This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2013) |
This is a list of hurricanes in Barbados in the Lesser Antilles, Caribbean.
Contents
Date : Storm name : Distance from storm eye-wall.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2013) |
This is a list of hurricanes in Barbados in the Lesser Antilles, Caribbean.
Date : Storm name : Distance from storm eye-wall.
September 2, 1951: Hurricane Dog passes 60 miles to the north.
October 5, 1954: Hurricane Hazel passes 45 miles to the south. [1]
September 22, 1955: Hurricane Janet passes to the south-east as a Category 2 hurricane. [2]
August 30, 1958: Hurricane Ella passes 50 miles to the north.
July 10, 1960: Hurricane Abby passes close to Barbados as a tropical depression.
September 25, 1963: Hurricane Edith passes 30 miles to the north as a Category 2 hurricane.
August 28, 1965: Hurricane Betsy passes 40 miles to the northeast as a tropical depression.
September 29, 1966: Tropical Storm Judith passes 20 miles to the north.
September 6, 1967: Hurricane Beulah passes 25 miles to the north as a tropical depression.
August 20, 1970: Tropical Storm Dorothy passes 45 miles to the north as a tropical storm. [3]
September 13, 1971: Hurricane Irene-Olivia passes 50 miles to the south as a tropical depression. [4]
August 19, 1971: Tropical Storm Chloe passes 40 miles to the north as a tropical depression. [5]
October 2, 1974: Hurricane Gertrude passes 55 miles to the south as a tropical storm. [6]
August 29, 1979: Hurricane David passes 75 miles to the north-east.
June 23, 1979: Tropical Storm Ana passes 60 miles to the north as a tropical storm. [7]
August 4, 1980: Hurricane Allen passes just north of the island. [8]
September 8, 1986: Tropical Storm Danielle passes 65 miles to the south.
September 21, 1987 Hurricane Emily passes 50 miles to the south.
September 9, 1988 Hurricane Gilbert passes 75 miles to the northeast.
August 14, 1993: Tropical Storm Cindy passes 60 miles to the north.
September 9, 1994: Tropical Storm Debby passes 20 miles to the north.
September 14, 1995: Hurricane Marilyn passes 50 miles to the northeast.
August 25, 1995 Hurricane Iris passes 70 miles to the north.
October 4, 2001 Hurricane Iris passes 25 miles to the south.
October 7, 2001: Tropical Storm Jerry passes 30 miles to the southwest.
September 23, 2002: Hurricane Lili passes 45 miles to the south.
August 4, 2004: Tropical Storm Bonnie passes 20 miles to the north.
September 7, 2004: Hurricane Ivan passes to the south as a tropical storm.
August 17, 2007: Hurricane Dean passes 65 miles to the north.
September 1, 2007: Hurricane Felix passes 70 miles to the south.

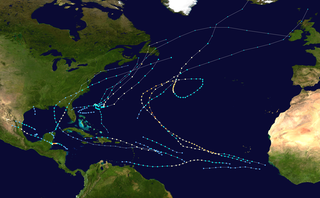
The 2000 Atlantic hurricane season was a fairly active hurricane season, but featured the latest first named storm in a hurricane season since 1992. The hurricane season officially began on June 1, and ended on November 30. It was slightly above average due to a La Niña weather pattern although most of the storms were weak. It was also the only season to have two of the storms affect Ireland. The first cyclone, Tropical Depression One, developed in the southern Gulf of Mexico on June 7 and dissipated after an uneventful duration. However, it would be almost two months before the first named storm, Alberto, formed near Cape Verde; Alberto also dissipated with no effects on land. Several other tropical cyclones—Tropical Depression Two, Tropical Depression Four, Chris, Ernesto, Nadine, and an unnamed subtropical storm—did not impact land. Five additional storms—Tropical Depression Nine, Florence, Isaac, Joyce, and Leslie—minimally affected land areas.
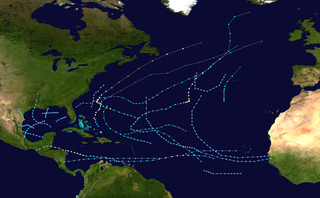
The 1978 Atlantic hurricane season was a slightly above average hurricane season in terms of number of named storms. Eleven tropical cyclones were named in all, and five of these became hurricanes; two of the five became a major hurricane. This was also the last Atlantic hurricane season to use an all-female naming list. The season officially began on June 1, 1978, and ended on November 30, 1978. These dates, adopted by convention, denote the period in each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic basin. However, the formation of subtropical or tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as shown by the formation of an unnamed subtropical storm on January 18.

The 1982 Atlantic hurricane season was an extremely inactive Atlantic hurricane season with five named tropical storms and one subtropical storm. Two storms became hurricanes, one of which reached major hurricane status. The season officially began on June 1, 1982, and lasted until November 30, 1982. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. Activity started early with Hurricane Alberto forming on the first day of the season. Alberto threatened the Southwestern Florida coast as a tropical storm, meadering offshore in the southeastern Gulf of Mexico and causing 23 fatalities in Cuba. The next system, a subtropical storm, formed later in June and affected the same area as Alberto, causing $10 million in damage.

The 1984 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active since 1971, though the season was below average in hurricanes and major hurricanes. It officially began on June 1, 1984, and lasted until November 30, 1984. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The 1984 season was an active one in terms of named storms, but most of them were weak and stayed at sea. Most of the cyclones tracked through the northwest subtropical Atlantic west of the 50th meridian to near the Eastern coast of the United States between mid-August and early October. The most damaging storm was Hurricane Klaus, which caused $152 million (1984 dollars) in damage in Puerto Rico. Hurricane Diana was the first hurricane to strike a nuclear power plant without incident; it was also the first major hurricane to strike the U.S. East Coast in nearly 20 years. Also of note was Hurricane Lili, which lasted well after the official end of the season. It was downgraded from a named storm on December 24. Damage overall from the tropical cyclones in 1984 totaled $228.7 million. Unusually, no hurricanes developed from tropical waves in 1984, which usually are the source of the strongest storms in an Atlantic hurricane season.

Hurricane Klaus was a minimal Atlantic hurricane that dropped heavy rainfall across the Lesser Antilles in October 1990. The eleventh tropical cyclone and sixth hurricane of the 1990 Atlantic hurricane season, Klaus developed from a tropical wave on October 3 a short distance east of Dominica. It drifted northwestward, and quickly intensified to attain hurricane status on October 5. Though its closest approach to the Lesser Antilles was within 12 miles (19 km), the strongest winds remained to its northeast due to strong wind shear, which caused Klaus to steadily weaken. After deteriorating into a tropical depression, Klaus briefly restrengthened over the Bahamas before dissipating on October 9 under the influence of developing tropical storm, Marco.
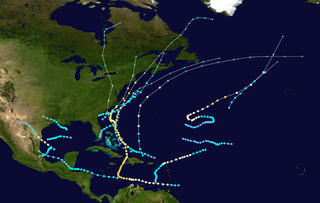
The 1954 Atlantic hurricane season was an above-average Atlantic hurricane season in terms of named storms, with 16 forming. Overall, the season resulted in $751.6 million in damage, the most of any season at the time. The season officially began on June 15, and nine days later the first named storm developed. Hurricane Alice developed in the Gulf of Mexico and moved inland along the Rio Grande, producing significant precipitation and record flooding that killed 55 people. Activity was slow until late August; only Barbara, a minimal tropical storm, developed in July. In the span of two weeks, hurricanes Carol and Edna followed similar paths before both striking New England as major hurricanes. The latter became the costliest hurricane in Maine's history.

The 2006 Atlantic hurricane season was the least active in the basin since 1997, with nine named storms as well as an additional unnamed tropical storm identified by the National Hurricane Center. 2006 was the first season since 2001 in which no hurricanes made landfall in the United States, and was the first since 1994 in which no tropical cyclones formed during October. Following the intense activity of 2003, 2004, and 2005, forecasters predicted that the 2006 season would be only slightly less active. Instead, it turned out to be a below average season, as activity was slowed by a rapidly forming moderate El Niño event, the presence of the Saharan Air Layer over the tropical Atlantic, and the steady presence of a robust secondary high-pressure area to the Azores High centered on Bermuda. There were no tropical cyclones after October 2.

The 1951 Atlantic hurricane season was the first hurricane season in which tropical cyclones were officially named by the United States Weather Bureau. The season officially started on June 15, when the United States Weather Bureau began its daily monitoring for tropical cyclone activity; the season officially ended on November 15. It was the first year since 1937 in which no hurricanes made landfall on the United States; as Hurricane How was the only tropical storm to hit the nation, the season had the least tropical cyclone damage in the United States since the 1939 season. As in the 1950 season, names from the Joint Army/Navy Phonetic Alphabet were used to name storms this season.

The 1949 Atlantic hurricane season was the last season that tropical cyclones were not publicly labeled by the United States Weather Bureau. It officially began on June 15, and lasted until November 15. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The first storm, a tropical depression, developed in the northern Gulf of Mexico on August 14. The final system, Tropical Storm Sixteen, dissipated in the southwestern Caribbean Sea on November 5. It was a fairly active season, featuring 16 tropical storms and seven hurricanes. Two of these strengthened into major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale.

Hurricane Alice is the only known Atlantic hurricane to span two calendar years and one of only two named Atlantic tropical cyclones, along with Tropical Storm Zeta of 2005, to do so. The twelfth tropical cyclone and the eighth hurricane of the 1954 Atlantic hurricane season, Alice developed on December 30, 1954, from a trough of low pressure in the central Atlantic Ocean in an area of unusually favorable conditions. The storm moved southwestward and gradually strengthened to reach hurricane status. After passing through the Leeward Islands on January 2, 1955, Alice reached peak winds of 90 mph (140 km/h) before encountering cold air and turning to the southeast. It dissipated on January 6 over the southeastern Caribbean Sea.

The 1975 Pacific hurricane season officially started May 15, 1975, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1975, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1975. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeast Pacific Ocean.

Tropical Storm Chantal was a North Atlantic tropical cyclone that moved across the Caribbean Sea in August 2001. The fourth depression and third named storm of the 2001 Atlantic hurricane season, Chantal developed from a tropical wave on August 14 in the tropical Atlantic Ocean. It tracked rapidly westward for much of its duration, and after degenerating into a tropical wave, it passed through the Windward Islands. Chantal reached a peak intensity of 70 mph (110 km/h) twice in the Caribbean Sea, and each time it was anticipated to attain hurricane status; however, wind shear and later land interaction prevented strengthening to hurricane status. On August 21 Chantal, moved ashore near the border of Mexico and Belize, before dissipating on the next day.

The 1987 Atlantic hurricane season was a below-average hurricane season that was limited by an ongoing El Niño. The season officially began on June 1, 1987, and lasted until November 30, 1987, although activity began on May 24 when a tropical depression developed 400 mi (640 km) east of the central Bahamas. The June through November dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The first cyclone to attain tropical storm status was an unnamed tropical storm which formed on August 9, nearly a month later than usual. The final storm of the year, Tropical Depression Fourteen, merged with a weak extratropical low on November 4. The season marked the first year tropical storm watches and warnings were issued; previously, gale watches and warnings were used for tropical storms, and this season was one of only a few seasons with no deaths in the United States; the last time this happened was in the 1981 season.

The 1987 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual Atlantic hurricane season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was a below-average season, having fewer named storms than in a normal year, that resulted in little impact throughout the Atlantic basin; the United States recorded no hurricane-related fatalities, making the 1987 season the fourth to do so since 1976. The season officially began on June 1, 1987 and ended November 30, 1987. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most systems form. Even so, a pre-season storm, Tropical Depression One, led to the season's starting on May 25. Storm activity ended several weeks early; the final storm of the season, Tropical Depression Fourteen, dissipated on November 4.

The 2012 Atlantic hurricane season was the final year in a string of three consecutive very active seasons since 2010, with 19 tropical storms. The 2012 season was also a costly one in terms of property damage, mostly due to Hurricane Sandy. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates that conventionally delimit the period during each year in which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean. However, Alberto, the first named system of the year, developed on May 19 – the earliest date of formation since Subtropical Storm Andrea in 2007. A second tropical cyclone, Beryl, developed later that month. This was the first occurrence of two pre-season named storms in the Atlantic basin since 1951. It moved ashore in North Florida on May 29 with winds of 65 mph (105 km/h), making it the strongest pre-season storm to make landfall in the Atlantic basin. This season marked the first time since 2009 where no tropical cyclones formed in July. Another record was set by Hurricane Nadine later in the season; the system became the fourth-longest-lived tropical cyclone ever recorded in the Atlantic, with a total duration of 22.25 days. The final storm to form, Tony, dissipated on October 25 – however, Hurricane Sandy, which formed before Tony, became extratropical on October 29.

The 2010 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was one of the most active Atlantic hurricane seasons since record keeping began in 1851 as 19 named storms formed. The season officially began on June 1, 2010, and ended on November 30, 2010, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin. The first storm to form was Hurricane Alex, on June 25; and the last to dissipate was Hurricane Tomas, on November 7.

Hurricane Tomas was a moderately powerful late-season tropical cyclone which is the latest Atlantic hurricane on record in the calendar year to strike the Windward Islands. The nineteenth named storm and twelfth hurricane of the 2010 Atlantic hurricane season, Tomas developed from a tropical wave east of the Windward Islands on October 29. Quickly intensifying into a hurricane, it moved through the Windward Islands and passed over Saint Lucia. After reaching Category 2 status on the Saffir–Simpson scale, Tomas quickly weakened to a tropical storm in the central Caribbean Sea, due to strong wind shear and dry air. Tomas later reintensified into a hurricane near the Windward passage.
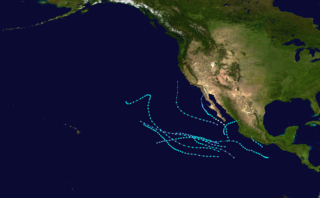
The 1965 Pacific hurricane season officially started May 15, 1965, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1965, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1965. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeast Pacific Ocean. A total of ten systems were observed. The most notable storm was Tropical Storm Hazel, which killed six people in Mexico.