
The Kingdom of the East Saxons, referred to as the Kingdom of Essex, was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex. From 825 Essex was ruled as part of a south-eastern kingdom of Essex, Kent, Sussex and Surrey. It was not until 860 that Essex was fully integrated into the crown of Wessex.

Mercia was one of the three main Anglic kingdoms founded after Sub-Roman Britain was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England.

Offa was King of Mercia, a kingdom of Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald. Offa defeated the other claimant, Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign, it is likely that he consolidated his control of Midland peoples such as the Hwicce and the Magonsæte. Taking advantage of instability in the kingdom of Kent to establish himself as overlord, Offa also controlled Sussex by 771, though his authority did not remain unchallenged in either territory. In the 780s he extended Mercian Supremacy over most of southern England, allying with Beorhtric of Wessex, who married Offa's daughter Eadburh, and regained complete control of the southeast. He also became the overlord of East Anglia and had King Æthelberht II of East Anglia beheaded in 794, perhaps for rebelling against him.

Æthelred was king of Mercia from 675 until 704. He was the son of Penda of Mercia and came to the throne in 675, when his brother, Wulfhere of Mercia, died from an illness. Within a year of his accession he invaded Kent, where his armies destroyed the city of Rochester. In 679 he defeated his brother-in-law, Ecgfrith of Northumbria, at the Battle of the Trent: the battle was a major setback for the Northumbrians, and effectively ended their military involvement in English affairs south of the Humber. It also permanently returned the Kingdom of Lindsey to Mercia's possession. However, Æthelred was unable to re-establish his predecessors' domination of southern Britain.

Wulfhere or Wulfar was King of Mercia from 658 until 675 AD. He was the first Christian king of all of Mercia, though it is not known when or how he converted from Anglo-Saxon paganism. His accession marked the end of Oswiu of Northumbria's overlordship of southern England, and Wulfhere extended his influence over much of that region. His campaigns against the West Saxons led to Mercian control of much of the Thames valley. He conquered the Isle of Wight and the Meon valley and gave them to King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons. He also had influence in Surrey, Essex, and Kent. He married Eormenhild, the daughter of King Eorcenberht of Kent.
The history of Herefordshire starts with a shire in the time of King Athelstan, and Herefordshire is mentioned in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle in 1051. The first Anglo-Saxon settlers, the 7th-century Magonsætan, were a sub-tribal unit of the Hwicce who occupied the Severn valley. The Magonsætan were said to be in the intervening lands between the Rivers Wye and Severn. The undulating hills of marl clay were surrounded by the Welsh mountains to the west; by the Malvern Hills to the east; by the Clent Hills of the Shropshire borders to the north, and by the indeterminate extent of the Forest of Dean to the south. The shire name first recorded in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle may derive from "Here-ford", Old English for "army crossing", the location for the city of Hereford.

Pengwern was a Brythonic settlement of sub-Roman Britain situated in what is now the English county of Shropshire, adjoining the modern Welsh border. It is regarded as possibly being the early seat of the kings of Powys before its establishment at Mathrafal, further west, but the theory that it was an early kingdom has also been postulated. Its precise location is uncertain.

Archenfield is the historic English name for an area of southern and western Herefordshire in England. Since the Anglo-Saxons took over the region in the 8th century, it has stretched between the River Monnow and River Wye, but it derives from the once much larger Welsh kingdom of Ergyng.

Æthelberht, also called Saint Ethelbert the King, was an eighth-century saint and a king of East Anglia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom which today includes the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. Little is known of his reign, which may have begun in 779, according to later sources, and very few of the coins he issued have been discovered. It is known from the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle that he was killed on the orders of Offa of Mercia in 794.

The Bishop of Lindsey was a prelate who administered an Anglo-Saxon diocese between the 7th and 11th centuries. The episcopal title took its name after the ancient Kingdom of Lindsey.
The Westerne were an Anglo-Saxon tribe, probably in western England. The name is a genitive plural and probably means "the westerners". They occur only in the Tribal Hidage, an early eighth-century catalogue of kingdoms and principalities produced in Mercia for the purposes of tax or tribute. Little is known about them, not even precisely where they were. Their position in the Tribal Hidage list suggests a location on the western fringe of the Mercian heartland and it is possible that they were associated with the Magonsaetan, who occupied the lands around Leominster and Hereford. There are very few Anglo-Saxon cemeteries from the area, which may indicate that Mercian rulers took over an existing British political region, possibly that of the Romano-British civitas of the Cornovii. The Tribal Hidage assessment for the Westerne ranks them alongside other minor kingdoms such as Lindsey, the Hwicce, the East Saxons and the South Saxons. It is likely that the area was ruled by an ealdorman, a senior noble representing the interest of the kings of Mercia.

Ergyng was a Welsh kingdom of the sub-Roman and early medieval period, between the 5th and 7th centuries. It was later referred to by the English as Archenfield.
Merewalh (sometimes given as Merwal or Merewald was a sub-king of the Magonsæte, a western cadet kingdom of Mercia thought to have been located in Herefordshire and Shropshire. Merewalh is thought to have lived in the mid to late 7th century, having acceded the throne during the time of Penda of Mercia, who, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle : implies, was his father. Though Merewalh's name implies that may have been a Briton. It is possible that Merewalh was a British leader, rewarded by Penda for his aid in war, perhaps at the Battle of Maserfelth. We know nothing of the origins of his first wife, who could have been a relative of Penda. A British origin might explain his control of lands around Leominster, where no evidence of early settlement by pagan Anglo-Saxons is to be found.

Saint Mildrith, also Mildthryth, Mildryth and Mildred,, was a 7th- and 8th-century Anglo-Saxon abbess of the Abbey at Minster-in-Thanet, Kent. She was declared a saint after her death, and, in 1030, her remains were moved to Canterbury.
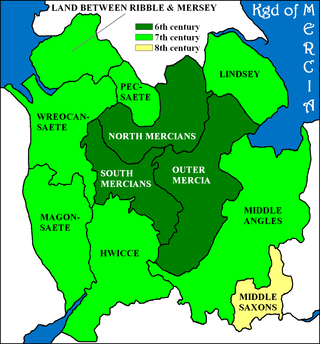
The Wreocensæte, sometimes anglicized as the Wrekinsets, were one of the peoples of Anglo-Saxon Britain. Their name approximates to "Wrekin-dwellers". It is also suggested that Wrexham also derived from Wreocensæte.

The Heptarchy were the seven petty kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England that flourished from the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain in the 5th century until they were consolidated in the 8th century into the four kingdoms of East Anglia, Mercia, Northumbria, and Wessex.
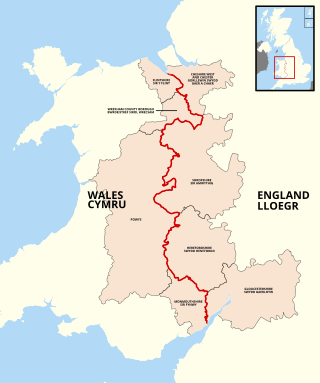
The England–Wales border, sometimes referred to as the Wales–England border or the Anglo-Welsh border, runs for 160 miles (260 km) from the Dee estuary, in the north, to the Severn estuary in the south, separating England and Wales.

Throughout its history the Kingdom of Mercia was a battleground between conflicting religious ideologies.
Repton Abbey was an Anglo-Saxon Benedictine abbey in Derbyshire, England. Founded in the 7th century, the abbey was a double monastery, a community of both monks and nuns. The abbey is noted for its connections to various saints and Mercian royalty; two of the thirty-seven Mercian Kings were buried within the abbey's crypt. The abbey was abandoned in 873, when Repton was overrun by the invading Great Heathen Army.














