Related Research Articles

Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 1867, acquired more businesses, and began branching out into military hardware and shipbuilding.
Westland Aircraft was a British aircraft manufacturer located in Yeovil, Somerset. Formed as a separate company by separation from Petters Limited just before the start of the Second World War, Westland had been building aircraft since 1915. During the war the company produced a number of generally unsuccessful designs, but their Lysander would serve as an important liaison aircraft with the Royal Air Force. After the war the company focused on helicopters, and was merged with several other British firms to create Westland Helicopters in 1961.

Yiewsley is a large suburban village in the London Borough of Hillingdon, England, 2 miles (3 km) south of Uxbridge, the borough's commercial and administrative centre. Yiewsley was a chapelry in the ancient parish of Hillingdon, Middlesex. The population of the ward was 12,979 at the 2011 Census.
PZL was the main Polish aerospace manufacturer of the interwar period, and a brand of their aircraft. Based in Warsaw between 1928 and 1939, PZL introduced a variety of well-regarded aircraft, most notably the PZL P.11 fighter, the PZL.23 Karaś light bomber, and the PZL.37 Łoś medium bomber.

America's manufacturers in World War II were engaged in the greatest military industrial effort in history. Aircraft companies went from building a handful of planes at a time to building them by the thousands on assembly lines. Aircraft manufacturing went from a distant 41st place among American industries to first place in less than five years.

Military production during World War II was the production or mobilization of arms, ammunition, personnel and financing by the belligerents of the war, from the occupation of Austria in early 1938 to the surrender and occupation of Japan in late 1945.

The Gloster Aircraft Company was a British aircraft manufacturer from 1917 to 1963.

Aeronca, contracted from Aeronautical Corporation of America, located in Middletown, Ohio, is a US manufacturer of engine components and airframe structures for commercial aviation and the defense industry, and a former aircraft manufacturer. From 1928 to 1951, the company was a major producer of general aviation aircraft, and also produced the engines for some of their early designs.

USS Drayton (DD-366) was a Mahan-class destroyer in the United States Navy before and during World War II. She was the second ship named for Captain Percival Drayton, a career naval officer who served during the American Civil War.
Arpin may refer to:

Heston Aerodrome was an airfield located to the west of London, England, operational between 1929 and 1947. It was situated on the border of the Heston and Cranford areas of Hounslow, Middlesex. In September 1938, the British Prime Minister, Neville Chamberlain, flew from Heston to Germany three times in two weeks for talks with Adolf Hitler, and returned to Heston from the Munich Conference with the paper referred to in his later "Peace for our time" speech from 10 Downing Street.
The Arpin A-1 was a two-seat low-wing monoplane which was powered by a single radial engine in pusher configuration, mounted behind the cabin between twin booms that carried the tail. An unconventional fixed tricycle undercarriage was fitted. Only one was built.

Government Aircraft Factories (GAF) was the name of an aircraft manufacturer owned by the Government of Australia. The primary factory was located at Fishermans Bend, a suburb of Melbourne in Victoria. It had its origins in the lead-up to World War II, during which it was known as the Department of Aircraft Production (DAP). In 1987, GAF was reorganized and renamed as Aerospace Technologies of Australia (ASTA) then privatised. ASTA was purchased by Rockwell International, that was in turn purchased by Boeing a few years later. ASTA subsequently formed the nucleus of Boeing Australia.
Cunliffe-Owen Aircraft was a British aircraft manufacturer of the World War II era. They were primarily a repair and overhaul shop, but also a construction shop for other companies' designs, notably the Supermarine Seafire. The company also undertook contract work for the Air Ministry, Lord Rootes, Shorts and Armstrong Siddeley worth £1.5 million. After the war, however, the company began to face financial difficulties and in February 1947 a request to Midland Bank to extend the company's overdraft was refused. In November of that year it became necessary to suspend production of the Concordia aircraft – upon which all the company's future hopes rested – and its financial collapse became inevitable.
The Nieuport & General Aircraft Company Ltd was a British aircraft manufacturer, established during the First World War to build French Nieuport aircraft under licence, which closed down in 1920.

London Air Park, also known as Hanworth Air Park, was a grass airfield in the grounds of Hanworth Park House, operational 1917–1919 and 1929–1947. It was on the southeastern edge of Feltham, now part of the London Borough of Hounslow. In the 1930s, it was best known as a centre for private flying, society events, visits by the Graf Zeppelin airship, and for aircraft manufacture by the Whitehead Aircraft Company during World War I and General Aircraft Limited (GAL) 1934–1949; in total over 1,650 aircraft were built here.
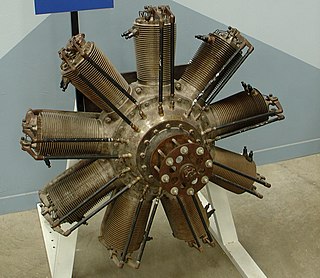
Clerget-Blin was a French precision engineering company formed in 1913 by the engineer and inventor Pierre Clerget and industrialist Eugène Blin. In 1939, the company was absorbed into the Groupe d'étude des moteurs à huile lourde, which was further merged into SNECMA in 1947.

The Great West Aerodrome, also known as Harmondsworth Aerodrome or Heathrow Aerodrome, was a grass airfield, operational between 1930 and 1944. It was on the southeast edge of the hamlet of Heathrow, in the parish of Harmondsworth. The Fairey Aviation Company owned and operated it, for assembly and flight testing of Fairey-manufactured aircraft. The area was to later be the site of London Heathrow Airport.

The 148th Infantry Brigade was an infantry brigade formation of the British Army that served in both the First and briefly in the Second World War as part of the 49th Infantry Division and disbanded after the war.

II Anti-Aircraft Corps was a high-level formation of Britain's Anti-Aircraft Command from 1940 to 1942. It defended the Midlands and North West of England and Wales during the Blitz and the middle years of the Second World War.
References
- ↑ "Company Registrations". Flight . 8 June 1939. p. 593.
- Gunston, Bill (1993). World Encyclopedia of Aircraft Manufacturers. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. p. 29.