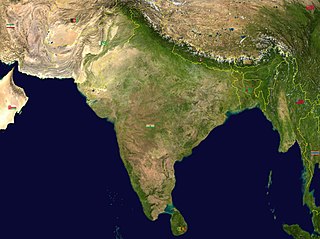
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of 3,287,263 square kilometres (1,269,219 sq mi). India measures 3,214 km (1,997 mi) from north to south and 2,933 km (1,822 mi) from east to west. It has a land frontier of 15,200 km (9,445 mi) and a coastline of 7,516.6 km (4,671 mi).

China is a country located in East Asia with an area of 9,596,960 km2 (3,705,410 sq mi). The exact land area can sometimes be challenged by border disputes, including those concerning Taiwan, Aksai Chin, the Trans-Karakoram Tract, the South China Sea Islands, the Senkaku Islands, and South Tibet. As sovereignty over Hong Kong and Macau were restored to China in 1997 and 1999, two special administrative regions were established under the One Country, Two Systems policy. The People's Republic of China is either the third or fourth largest country in the world, being either slightly larger or slightly smaller than the United States depending on how the area of the United States is measured.

The Himalayas, or Himalaya, are a mountain range in Asia separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding 7,200 m (23,600 ft) in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia is 6,961 m (22,838 ft) tall.

Saser Kangri is a mountain in India. It is the highest peak in the Saser Muztagh, the easternmost subrange of the Karakoram range. Sasir Kangri is located within Ladakh, the northernmost union territory in India.

Melungtse is the highest mountain of the Rolwaling Himal in the Himalayas.
K12 is the second highest peak in the Saltoro Mountains, a subrange of the Karakoram range in the Siachen region, in Ladakh, India. Its name comes from its designation given during the original survey of the Karakoram range. In 1984, an Indian army expedition under Colonel Prem Chand took hold of this peak, from the side of Siachen glacier by traversing from the west.

Blanca Peak is the fourth highest summit of the Rocky Mountains of North America and the U.S. state of Colorado. The ultra-prominent 14,351-foot (4,374 m) peak is the highest summit of the Sierra Blanca Massif, the Sangre de Cristo Range, and the Sangre de Cristo Mountains. The fourteener is located 9.6 miles (15.5 km) north by east of the Town of Blanca, on the drainage divide separating Rio Grande National Forest and Alamosa County from the Sangre de Cristo Land Grant and Costilla County. The summit is the highest point of both counties and the entire drainage basin of the Rio Grande. Below the steep North Face of Blanca Peak two live Glaciers once developed, until extinction sometime after 1903. North & South Blanca Glaciers were located at 37° 35N.,longitude 105° 28W. Blanca Peak is higher than any point in the United States east of its longitude.

Cloud Peak is the highest peak within the Bighorn Mountains in the U.S. state of Wyoming. It rises to an elevation of 13,171 feet (4,015 m) and provides onlookers with dramatic views and vistas. The mountain can be climbed most easily from the western side, accessed by either the Battle Park or West Tensleep trail-heads and is roughly 24 miles round-trip from both. The peak is located in the 189,000 acre (765 km²) Cloud Peak Wilderness within Bighorn National Forest. The northeast slope of Cloud Peak is a deep cirque which harbors Cloud Peak Glacier, the last active glacier in the Bighorn Mountains.

The Pat-kai (Pron:pʌtˌkaɪ) or Patkai Bum are a series of mountains in the Indo-Myanmar border falling in the north-eastern Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and Upper Burma region of Myanmar. They were created by the same tectonic processes that created the Himalayas in the Mesozoic. In Tai-Ahom language, Pat means to cut and Kai means chicken.

Geography of West Bengal, a state in eastern India, is diverse, of high peaks of Himalaya in the northern extremes to where Himalayas are in the north and sea is at the south, with both plains and plateaus covering the remaining region.
Darjeeling Himalayan hill region or Darjeeling Himalaya is the mountainous area on the north-western side of the state of West Bengal in India. This region belongs to the Eastern Himalaya range. The Darjeeling district except the Siliguri subdivision and the entire Kalimpong district constitute this region. It arises abruptly from the Terai region. The region slopes from a south to north direction. The river Teesta divides the region in two parts — the region to the east of Teesta and the region to the west of Teesta.

The state of Himachal Pradesh is spread over an area 55,673 km2 (21,495 sq mi) and is bordered by Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh on the north, Punjab on the southwest, Haryana on the south, Uttarakhand on the southeast, a small border with Uttar Pradesh in the south, and Tibet on the east. Entire Himachal Pradesh lies in the mountainous Himalaya region, rich in natural resources

The geographical region of Ladakh union territory is the highest altitude plateau region in India, incorporating parts of the Himalayan and Karakoram mountain ranges and the upper Indus River valley.
An ultra-prominent peak, or Ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) or more; it is also called a P1500. The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or from sea level if there is no higher peak. There are approximately 1,524 such peaks on Earth. Some well-known peaks, such as the Matterhorn and Eiger, are not Ultras because they are connected to higher mountains by high cols and therefore do not achieve enough topographic prominence.
Saipal is a mountain in the Himalayas of north-west Bajhang district in Nepal.

The Shan Hills, also known as Shan Highland, is a vast mountainous zone that extends through Yunnan to Myanmar and Thailand. The whole region is made up of numerous mountain ranges separated mostly by narrow valleys as well as a few broader intermontane basins. The ranges in the area are aligned in such a way that they link to the foothills of the Himalayas further to the northwest.

Noijin Kangsang is the highest peak of Lhagoi Kangri mountain range in the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. It lies between the Yarlung Tsangpo River, Yamdrok Lake and the Himalayas mountain range.
Lists of mountains can be organized by continent and more specifically by country and province/state:






















