
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid that acts as a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. As an extract, it is mainly used recreationally and often illegally for its euphoric and rewarding effects. It is also used in medicine by Indigenous South Americans for various purposes and rarely, but more formally, as a local anaesthetic or diagnostic tool by medical practitioners in more developed countries. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South America: Erythroxylum coca and E. novogranatense. After extraction from the plant, and further processing into cocaine hydrochloride, the drug is administered by being either snorted, applied topically to the mouth, or dissolved and injected into a vein. It can also then be turned into free base form, in which it can be heated until sublimated and then the vapours can be inhaled.

Kainate receptors, or kainic acid receptors (KARs), are ionotropic receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter glutamate. They were first identified as a distinct receptor type through their selective activation by the agonist kainate, a drug first isolated from the algae Digenea simplex. They have been traditionally classified as a non-NMDA-type receptor, along with the AMPA receptor. KARs are less understood than AMPA and NMDA receptors, the other ionotropic glutamate receptors. Postsynaptic kainate receptors are involved in excitatory neurotransmission. Presynaptic kainate receptors have been implicated in inhibitory neurotransmission by modulating release of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA through a presynaptic mechanism.

The metabotropic glutamate receptors, or mGluRs, are a type of glutamate receptor that are active through an indirect metabotropic process. They are members of the group C family of G-protein-coupled receptors, or GPCRs. Like all glutamate receptors, mGluRs bind with glutamate, an amino acid that functions as an excitatory neurotransmitter.

Vanoxerine is an investigational drug which is being evaluated for the treatment of heart arrhythmias and cocaine dependence. Vanoxerine is a piperazine derivative which has multiple pharmacological activities including acting as an dopamine reuptake inhibitor, serotonin transporter inhibitor, and as a blocker of the cardiac hERG repolarizing potassium channel (IKr).
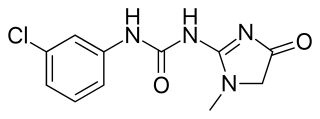
Fenobam is an imidazole derivative developed by McNeil Laboratories in the late 1970s as a novel anxiolytic drug with an at-the-time-unidentified molecular target in the brain. Subsequently, it was determined that fenobam acts as a potent and selective negative allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5, and it has been used as a lead compound for the development of a range of newer mGluR5 antagonists.
Cocaine dependence is a neurological disorder that is characterized by withdrawal symptoms upon cessation from cocaine use. It also often coincides with cocaine addiction which is a biopsychosocial disorder characterized by persistent use of cocaine and/or crack despite substantial harm and adverse consequences. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, classifies problematic cocaine use as a stimulant use disorder. The International Classification of Diseases, includes "Cocaine dependence" as a classification (diagnosis) under "Disorders due to use of cocaine".

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is an excitatory Gq-coupled G protein-coupled receptor predominantly expressed on the postsynaptic sites of neurons. In humans, it is encoded by the GRM5 gene.

Protein fosB, also known as FosB and G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 3 (G0S3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (FOSB) gene.

Tezampanel is a drug originally developed by Eli Lilly which acts as a competitive antagonist of the AMPA and kainate subtypes of the ionotropic glutamate receptor family, with selectivity for the GluR5 subtype of the kainate receptor. It has neuroprotective and anticonvulsant properties, the former of which may, at least in part, occur via blockade of calcium uptake into neurons.

2-Methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)pyridine (MPEP) is a research drug which was one of the first compounds found to act as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. After being originally patented as a liquid crystal for LCDs, it was developed by the pharmaceutical company Novartis in the late 1990s. It was found to produce neuroprotective effects following acute brain injury in animal studies, although it was unclear whether these results were purely from mGluR5 blockade as it also acts as a weak NMDA antagonist, and as a positive allosteric modulator of another subtype mGlu4, and there is also evidence for a functional interaction between mGluR5 and NMDA receptors in the same populations of neurons. It was also shown to produce antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animals, and to reduce the effects of morphine withdrawal, most likely due to direct interaction between mGluR5 and the μ-opioid receptor.

3-( ethynyl)pyridine (MTEP) is a research drug that was developed by Merck & Co. as a selective allosteric antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. Identified through structure-activity relationship studies on an older mGluR5 antagonist MPEP, MTEP has subsequently itself acted as a lead compound for newer and even more improved drugs.
Self-administration is, in its medical sense, the process of a subject administering a pharmacological substance to themself. A clinical example of this is the subcutaneous "self-injection" of insulin by a diabetic patient.

SIB-1757 is a drug used in scientific research which was one of the first compounds developed that acts as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. It has anti-hyperalgesia effects in animals. SIB-1757 along with other mGluR5 antagonists has been shown to have neuroprotective and hepatoprotective effects, and it is also used to study the role of the mGluR5 receptor in brain development.

CDPPB is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a positive allosteric modulator selective for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. It has antipsychotic effects in animal models, and mGluR5 modulators are under investigation as potential drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia, as well as other applications.

Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include substance use problems and problematic drug or alcohol use.

Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can alter brain function in synapses similar to natural rewards like food or falling in love in ways that perpetuate craving and weakens self-control for people with pre-existing vulnerabilities. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological factors that are implicated in the development of addiction. While mice given cocaine showed the compulsive and involuntary nature of addiction, for humans this is more complex, related to behavior or personality traits.
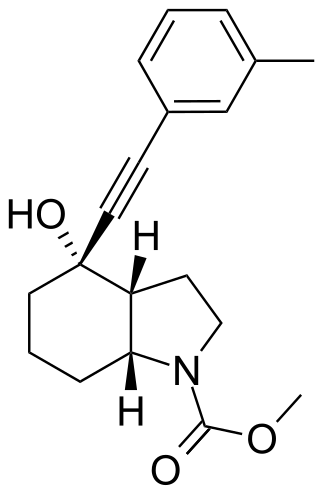
Mavoglurant (developmental code name AFQ-056) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of fragile X syndrome and other conditions. It exerts its effect as an antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5).
About 1 in 7 Americans reportedly suffered from active addiction to a particular substance. Addiction can cause physical, emotional and psychological harm to those affected by it. The American Society of Addiction Medicine defines addiction as "a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual's life experiences. People with addiction use substances or engage in behaviors that become compulsive and often continue despite harmful consequences."
Camilla Bellone is an Italian neuroscientist and assistant professor in the Department of Basic Neuroscience at the University of Geneva, in Switzerland. Bellone's laboratory explores the molecular mechanisms and neural circuits underlying social behavior and probes how defects at the molecular and circuit level give rise to psychiatric disease states such as Autism Spectrum Disorders.

AZD 9272 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. It was unsuccessful in human trials as an analgesic, but continues to be widely used in research especially as its radiolabelled forms.
















