Related Research Articles

Kashmir is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompasses a larger area that includes the India-administered territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, the Pakistan-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, and the Chinese-administered territories of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract.

K2, at 8,611 metres (28,251 ft) above sea level, is the second-highest mountain on Earth, after Mount Everest at 8,849 metres (29,032 ft). It lies in the Karakoram range, partially in the Gilgit-Baltistan region of Pakistan-administered Kashmir and partially in the China-administered Trans-Karakoram Tract in the Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County of Xinjiang.

The Karakoram is a mountain range in the Kashmir region spanning the border of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwestern extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the jurisdiction of Gilgit-Baltistan, which is controlled by Pakistan. Its highest peak, K2, is located in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. It begins in the Wakhan Corridor (Afghanistan) in the west, encompasses the majority of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan and extends into Ladakh and Aksai Chin.

Ladakh is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India and China since 1959. Ladakh is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east, the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh to the south, both the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir and the Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan to the west, and the southwest corner of Xinjiang across the Karakoram Pass in the far north. It extends from the Siachen Glacier in the Karakoram range to the north to the main Great Himalayas to the south. The eastern end, consisting of the uninhabited Aksai Chin plains, is claimed by the Indian Government as part of Ladakh, but has been under Chinese control.

Baltistan also known as Baltiyul or Little Tibet, is a mountainous region in the Pakistani-administered territory of Gilgit-Baltistan and constitutes an northern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947. It is located near the Karakoram and borders Gilgit to the west, China's Xinjiang to the north, Indian-administered Ladakh to the southeast, and the Indian-administered Kashmir Valley to the southwest. The average altitude of the region is over 3,350 metres (10,990 ft). Baltistan is largely administered under the Baltistan Division.

Skardu is a city located in Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. Skardu serves as the capital of Skardu District and the Baltistan Division. It is situated at an average elevation of nearly 2,500 metres above sea level in the Skardu Valley, at the confluence of the Indus and Shigar rivers. The city is an important gateway to the eight-thousanders of the nearby Karakoram mountain range. The Indus River running through the region separates the Karakoram from the Ladakh Range.

The Trans-Karakoram Tract, also known as the Shaksgam Tract, is an area of approximately 5,200 km2 (2,000 sq mi) north of the Karakoram watershed, including the Shaksgam valley. The tract is administered by China as part of its Taxkorgan and Yecheng counties in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. Although the Shaksgam tract was originally under the control of India following the accession of Jammu and Kashmir to India in 1947, Pakistan took control of the region after the First India-Pakistan War and subsequently ceded it to China in 1963 through the Sino-Pakistan Agreement, and a border based on actual ground positions was recognized as the international border by China and Pakistan. The Shaksgam Tract, along with the entire Kashmir region, is claimed by India. Further, New Delhi has never accepted the China-Pakistan boundary pact, asserting that Islamabad "unlawfully" attempted to cede the area to Beijing.

Leh district is a district in Indian-administered Ladakh in the disputed Kashmir-region. Ladakh is an Indian-administered union territory. With an area of 45,110 km2, it is the second largest district in the country, second only to Kutch. It is bounded on the north by Gilgit-Baltistan's Kharmang and Ghanche districts and Xinjiang's Kashgar Prefecture and Hotan Prefecture, to which it connects via the historic Karakoram Pass. Aksai Chin and Tibet are to the east, Kargil district to the west, and Lahul and Spiti to the south. The district headquarters is in Leh. It lies between 32 and 36 degree north latitude and 75 to 80 degree east longitude.

Chilas is a city in Pakistani-administered Gilgit–Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. It is the divisional capital of Diamer Division and is located on the Indus River. It is part of the Silk Road, connected by the Karakoram Highway and N-90 National Highway to Islamabad and Peshawar in the southwest, via Hazara and Malakand divisions of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. To the north, Chilas connects to the cities of Tashkurgan and Kashgar in Xinjiang, China, via Gilgit, Aliabad, Sust, and the Khunjerab Pass.

Ghanche District is a district of Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. It is the eastern-most district of Gilgit-Baltistan. It is the coldest place within Pakistan as it is situated on the "third pole", with temperatures reaching below -20 °C in the winter. The Khaplu Valley and the Hushe Valley form the gateway for the great Baltoro Muztagh, the subrange of the Karakoram Mountains that includes the mighty peaks of K2, Broad Peak, the Gasherbrums and Masherbrum ,all of which are also included in the Skardu District).

The Skardu District is a district of Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. Skardu District is bounded on the east by the Ghanche District, on the south by the Kharmang District, on the west by the Astore District, on the north-west by the Rondu District and on the north by the Shigar district. The district headquarters is the town of Skardu, which is also the division headquarters.

The Gilgit District is one of the 14 districts of Pakistan-administered territory of Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. The headquarters of the district is the town of Gilgit. At the 1998 census, the Gilgit District had a population of 243,324. The district includes Gilgit, the Bagrot Valley, Juglot, Danyore, Sultanabad, Naltar Peak, and the Nomal Valley. The highest peak in the district is Distaghil Sar 7,885 metres (25,869 ft), which is the seventh-highest peak in Pakistan and 19th highest in the world.

Astore District is a district of Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. It is one of the 14 districts of the Pakistani-administered territory of Gilgit−Baltistan. Its administrative headquarters are located at Eidgah in the Astore Valley. Astore District is bounded by Gilgit District to the north, Roundu District to the northeast, Skardu District to the east, Kharmang District to the southeast, Diamer District to the west, the Neelum District of Azad Jammu and Kashmir to the southwest, and the Bandipore District of Indian-administered disputed Kashmir region to the south.

Gilgit-Baltistan, formerly known as the Northern Areas, is a region administered by Pakistan as an administrative territory and consists of the northern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and between India and China since 1959. It borders Azad Kashmir to the south, the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the west, the Wakhan Corridor of Afghanistan to the north, the Xinjiang region of China to the east and northeast, and the Indian-administered union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the southeast.
Gilgit-Baltistan is an administrative territory of Pakistan that borders the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the west, Azad Kashmir to the southwest, Wakhan Corridor of Afghanistan to the northwest, the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China to the north, and the Indian-administered region of Jammu and Kashmir to the south and south-east.

Shigar District is a district in Gilgit-Baltistan area of Pakistan in the disputed Kashmir region. It is home to the world's second highest peak, K2, also known as Chhogori and Mount Godwin-Austen. The district is bounded on the north by the Nagar District, the Hunza District, and the Kashgar Prefecture of China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, on the south-east by the Ghanche District, on the south-west by the Rondu and Skardu districts, and on the west by the Gilgit District. Shigar District was established in 2015, prior to which it had been part of the Skardu District.
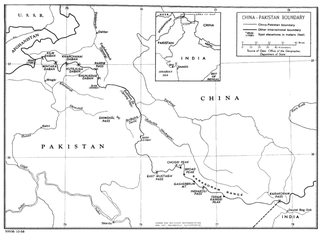
The China–Pakistan border is 596 kilometres (370 mi) and runs west–east from the tripoint with Afghanistan to the disputed tripoint with India in the vicinity of the Siachen Glacier. It traverses the Karakoram Mountains, one of the world's tallest mountain ranges. Hunza District,. Nagar District,Shigar District and Ghanche District in Gilgit-Baltistan administered by Pakistan, border Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County and Kargilik/Yecheng County in Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China.

Hunza District is a district of Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. It is one of the 14 districts of the Gilgit-Baltistan region. It was established in 2015 by the division of the Hunza–Nagar District in accordance with a government decision to establish more administrative units in Gilgit-Baltistan. The district headquarters is the town of Karimabad.
References
- ↑ "Mount Everest | Height, Location, Map, Facts, Climbers, & Deaths". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ↑ "K2". Encyclopedia Britannica. 18 November 2019. Retrieved 27 February 2021. Quote: "K2 is located in the Karakoram Range and lies partly in a Chinese-administered enclave of the Kashmir region within the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang, China, and partly in the Gilgit-Baltistan portion of Kashmir under the administration of Pakistan."
- ↑ "K2 | Geography & history". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ↑ "Kanchenjunga | mountain, Asia". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2021-03-11.
- ↑ "Nanga Parbat | mountain, Jammu and Kashmir INDIA". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2021-03-05.
- ↑ Wholly claimed by China as a part of its Tibet Autonomous Region; Actually Bhutan • China
- ↑ Strictly not in the Himalaya, but in the Nyenchen Tanglha Shan in East Tibet
- ↑ "Gyala Peri - Peakbagger.com". www.peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2021-03-05.
- ↑ Wholly claimed by Bhutan, but on the border of the Tibet Autonomous Region according to China.
- ↑ "Noijin Kangsang". PeakVisor. Retrieved 2021-03-05.
- ↑ Strictly not in the Himalaya, but in the Transhimalaya on the Tibetan plateau
- ↑ Godin, L.; et al. (1999). Allison MacFarlane; Rasoul B. Sorkhabi; Jay Quade (eds.). "High strain zone in the hanging wall of the Annapurna detachment". Himalaya and Tibet: Mountain Roots to Mountain Tops (328). GSA: 201.
- ↑ Kumar, Mayank (September 26, 2019). "Not Khardung La, This Is the World's Highest Motorable Pass. Yes, It's in India!".