The Book of Micah is the sixth of the twelve minor prophets in the Hebrew Bible. Ostensibly, it records the sayings of Micah, whose name is Mikayahu, meaning "Who is like Yahweh?", an 8th-century BCE prophet from the village of Moresheth in Judah.

Matthew 1 is the first chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. It contains two distinct sections. The first lists the genealogy of Jesus from Abraham to his legal father Joseph, husband of Mary, his mother. The second part, beginning at verse 18, provides an account of the virgin birth of Jesus Christ.

Matthew 1:22 is the twenty-second verse of the first chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. Joseph has just been spoken to in a dream by an angel.

Matthew 2 is the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. It describes the events after the birth of Jesus, the visit of the magi and the attempt by King Herod to kill the infant messiah, Joseph and his family's flight into Egypt, and their later return to live in Israel, settling in Nazareth.

Matthew 2:15 is the fifteenth verse of the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. In the verse, Joseph has taken Jesus and his family to Egypt to flee the wrath of King Herod.

Matthew 2:18 is the eighteenth verse of the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. Herod has ordered the Massacre of the Innocents and this verse quotes from the Book of Jeremiah to show that this event was predicted by the prophets.

Matthew 2:23 is the twenty-third verse of the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The young Jesus and the Holy Family have just returned from Egypt and in this verse are said to settle in Nazareth. This is the final verse of Matthew's infancy narrative.

Matthew 3:3 is the third verse of the third chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The verse occurs in the section introducing John the Baptist, and links him to messianic prophecies.
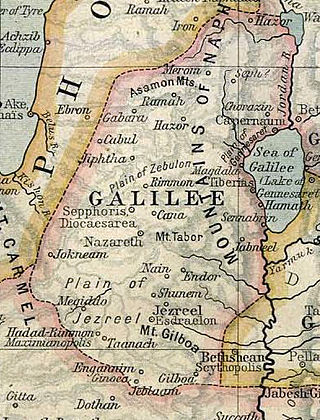
Matthew 4:14–15 are the fourteenth and fifteenth verses of the fourth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. In the previous verses Jesus returned to Galilee after hearing of the arrest of John the Baptist and then left Nazareth for Capernaum. These introduce and then contain the first portion of a quote from the Book of Isaiah showing how these movements were preordained by scripture.
Bible prophecy or biblical prophecy comprises the passages of the Bible that are claimed to reflect communications from God to humans through prophets. Christians usually consider the biblical prophets to have received revelations from God.

Matthew 24 is the twenty-fourth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It commences the Olivet Discourse or "Little Apocalypse" spoken by Jesus Christ, also described as the Eschatological Discourse, which continues into chapter 25. It contains Jesus' prediction of the destruction of the Temple in Jerusalem. Mark 13 and Luke 21 also cover the same material.

Matthew 7:15 is the fifteenth verse of the seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament and is part of the Sermon on the Mount. This verse begins the section warning against false prophets.

Matthew 21 is the twenty-first chapter in the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament section of the Christian Bible. Jesus triumphally or majestically arrives in Jerusalem and commences his final ministry before his Passion.

Matthew 8:17 is the 17th verse in the eighth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament.
The books of the New Testament frequently cite Jewish scripture to support the claim of the Early Christians that Jesus was the promised Jewish Messiah. Scholars have observed that few of these citations are actual predictions in context; the majority of these quotations and references are taken from the prophetic Book of Isaiah, but they range over the entire corpus of Jewish writings.
Matthew 27:9-10 are the ninth and tenth verses of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. These verses end the final story of Judas Iscariot, with a quotation from scripture showing how the events around his final days were predicted.
Isaiah 42 is the forty-second chapter of the Book of Isaiah in both the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet Isaiah, and is a part of the Books of the Prophets. Chapters 40-55 are known as "Deutero-Isaiah" and date from the time of the Israelites' exile in Babylon. This chapter contains a poem known as the first of the "Servant songs" about the servant, whom Jewish tradition holds that Isaiah identifies as either the Israelites themselves or Cyrus.
Isaiah 40 is the fortieth chapter of the Book of Isaiah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible, and the first chapter of the section known as "Deutero-Isaiah", dating from the time of the Israelites' exile in Babylon. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet Isaiah, and is one of the Books of the Prophets. Parts of this chapter are cited in all four canonical Gospels of the New Testament.

Ezekiel 17 is the seventeenth chapter of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet/priest Ezekiel, and is one of the Books of the Prophets. This chapter tells, and then interprets, the riddle of the great eagle. The original text of this chapter is written in the Hebrew language. This chapter is divided into 24 verses.

Jeremiah 18 is the eighteenth chapter of the Book of Jeremiah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains prophecies attributed to the prophet Jeremiah, and is one of the Books of the Prophets. This chapter includes the fourth of the passages known as the "Confessions of Jeremiah".













