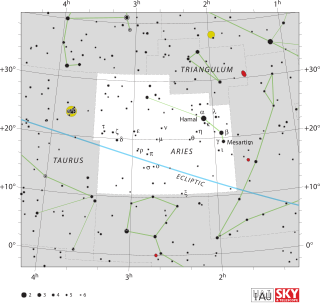
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram. Its old astronomical symbol is (♈︎). It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation ranking 39th in overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees.

Messier 100 is a grand design intermediate spiral galaxy in the southern part of the mildly northern Coma Berenices. It is one of the brightest and largest galaxies in the Virgo Cluster and is approximately 55 million light-years from our galaxy, its diameter being 107,000 light years, and being about 60% as large. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 and 29 days later seen again and entered by Charles Messier in his catalogue "of nebulae and star clusters".. It was one of the first spiral galaxies to be discovered, and was listed as one of fourteen spiral nebulae by Lord William Parsons of Rosse in 1850. NGC 4323 and NGC 4328 are satellite galaxies of M100; the former is connected with it by a bridge of luminous matter.

NGC 4567 and NGC 4568 are a set of unbarred spiral galaxies about 60 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. They were both discovered by William Herschel in 1784. They are part of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies.
NGC 6756 is a small open star cluster in the constellation Aquila, close to NGC 6755.

NGC 1725 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Eridanus. The galaxy is listed in the New General Catalogue. It was discovered on November 10, 1885 by the astronomer Edward Emerson Barnard.

NGC 1169 is an intermediate barred spiral galaxy in the constellation of Perseus. NGC 1169 has a reddish center, indicating the region is dominated by older stars. In contrast, the outer ring contains larger blue-white stars, a sign of recent star formation. The entire galaxy is rotating at approximately 265 km/s.

NGC 2266 is an open cluster in the constellation Gemini. Its apparent size is 5 arc minutes. Its distance is 3,400 parsecs (11,000 ly). It was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel on 7 December 1785.

NGC 2936 is an interacting spiral galaxy located at a distance of 326 million light years, in the constellation Hydra. NGC 2936 is interacting with elliptical galaxy NGC 2937, located just beneath it. They were both discovered by Albert Marth on Mar 3, 1864. To some astronomers, the galaxy looks like a penguin or a porpoise. NGC 2936, NGC 2937, and PGC 1237172 are included in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies as Arp 142 in the category "Galaxy triplet".

NGC 6902 is an unbarred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Sagittarius at an approximate distance of 131.80 Mly. NGC 6902 was discovered in 1836 by John Herschel.
NGC 4230 is a loosely scattered open cluster in the constellation of Centaurus. It was discovered by John Herschel on April 5, 1837.

NGC 7773 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Pegasus at an approximate distance of 400 million light years. NGC 7773 was discovered on October 9, 1790 by William Herschel.

NGC 4694 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 15, 1784

NGC 4900 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 30, 1786. It is a member of the NGC 4753 Group of galaxies, which is a member of the Virgo II Groups, a series of galaxies and galaxy clusters strung out from the southern edge of the Virgo Supercluster.

NGC 1345 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Eridanus. It was discovered by John Herschel on Dec 11, 1835.

NGC 3717 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Hydra at an approximate distance of 81.43 million light years. NGC 3717 was discovered in 1834 by Sir John Herschel.

NGC 3749 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Centaurus at an approximate distance of 130.52 million light-years. NGC 3749 was discovered in 1835 by John Herschel.

NGC 980 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Andromeda about 256 million light years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by the German - British astronomer William Herschel in 1786.

NGC 941 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Triangulum. It is an estimated 55 million light-years from the Milky Way and has a diameter of approximately 55,000 light years. The galaxies NGC 926, NGC 934, NGC 936, NGC 955 are located in the same sky area. NGC 941 was discovered by the astronomer William Herschel using on 6 January 1785.
















