Progressive Era to the end of World War II, which have been achieved by inventors who are either native-born or naturalized citizens of the United States. Copyright protection secures a person's right to the first-to-invent claim of the original invention in question, highlighted in Article I, Section 8, Clause 8 of the United States Constitution which gives the following enumerated power to the United States Congress:
To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries.
The following timeline tables list the discoveries and inventions in the history of electrical and electronic engineering.

The first Light-Emitting Diode (LED) was created in 1927 by Russian inventor Oleg Losev, and used silicon carbide as a semiconductor. However, electroluminescence as a phenomenon was discovered twenty years earlier by the English experimenter Henry Joseph Round of Marconi Labs, using the same crystal and a cat's-whisker detector. Despite having distributed his report in Soviet, German and British scientific journals, Losev's LED found no practical use for several decades, partly due to the very inefficient light-producing properties the semiconductor used.


















