
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta, also known as Coniferophyta or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews. The division Pinophyta contains seven families, 60 to 65 genera, and more than 600 living species.

Araucariaceae – also known as araucarians – is a family of coniferous trees, with three living genera, Araucaria, Agathis, and Wollemia. While the family was distributed globally during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, they are now largely confined to the Southern Hemisphere, except for a few species of Agathis in Southeast Asia.

The gymnosperms are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term gymnosperm comes from the composite word in Greek: γυμνόσπερμος, literally meaning 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds. The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or on their own as in yew, Torreya, Ginkgo. Gymnosperm lifecycles involve alternation of generations. They have a dominant diploid sporophyte phase and a reduced haploid gametophyte phase which is dependent on the sporophytic phase. The term "gymnosperm" is often used in paleobotany to refer to all non-angiosperm seed plants. In that case, to specify the modern monophyletic group of gymnosperms, the term Acrogymnospermae is sometimes used.

Podocarpaceae is a large family of mainly Southern Hemisphere conifers, known in English as podocarps, comprising about 156 species of evergreen trees and shrubs. It contains 19 genera if Phyllocladus is included and Manoao and Sundacarpus are recognized.

Antarctic flora are a distinct community of vascular plants which evolved millions of years ago on the supercontinent of Gondwana. Presently, species of Antarctica flora reside on several now separated areas of the Southern Hemisphere, including southern South America, southernmost Africa, New Zealand, Australia, and New Caledonia. Joseph Dalton Hooker was the first to notice similarities in the flora and speculated that Antarctica had served as either a source or a transitional point, and that land masses now separated might formerly have been adjacent.

Lagarostrobos franklinii is a species of conifer native to the wet southwestern corner of Tasmania, Australia. It is often known as the Huon pine or Macquarie pine, although it is actually a podocarp (Podocarpaceae), not a true pine (Pinaceae). It is the sole species in the genus Lagarostrobos; one other species L. colensoi formerly included has been transferred to a new genus Manoao. The genus was also formerly included in a broader circumscription of the genus Dacrydium.

Podocarpus is a genus of conifers, the most numerous and widely distributed of the podocarp family, the Podocarpaceae. The name comes from Greek πούς + καρπός. Podocarpus species are evergreen shrubs or trees, usually from 1 to 25 m tall, known to reach 40 m (130 ft) at times. The cones have two to five fused cone scales, which form a fleshy, berry-like, brightly coloured receptacle at maturity. The fleshy cones attract birds, which then eat the cones and disperse the seeds in their droppings. About 97 to 107 species are placed in the genus depending on the circumscription of the species.

Prumnopitys is a genus of conifers belonging to the family Podocarpaceae. The nine recognized species of Prumnopitys are densely branched, dioecious evergreen trees up to 40 metres in height.

Glossopteris is the largest and best-known genus of the extinct Permian order of seed plants known as Glossopteridales. The genus Glossopteris refers only to leaves, within a framework of form genera used in paleobotany. Species of Glossopteris were the dominant trees of the middle to high-latitude lowland vegetation across the supercontinent Gondwana during the Permian Period. Glossopteris fossils were critical in recognizing former connections between the various fragments of Gondwana: South America, Africa, India, Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica.

The New Caledonia rain forests are a terrestrial ecoregion, located in New Caledonia in the South Pacific. It is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion, part of the Australasian realm.

Retrophyllum is a genus of conifers in the family Podocarpaceae. It contains five generally recognized extant species with a disjunct distribution in the Southern Hemisphere, found in Papuasia and also in South America. Retrophyllum are evergreen trees typically occurring in tropical rainforests and cloud forests.

Diselma archeri is a species of plant of the family Cupressaceae and the sole species in the genus Diselma. It is endemic to the alpine regions of Tasmania's southwest and Central Highlands, on the western coast ranges and Lake St. Clair. It is a monotypic genus restricted to high altitude rainforest and moist alpine heathland. Its distribution mirrors very closely that of other endemic Tasmanian conifers Microcachrys tetragona and Pherosphaera hookeriana.

Halocarpus bidwillii, commonly known as the mountain pine or bog pine, is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It is endemic to New Zealand.
The natural history of New Zealand began when the landmass Zealandia broke away from the supercontinent Gondwana in the Cretaceous period. Before this time, Zealandia shared its past with Australia and Antarctica. Since this separation, the New Zealand landscape has evolved in physical isolation, although much of its current biota has more recent connections with species on other landmasses. The exclusively natural history of the country ended in about 1300 AD, when humans first settled, and the country's environmental history began. The period from 1300 AD to today coincides with the extinction of many of New Zealand's unique species that had evolved there.
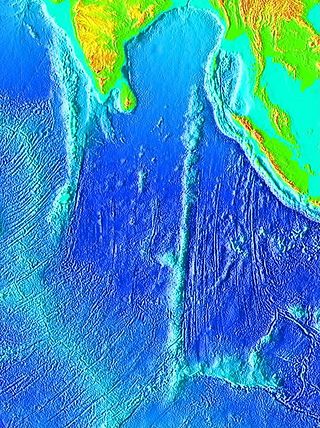
The Ninety East Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge on the Indian Ocean floor named for its near-parallel strike along the 90th meridian at the center of the Eastern Hemisphere. It is approximately 5,000 kilometres (3,100 mi) in length and can be traced topographically from the Bay of Bengal southward towards the Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR), though the feature continues to the north where it is hidden beneath the sediments of the Bengal Fan. The ridge extends between latitudes 31°S and 9°N and has an average width of 200 km.

The flora of Australia comprises a vast assemblage of plant species estimated to over 21,000 vascular and 14,000 non-vascular plants, 250,000 species of fungi and over 3,000 lichens. The flora has strong affinities with the flora of Gondwana, and below the family level has a highly endemic angiosperm flora whose diversity was shaped by the effects of continental drift and climate change since the Cretaceous. Prominent features of the Australian flora are adaptations to aridity and fire which include scleromorphy and serotiny. These adaptations are common in species from the large and well-known families Proteaceae (Banksia), Myrtaceae, and Fabaceae.

The biodiversity of Tasmania is of exceptional biological and paleoecological interest. A state of Australia, it is a large South Pacific archipelago of one large main island and a range of smaller islands. The terrain includes a variety of reefs, atolls, many small islands, and a variety of topographical and edaphic regions on the largest island, all of which promote the development of unusually concentrated biodiversity. During long periods geographically and genetically isolated, it is known for its unique flora and fauna. The region's climate is oceanic.

Elizabeth Marchant Truswell is a former Chief Scientist at the Australian Geological Survey Organisation and is known for her application of recycled palynomorph distribution as an indicator of sub-ice geology.

The vegetation in Tasmania's alpine environments is predominately woody and shrub-like. One vegetation type is coniferous shrubbery, characterised by the gymnosperm species Microcachrys tetragona, Pherosphaera hookeriana, Podocarpus lawrencei, and Diselma archeri. Distribution of these species is relevant with abiotic factors including edaphic conditions and fire frequency, and increasingly, the threat of climate change towards species survival exists. Conservation and management of coniferous shrubbery are necessary considering that the paleoendemic species, Microcachrys,Pherosphaera and Diselma, have persisted in western Tasmanian environments for millions of years.

The Tupuangi Formation is a geological formation in New Zealand, only exposed on Pitt Island in the Chatham Islands. It is the oldest exposed sedimentary unit within the archipelago. It was deposited in terrestrial deltaic to paralic conditions during the Cenomanian to Turonian ages of the Late Cretaceous. During this time period the Chatham Islands were attached to Antarctica within the Antarctic Circle, at approximately 70° to 80° south.




















